Spondylitis is a painful and inflammatory condition of the joints that affects many people the world over. If you have lately been experiencing pain, swelling and stiffness I your spinal joint, you are probably suffering from this disorder. Read and know all about this disease, including its possible causes, symptoms and treatment options.
Spondylitis Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Spondylitis Definition
- 2 Spondylitis ICD9 Code
- 3 Spondylitis Types
- 4 What is Undifferentiated Spondylitis?
- 5 Spondylitis Causes
- 6 Spondylitis Risk Factors
- 7 Spondylitis Incidence
- 8 Spondylitis Symptoms
- 9 Spondylitis Diagnosis
- 10 Spondylitis Differential Diagnosis
- 11 Spondylitis Treatment
- 12 Spondylitis Complications
- 13 Spondylitis Prognosis
- 14 Spondylitis – Recovery and Return to Work
- 15 Spondylitis Pictures
Spondylitis is an arthritic condition that affects the spine directly. It is one of the common causes of pain in the neck and back area and typically occurs due to a swelling of the facet joints located between the vertebrae.
Spondylitis is sometimes also referred to as Ankylosing Spondylitis although the term actually refers to a subtype of the condition. The disorder should not be confused with Spondylolysis, Spondylosis or Spondylolisthesis.
Spondylitis ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code for this disorder is 721.90.
Spondylitis Types
The condition has been classified into a number of types. The major types of Spondylitis include:
Cervical Spondylitis
It refers to a painful condition of the neck that affects the cervical spine. The pain may spread to other regions of the body, such as the collar bone, posterior area of the neck, shoulder joints and both sides of the shoulder. This form of the disorder limits the motion of the neck and the muscles become weak leading to loss of range of motion in the arms.
Lumbar Spondylitis
It is a painful condition of the lumbar region.
Spondylitis Deformans
This is an autoimmune disorder that involves the sacroiliac joints and the spine. Due to this reason, it is a form of Spondylarthritis. It is also known as Ankylosing Spondylitis. The condition affects a number of areas of the body, such as:
- Hip joints
- Shoulders
- Sacroiliac joints
- Vertebral column
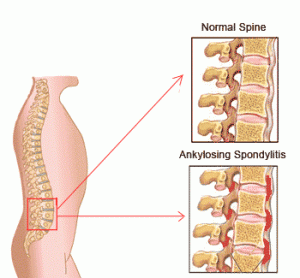
In this type, the spines generally turn extremely stiff. The rigidity may also be observed in other areas like the hips, neck, knees, shoulders, jaw and heels.
What is Undifferentiated Spondylitis?
It is a term used by certain doctors to describe back pain originating without any apparent causes and which seems to be related with degenerative changes on imaging exams like CT or MRI scans.
The condition is not related with an underlying Spondyloarthropathy.
Spondylitis Causes
The majority of scientists and medical researchers are of the opinion that this is a hereditary disorder. A specific gene known as HLA-B27 has been found to be associated directly to the disorder. Although there is definitely an association between Spondylitis and this gene, many individuals with HLA-B27 never develop the disorder. Due to this reason, scientists suspect that there are also some other factors involved with this disease.
Spondylitis and Associated Conditions
The conditions associated with this disorder include the following:
Psoriatic arthritis
It arises in certain people affected with a chronic skin condition by the name Psoriasis. Around one out of 20 individuals suffering from Psoriasis ted to develop arthritic symptoms along with the skin condition. Generally, people with psoriasis are found to be more prone to arthritis than members of the general population. The cause of psoriatic arthritis is unknown. However, genetic factors are supposed to play a role in the development of the disease.
Reiter’s syndrome
It is an inflammatory complication of some prior case of infection affecting any other area of the body. Its symptoms include:
- Reactive arthritis
- Skin lesions
- Urethritis, or inflammation of the urethra
- Conjunctivitis, or inflammation of the eye
The disease is most common in men who are less than 40 years of age.
Spondylitis Risk Factors
Apart from a genetic association, a few other factors are supposed to raise the risk of getting this disorder in an individual. These include:
Being male
Men are more susceptible to this condition than women, particularly between 20 and 30 years of age. This may be ascribed to the fact that men are usually more actively involved in sports than women during this age and are hence prone to injuries that may progress to Spondylitis.
Being Native American
Native Americans are also found to be slightly more susceptible to Ankylosing Spondylitis as compared to people of other racial origin.
Having certain inflammatory conditions
The presence of some inflammatory disorders like Ulcerative colitis, Psoriasis or Crohn’s disease heightens the risk of Spondylitis. The disease affects around 5% people with Psoriatic arthritis.
Spondylitis Incidence
The exact incidence of this disease is unknown as it is often a feature of a group of disorders. In the United States, 0.21% of people over 15 years of age are affected by this disorder. The condition is assessed to be prevalent in 197 out of every 10,000 individuals in the U.S.
Spondylitis Symptoms
This arthritic condition has a direct effect on the spine of its sufferers. It gives rise to general discomfort and chronic pain in the lower and upper back of affected individuals. Sufferers also frequently experience an overall sensation of stiffness in the back. In the course of time, patients may lose some amount of mobility.
The disease always begins with the spine. Over a period of time, however, it can spread to various organ systems through the body and give rise to a variety of different symptoms. In the initial stages, a patient is likely to experience stiffness and pain – specifically in the lower section of the spinal column that is close to the buttocks. In the later stages, the pain may be felt in the upper parts of the spine as well as in other joints in the body (such as the hips). When the condition progresses to an advanced stage, sufferers may discover that their spine has become inflexible. They may begin to suffer from chronic fatigue or start losing weight.
As is the case with other types of arthritis, this is an inflammatory disorder. The inflammation caused by this condition can make the immune system react as if some type of injury has occurred. A new bone may begin to grow in the spine and eventually result in an overall immobilization of the spinal column. This condition is referred to as Spinal fusion. Although not very common, Spinal fusion can occur if Spondylitis is left without being treated.
The disorder often goes undetected until it develops completely and results in pain. The pain is generally concentrated around the cervical area of the spine, lower spine and shoulder with stinging pain that is moving downwards.
Spondylitis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disorder involves:
Consideration of medical history
The medical history of patients should be taken into account. Sufferers may complain about joint pain, fatigue, morning sickness, neck pain, hip pain and back pain. Some patients may complain about other bodily problems like night sweats and weight loss. Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disorder or skin disease (Psoriasis) may precede or follow the start of Spondylitis problems in the back. Doctors may ask patients about a history of recent or past ailments as well as a family history of Spondyloarthropathies.
Physical exam
Patients may be physically examined, which may reveal problems like muscular spasms, inflammation, tenderness in the joints, or reduced movement in the spinal column. It is only in rare cases that vision is affected although ocular inflammation may be present. Psoriatic involvement of the skin may be obvious.
Medical tests
In order to determine signs of possible infection and the degree of inflammation, physicians put the majority of affected individuals through the following tests:
- Blood cultures
- Spinal x-rays
- Hemoglobin
- Hematocrit
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Doctors may conduct an HLA-B27 assay and a serological test for rheumatoid factor (RF) in order to exckude the possibility of presence of Rheumatoid arthritis. The HLA-B27 antigen is often detected in people suffering from the following problems:
- Reiter’s syndrome
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic arthropathy
- Enteropathic arthropathy (arthritis associated with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease)
Other tests that are conducted are associated to the specific cause of the spondylitis. These may include:
- Tuberculin skin testing (PPD)
- Biopsy for culture and sensitivity to exclude presence of tuberculosis, brucellosis and infectious arthritis (septic arthritis)
- CT scans, to determine changes in soft tissue in and around the joints
- MRI scans, for diagnosis and follow-up assessment (in a few cases)
Diagnoses depend on clinical findings of arthritis as well as other conditions. The clinical features needed to establish a diagnosis of this disorder involve a typical pattern of:
- Radiographic sacroiliitis
- Peripheral arthritis
- Absence of rheumatoid factor
- Association with HLA-B27
- Extra-articular features such as Uveitis
Spondylitis Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnoses of Spondylitis include ensuring that the symptoms experienced by patients are not the result of any of the following disorders:
- Osteoarthritis
- Spinal fracture
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Herniated intervertebral disc
- Muscle abscess
- Metastatic bone tumor
Spondylitis Treatment
The treatment for this condition aims at the following:
- Relieving joint pain
- Maintaining mobility
- Delaying or preventing deformities
A range of prescription medications and Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Aspirin are used to decrease pain and inflammatory symptoms related with the disease. In severe cases of ankylosing spondylitis, patients may require surgery. Operative procedures may help improve gross lumbar flexion deformity, chin-on-chest deformity and other defects. Any underlying disorder or concomitant infection will be simultaneously cured.
Spondylitis Complications
The complications associated with this condition are mainly those of underlying disorders like:
- Psoriasis
- Reiter’s syndrome
- Inflammatory bowel disease
Deformities may arise due to progressive cases of the disease. In patients of Ankylosing spondylitis, the following problems may occur:
- Loss of lumbar lordosis (Abnormal flattening of the lower spine)
- Kyphosis, or exaggeration of the curve of the thoracic spine (middle spine). Physicians may be able to cure this deformity
Spondylitis Prognosis
The outcome tends to be variable for cases of Spondylitis that are related with problems like:
- Psoriasis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Reiter’s syndrome
Spontaneous remission, as well as exacerbation, is common. However, the outcome is generally favorable. In a few sufferers, the disorder may progress to complete immobility of the affected joints. This problem is known as Ankylosis. However, the course of the disorder is unpredictable as relapses may occur at any phase. Spondylitis can be aggravated due to the presence of infection or active chronic inflammatory disorders like Psoriatic arthritis or Crohn’s disease.
Spondylitis – Recovery and Return to Work
Usually, rheumatologic disorders such as these are frequently cured with the aid of medications along with physical therapy. The management can be done with the aid of general aerobic conditioning and exercises that improve strength and flexibility of affected regions. It is important to teach proper lifting techniques to patients and educate them about body mechanics to make them fit for going back to work.
Stretching or flexibility exercises may be taught to promote the range of motion in the spinal column. In order to help patients prevent poor posture, exercises may be introduced to strengthen the muscles in the abdominal and the lower back region. Even if patients suffer from mild symptoms of Spondylitis, activities like swimming and walking may be recommended. These can be done without putting the spine under great stress. It is advised that sufferers take up workout programs slowly and build up speed gradually as well as increase the duration of exercises over time to elevate tolerance and mobility without worsening the condition.
Some individuals, who have jobs that need standing, lifting or bending for long hours, may need to shift to more sedentary duties. If the condition heals with residual deformity, patients may no longer be able to carry out heavy duties. They may need to be trained again in a different domain. A prolonged leave may be necessary in some cases. If that is not possible, a change of job nature may be required.
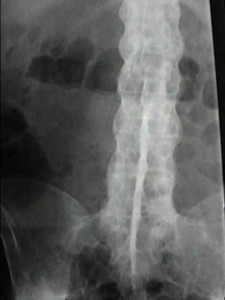
Spondylitis Pictures
The following images would let you know how this condition affects the spine of affected individuals.
Picture 1 – Spondylitis
Picture 2 – Spondylitis Image
If you suspect yourself to be having this disorder, do not delay treatment. Seek medical attention on an early basis and get yourself tested by a professional healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment will help you recover from this disease on an early basis and ensure good health for you.
References:
http://www.mdguidelines.com/spondylitis
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-spondylitis.htm
http://www.yogawiz.com/askquestion/1784/what-is-spondylitis.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spondylitis