Are you getting scared out of your wits at the sight of a red thing sticking out of your anus after a bowel movement? Relax, for this is a benign condition called Rectal Prolapse which is non-fatal in nature. Read and find out about the common causes, symptoms, treatment options and more about this disorder.
What is Rectal Prolapse?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Rectal Prolapse?
- 2 Rectal Prolapse ICD 9 Code
- 3 Rectal Prolapse Types
- 4 Rectal Prolapse Incidence
- 5 Rectal Prolapse Risk Factors
- 6 Rectal Prolapse Symptoms
- 7 What Causes Rectal Prolapse?
- 8 Is Rectal Prolapse Same as Hemorrhoid?
- 9 Rectal Prolapse Diagnosis
- 10 Rectal Prolapse Differential Diagnosis
- 11 Rectal Prolapse Treatment
- 12 Rectal Prolapse Home Remedies
- 13 Rectal Prolapse Prognosis
- 14 Rectal Prolapse Recovery Time
- 15 Rectal Prolapse Complications
- 16 Rectal Prolapse Prevention
- 17 Rectal Prolapse Pictures
It is a condition characterized by the protrusion or stretching out of the rectum through the anus. As a result, the rectum becomes visible outside the body.
Rectal Prolapse ICD 9 Code
The ICD 9 Code for this disease is 569.1.
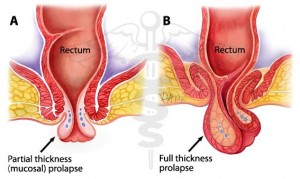
Rectal Prolapse Types
The disorder can be categorized into the following three types:
Picture 1 – Rectal Prolapse
Complete Rectal Prolapse
In this form, the rectal wall projects through the anal opening in its full thickness.
Incomplete (Partial) Rectal Prolapse
This arises when the mucosa or the inner tissue layer of the rectum alone projects through the anal aperture.
Internal Rectal Prolapse
It happens when either the muscular or the mucosal layer collapses into the rectum although the prolapsed tissue is not found to project beyond the anus or outside the body.
Rectal Prolapse Incidence
The overall prevalence of this disorder is 0.42% in the U.S. In people aged over 65 years, there is a rise in incidence by 1%. However, some studies suggest that the prevalence of the disease is underreported in elderly people.
The condition is rare in infants of the U.S, but is more common in children in developing nations. The disease is supposed to be associated to the nutritional status of a child.
Rectal Prolapse Risk Factors
The risk factors of this disorder are:
Age
Increasing age is believed to make individuals more susceptible to the disease. Elderly people are found to be more at risk of suffering from this condition.
Gender
Women are found to be affected by this disorder six times more than men. Around 80-90% of sufferers of this disease are found to be women and between 40-80 years of age. There is an even distribution of this condition in men, with age taken into account.
Disorders
Individuals suffering from certain health issues are more likely to suffer from the syndrome. Such disorders involve:
- Cystic fibrosis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Paralysis
- Pinworms
- Whooping cough
Rectal Prolapse Symptoms
As already mentioned, the disorder is usually characterized by a red mass of tissue jutting out of the anal opening in sufferers. This is commonly observed after a bowel movement, or an episode of defecation. The lining of the rectal tissue might be observed. In some cases, there can also be a little bleeding in the area.
Patients may also suffer from one or more of various other problems, which include:
- Discharge of mucus from the anus
- Difficulty in bowel regulation (Fecal incontinence)
- A sensation of incomplete evacuation after a bowel movement
- Discomfort in the area close to the anus (Perianal region)
- Constant spasms of the rectum, along with the urge to defecate (tenesmus)
What Causes Rectal Prolapse?
The exact cause of this disease has not been completely understood. However, doctors and medical researchers have laid bare their thoughts on some of the possible factors for this disease – which include:
- Poor bowel habits (particularly constipation)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Whipworm infection (Trichuriasis)
- Neurological disease (spinal cord injury, cauda equina lesion or senility)
- Malnutrition and malabsorption (such as Celiac disease)
- A weak internal anal sphincter (patulous anus)
- Pinworms (enterobiasis)
- Certain surgical procedures (abdomino-anal pull-through, fistulectomy and hemorrhoidectomy)
- An earlier injury to the pelvic or anal region
The condition may also arise due to various anatomical defects, such as:
- Lack of attachment of the rectum to the sacrum
- Diastasis of Levator ani muscle
- Deep pouch of Douglas
- Intussusception secondary to a colonic lesion
The problem is common in individuals who strain too much during each bowel movement, as is usual in people suffering from constipation. The condition may also occur as a late consequence of childbirth. Women who give birth to many children are more susceptible to this disorder although around 35% of female sufferers can have it without being pregnant.
A number of individuals with the condition are found to have a history of psychological disorders or some other mental problem that may even demand admitting patients to special care centers or institutions.
Is Rectal Prolapse Same as Hemorrhoid?
The two conditions are unique although some of the symptoms are similar, such as:
- Protrusion of tissue through the rectum
- Anal bleeding
Rectal Prolapse involves a section of the bowel that is situated higher up within the human body. On the other hand, hemorrhoids are found to develop close to the opening of the anus.
Rectal Prolapse Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this condition initially begins with a physical examination of the patient. This may also include an examination of the rectum. During detection, physicians also take the medical history of sufferers into account. This is done in order to determine the exact causative factor for the disorder.
In many cases, tests need to be performed to find out and confirm the underlying cause of the problem. This involves carrying out medical exams like:
- Anal manometry – It is used to determine the extent of defect in the anal sphincter.
- Barium enema – It involves injecting a contrast medium into the rectum to check any possible impairment.
- Electromyogram (EMG) – It is a neurophysiological exam to quantify the function of the muscles and the nerve.
- Colonoscopy – The process includes inserting a colonoscope (a long fiberoptic endoscope) to examine the lining of the complete large intestine or colon.
- X-rays – It is used to find out whether there has been a development of any unusual growths, or neoplasms, in the lower intestine.
- Colon Transit Study – The test involves studying the rate of passage of a radioactive material through the intestine to determine whether the condition is associated with an abnormally severe case of constipation.
Rectal Prolapse Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disease involves distinguishing the disorder from conditions that give rise to similar symptoms, such as rectal polyp, prolapsed of an intussusception or hemorrhoid.
Rectal Prolapse Treatment
It is necessary to get in touch with a professional healthcare provider if you are suffering from this disorder. Treatment may comprise of:
Medications
There are no specific medicines to cure this problem. However, stool softeners might be prescribed by physicians if the condition is found to be a result of straining during bowel movement in constipated persons.
Surgery
This is the primary treatment option for all forms of the disease. Operation is mainly needed in case of chronic rectal prolapse. Surgery may also decrease fecal incontinence in sufferers. Operative cure is normal for cases of this condition. In frail elders and infants, physicians always try to cure the disease in a non-surgical manner. For cases of internal prolapse, operation is not generally performed. Conservative treatment involves training to ameliorate poor defecating habits, use of stool softeners and coordinating muscles of the pelvic floor at the time of defecation.
Only operative means are adequate for curing individuals suffering from the complete form of the disease. More than fifty operative procedures can be carried out for remedying the condition. These include:
- Transabdominal procedures – These involve making an incision in the abdominal region under the effects of general anesthesia. It is the preferred treatment option for individuals who are younger and healthier.
- Perineal surgery – These require entering the body of patients through the anal aperture. Although these are less invasive options and can be carried out under spinal anesthesia, physicians prefer perineal procedures more these days.
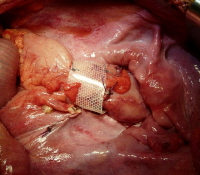
- Encirclement – This procedure involves placing a band of mesh in the region surrounding the anus to prevent prolapsing of the rectum. This is the chosen method of treatment in people who are frail and debilitated. This can be carried out under general anesthesia.
- Laparoscopic surgery – This is a faster and more effective way to repair a rectal prolapse. This operative process is becoming increasingly popular among patients and surgeons as it can reduce the duration of hospital stay for sufferers.
In some cases where the disease arises as a result of straining at the time of bowel movement, the condition may resolve on its own after some time.
Rectal Prolapse Home Remedies
In occasional cases of the disorder, following self-care measures at home may be beneficial. Such home remedial measures involve:
Picture 2 – Rectal Prolapse Image
- Drinking lots of fluids
- Eating a high-fiber diet
- Using stool softeners
- Taking laxatives
- Use of stool-bulking agents
Regular exercise may also be beneficial. Workouts can promote a normal bowel movement and boost metabolism, thus relieving patients of constipation.
Rectal Prolapse Prognosis
Proper treatment of the underlying cause of the disorder is generally enough to cure the problem. However, the outcome for the incomplete form of the disease is usually variable in nature. Left untreated or maltreated over a period of time, the prolapsed may worsen to a point where surgery might become essential. If medications and non-invasive means fail to bring about an improvement in the condition, surgical repair might be necessary for addressing the physical issues that increase the likelihood of the recurrence of prolapse.
The rate of recurrence for the complete form is the lowest, less than even 10%, when Transabdominal surgery is used for curing patients. The recurrence rate is highly variable in cases treated via Perineal surgery and ranges between 5.5 to 54%, depending on the type of procedure that is adopted for cure. The number of complications is also lower in case of Perineal surgery than in Transabdominal surgery. Encirclement is not a very dependable process as the mesh of the prosthesis can break down and increase the risk of recurrence. This actually occurs in around 25% individuals who are treated by this method.
Rectal Prolapse Recovery Time
The recovery time for patients of complete rectal prolapse may be up to several weeks. Patients can return to normal work after that period. Until that time, activities involving strenuous labor such as climbing or lifting might have to be restricted to allow the body enough time for complete recovery. Those suffering from an incomplete form of the disease will not face any restrictions while recovering and might return to work as usual. Some exercises might be recommended to ensure speedier recovery and reduce postoperative pain. These generally include deep-breathing and progressive relaxation techniques.
Rectal Prolapse Complications
Fortunately, the condition does not give rise to any life-threatening or debilitating complications. The difficulties that might arise from the disorder involve constipation or other problems that caused the disease in the first place. Women affected with this condition are often found to suffer from related health issues, like associated cystocele or prolapsed of the uterus or the bladder.
In the absence of proper treatment, the rectum might permanently protrude through the anus. This can cause discomfort while sitting or walking and often leads to depression and extreme mental agony.
Rectal Prolapse Prevention
Proper treatment of an underlying problem, that causes the condition, is generally an adequate measure to prevent the occurrence or even the recurrence of the disease.
Rectal Prolapse Pictures
You will find these images quite useful and assistive in understanding how the anal aperture looks like in this condition. The pictures would also help you find out whether or not you are suffering from a similar problem.
If you suspect yourself or a family member to be suffering from Rectal Prolapse, do not neglect the condition. Get in touch with a healthcare provider as early as possible and seek immediate medical attention. Early medical cure will help you treat the disease in time and prevent the condition from turning chronic or one that stays life-long. During treatment, it is also important that you take up a healthier diet, drink lots of fluids and incorporate workouts into your lifestyle to make a complete recovery from this discomforting disease.
References:
Lembo AJ, Ullman SP. Constipation. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisinger & Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 9th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saudners Elsevier;2010:chap 18.
Feldman, M., L. S. Friedman, and M. H. Sleisenger, eds. Sleisenger & Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, 2002.
Watkins BP, Landercasper J, Belzer GE, et al; Long-term follow-up of the modified Delorme procedure for rectal prolapse. Arch Surg. 2003 May;138(5):498-502; discussion 502-3. [abstract]