Are you suffering from painful sensations in multiple joints of your body? It might be a case of Polyarthritis that is your underlying problem. Read on and find out all about this disorder, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Polyarthritis Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Polyarthritis Definition
- 2 Polyarthritis ICD9 Code
- 3 Polyarthritis Causes
- 4 Migratory Polyarthritis
- 5 Inflammatory Polyarthritis
- 6 Polyarthritis Symptoms
- 7 Polyarthritis Diagnosis
- 8 Polyarthritis Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Polyarthritis Treatment
- 10 Polyarthritis Support Groups
- 11 Polyarthritis in Cats
- 12 Polyarthritis in Dogs
- 13 Polyarthritis Prognosis
It is a form of arthritis that affects 5 or more joints of the body at the same time. The term “Polyarthritis” can be applied to any of the three types of arthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Septic arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
The condition can arise at any age and does not show preference to any specific gender. The disease is also known by the name Alphavirus Polyarthritis Syndrome. It is considered to be a type of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA).
Polyarthritis ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code for this disorder is 716.5.
Polyarthritis Causes
The condition most often results from any autoimmune disorder like:
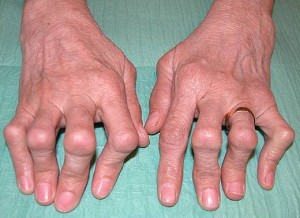
Picture 1 – Chronic Polyarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Amyloidosis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Lupus erythematosus
However, it may also result due to an infection caused by an alphavirus like Ross River Virus or Chikungunya Virus.
Polyarthritis may also have its origin in a degenerative joint disorder, such as Osteoarthritis, or other conditions like:
- Cancer
- Reactive arthritis
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Still’s disease
- Gout
- Hemochromatosis
- Whipple’s disease
One of the most widely distributed alphaviruses leading to Polyarthritis is the Sindbis Virus, which is endemic to Australia, Middle East, Africa and Northern Europe. However, an infection caused by this virus is generally asymptomatic or mild in nature.
The disease may also result from conditions like Hepatitis and AIDS. Hepatitis impacts the liver of sufferers and is often related with conditions affecting the joints. AIDS attacks the immune system of sufferers and makes an individual more susceptible to Polyarthritis.
Assocoiated Conditions
Certain disorders might be associated to the occurrence of this condition. These include:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
It is a form of arthritis affecting all the joints present in the body. This is a highly painful condition that can give rise to a range of problems, such as:
- Cardiac problems
- Eye problems
- Fatigue
- Liver damage
- Weight loss
Lupus Arthritis
This is a painful condition. However, it does not cause any permanent damage to the joints. It often affects the soft tissue in the joints of the following bodily regions:
- Hands
- Shoulders
- Knees
- Wrists
Psoriatic Arthritis
The fingers or spine are usually affected by this type of arthritis. It generally affects people suffering from the skin condition referred to as Psoriasis. It changes the bones located in the hand; naturally it leads to deformities in fingers. When this condition arises, affected individuals find it extremely difficult to gain proper control over their fingers and carry out their daily activities.
Migratory Polyarthritis
It is a form of arthritis that seems to migrate from one joint of the body to the other. It can arise due to any cause, such as bacterial endocarditis, hepatitis, rheumatic fever or AIDS. It is characterized by sudden onset of inflammation in one or two joints. This resolves in the course of a few days. As the signs resolve, other similar problems begin to emerge in another joint – generally in an asymmetric region.
Inflammatory Polyarthritis
It is a pecusror to rheumatoid arthritis and is characterized by swelling in more than four joints. It tends to be worse as a person wakes up and its symptoms ease as the day progresses. It is an extremely discomforting disorder and needs immediate treatment.
Polyarthritis Symptoms
The disorder is primarily characterized by one or more of the following signs and symptoms:
- Rashes
- Swelling
- High fever
- Restricted movement of the joints
- Enlargement of liver, spleen and lymph nodes
Affected individuals may not suffer from all of the symptoms. Some patients may suffer from difficulties and discomfort in moving their joints while others may only experience warm sensations in their joints.
The incubation period for this condition varies from 3 days to 3 weeks, based on the particular virus. In case of an alphavirus infection, patients suffer from a gradual or an abrupt onset of symptoms like headache, fever, lymphadenitis, arthralgias and conjunctivitis in some types. 4-8 days after the onset of symptoms, a maculopapular rash may arise along with a further elevation in body temperature. Many months after the first onset of symptoms of this disease, joint pains related with this syndrome may arise again.
Polyarthritis Diagnosis
The condition is usually diagnosed with the aid of a physical examination and asking questions to patients about the symptoms experienced by them. In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays might be necessary to detect underlying problems that might be the cause of Polyarthritis symptoms.
Other screening tools, which might be put to use, include:
- Blood tests, which show whether or not a marker (rheumatoid factor) is present in the blood
- Exams, for detecting possible skin abnormalities
- Testing of muscular activity
Polyarthritis Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disease includes clearly distinguishing its symptoms from the signs of similar disorders, such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Reactive arthritis
Polyarthritis Treatment
The treatment for this condition is based on the exact symptoms manifested in sufferers. Usually, treatment primarily aims at reducing the painful sensations than curing the underlying problem. This can be done by either of the following ways:
Lifestyle management
In some cases, lifestyle modification measures are enough to cure the problem. Affected individuals often find relief by sleeping on a flat pillow or over a hard mattress. Some sufferers are suggested to reduce body weight to lower the amount of pressure on their joints. Patients are also commonly recommended to take supplements the glucosamine, an amino derivative of glucose that is found to be effective in curing some types of arthritis. Treatment tends to vary from one patient to another, depending on the symptoms exhibited by patients and the exact nature of the problem in affected individuals.
Medications
The medicines used for curing this condition involve:
Pain-relievers
Analgesics (pain-relieving medications) and physiotherapy are commonly used to alleviate painful symptoms in sufferers. If over-the-counter analgesics fail to manage pain, stronger medications are likely to be used to reduce the painful sensations daily suffered by patients.
In the majority of cases, doctors recommend patients to use mild over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs like Ibuprofen or Aspirin for several weeks and observe whether the condition shows any improvement.
In case an individual is found to suffering from a chronic disorder or a systemic disease, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) or SLE (Lupus), he or she may be put on medications that have to be continued for the rest of the life.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Most over-the-counter analgesics do not contain the organic compounds, known as steroids, and are beneficial for reducing arthritic pain and inflammation. These show fast results and have reduced number of side-effects. Non Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), such as Mortin or Aleve, are such types of drugs that alleviate discomfort in Polyarthritic patients. However, long-term usage of these medications may result in cause liver damage or abdominal pain.
Corticosteroids
These types of medications produce an effect on the immune system of patients and try to block the natural response of the body to attack.
Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
These help cure the underlying causes of this disorder. However, they are disadvantageous in the aspect that they may take several weeks to show effects. The medications also inhibit the immune system of sufferers and are quite effective in case of patients of rheumatoid arthritis.
Anti TNF Drugs
They alter the natural response of the body and block the inflammation that arises as a result of the tumor necrosis factor. Usually, Anti TNF Drugs are administered into the body through injection or IV. However, they can increase the risk of infection and give rise to a number of side effects like aches, chills and fever.
Exercises
A proper workout regime, performed regularly, can help a person reduce pain and stiffness in the joints. Exercises help increase flexibility in the muscles in the affected joints. Many patients seek assistance of a qualified physical therapist to seek guidance about the workouts to be performed and also assure that the affected joints do not suffer from any further damage.
Certain low-intensity exercises, which can be attempted by Polyarthritic patients, include:
Stretching
Stretches, when performed in a proper way, can help increase the range of motion of affected individuals. These are simple exercises that can be performed anywhere and often make the shoulders, knees or fingers workable.
Swimming
Swimming and other exercises performed in warm water (Hydrotherapy) can be performed to reduce strain on joints and soothe muscles in the affected body regions. Such workouts reduce stiffness and help patients gain flexibility and strength.
Tai Chi
It calms the mind and body of patients, makes them more flexible and also helps them breathe better.
Polyarthritis Support Groups
If you are suffering from this disorder and concerned about the problem, you may register with the Arthritis Foundation online to avail documents and materials to obtain necessary information about the condition. This would help you understand about Polyarthritis.
You may also consider contacting the following organizations for support and more information about this arthritic disorder.
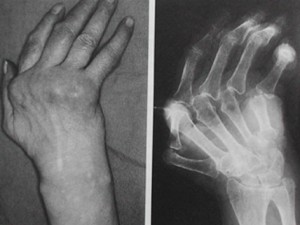
Picture 2 – Polyarthritis Image
Arthritis Support Group
35 8th Street North
Brandon, MB R7A 2R3
PH: 204-726-5995
Arthritis Australian Capital Territory
Level 2B
Grant Cameron Community Centre
27 Mulley Street
HOLDER ACT 2611
P.O Box – 4017
WESTON CREEK ACT 2611
PHONE: (02) 6288 4244
FAX: (02) 6288 4277
EMAIL: [email protected]
Polyarthritis in Cats
In most cats and dogs, the condition tends to affect joints like the tarsi (hocks) and the carpi (wrists). The other joints, affected to a lesser extent, include the elbows and stifles (knees). Feline Polyarthritis is a condition associated with immunity that only affects male cats. Female cats are at no risk of having this disease. Cats are usually affected by this disorder between 1 ½ years and 4 ½ years of age. The condition may affects cats of any breed and is usually characterized by the following symptoms:
- Reluctance to exercise or even walk
- Loss of appetite, leading to anorexia
- Weight Loss
- Depression
- Chromic Lameness
The condition can be treated with immunosuppressive medications. Proper medical care and drugs are enough to ensure a good outcome for this disorder.
Polyarthritis in Dogs
In dogs, the disease manifests as inflammation of multiple joints and is referred to as “Canine Polyarthritis.”An affected dog may become feverish, disinterested in food and depressed. There are four types of this condition in canines and treatment as well as prognosis depends on the form that a dog suffers from.
Polyarthritis Prognosis
With proper and timely treatment, the condition shows a positive outcome. In the majority of cases, the outcome is mainly dependant on the extent of problems in sufferers and how early medical treatment or curative measures have been opted for.
If you, or your pet, is suffering from this disorder, seek medical attention as early as possible. Proper and timely treatment is of utmost essence in remedying such conditions fast and ensuring early recovery for sufferers.
References:
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-polyarthritis.htm
http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/polyarthritis.aspx
http://aspenmeadowvet.com/polyarthritis/
http://www.healthzillion.com/arthritis/understanding-all-aspects-of-polyarthritis/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polyarthritis