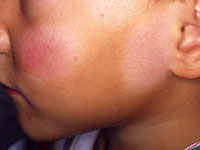
Approximately five percent of young people around the world are found to suffer from conspicuous cases of Pityriasis alba. Read on to know what is Pityriasis alba and also learn all about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
Pityriasis alba Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Pityriasis alba Definition
- 2 Pityriasis alba Incidence
- 3 Pityriasis alba Symptoms
- 4 Pityriasis alba Causes
- 5 Pityriasis alba Trigger Factors
- 6 Pityriasis alba Diagnosis
- 7 Pityriasis alba Differential Diagnosis
- 8 Pityriasis alba Treatment
- 9 Pityriasis Alba Creams
- 10 Pityriasis alba Natural Treatment
- 11 Pityriasis alba Prognosis
- 12 Pityriasis alba Recurrence
- 13 Pityriasis alba Complications
- 14 Pityriasis alba Prevention
- 15 Pityriasis alba Pictures
It is a common skin disease that is similar to very mild forms of eczema. People under the age of 20 are primarily afflicted by this disorder. However, it is most common in children.
The name of this condition comes from the fine scaly appearance that is initially evident in suffering individuals (Pityriasis) as well as the pallid patches that develop over the skin. The word “alba” is Latin for “white”. However, the white patches in this condition are not entirely de-pigmented.
Pityriasis alba Incidence
This is considered to be one of the most common skin conditions. It is said to be more rampant in adolescents and children with darker skin. However, many medical researchers speculate that the disease affects patients with both light as well as dark skin tones, but is more apparent in the latter.
As aforesaid, this disorder is seen most frequently in kids. It particularly affects those who are aged between 3 and 16 years. The disease is found to affect males slightly more than females.
Up to one-third of the school-going population of US children are affected by this condition at some stage of their life. The rate of prevalence of this disease in various countries has been given below:
- India – 8.4 – 31%
- Brazil – 9.9%
- Egypt – 13.49%
- Romania – 5.1%
- Turkey – 12%
- Hong Kong – 1%
Pityriasis alba Symptoms
In most patients, the condition develops through three distinct stages. These are:
First stage
It is primarily manifested by the development of oval or round lesions over the skin surface on the face, neck, upper arms or upper middle region of the body. These are anywhere from 0.5 – 2 cm in size. Any number of lesions, usually within 5 and 20, may develop on the body. These are generally red in color and elevated in appearance. Typically, no discomforting symptoms are experienced. However, some people may suffer from itchiness in the spots.
Second stage
In this phase, the lesions turn pale in color. In most cases, no pain or irritation is experienced. However, those with extremely dry skin may develop scales over the spots. If skin is exposed to high temperatures or direct sunlight for extended points of time, scaly areas of skin may develop into flakes. Dry scales are especially noticeable during winter months, when the air is depleted of a major amount of moisture.
Third stage
The raised lesions may turn into smooth flat patches over the skin. These are white in appearance, which hints at the “alba” in the name of the disease. During summer, the patches do not get tanned but may rapidly turn red in the sun. This makes them more prominent, especially in people with a lighter complexion.
In some children, the spots may continue to exist for many months. By early years of adulthood, these get dissipated completely.
Pityriasis alba Causes
Doctors and medical researchers have still been unable to understand causes of Pityriasis alba completely. Medical research does not indicate any particular environmental or genetic factors to predispose individuals to this condition. However, it is believed to be associated with eczema.
Pityriasis alba Trigger Factors
Although the causes of the condition have not fully been know or understood, its trigger factors have been more or less recognized. These include:
Heat
The skin is found to be highly sensitive during the summer months and quite vulnerable to skin disorders. Prolonged exposure to sunlight can also worsen the skin patches arising due to the disorder.
Humidity
High humidity in atmosphere precipitates dryness of the human skin. Due to this, it is regarded as an inducing factor.
Skin soaps
Using new brands of soaps, that the skin is not adjusted to, may also produce acute reactions in children and young adults. This can lead to the development of this condition. Some medical experts believe that soaps containing fragrances can particularly be susceptible as trigger factors for this disease.
Clothing detergents
Certain detergent products used for cleaning garments consists of substances that are hypoallergenic (slightly allergenic). These may cause skin irritation, thus resulting in skin disorders.
Pityriasis alba Diagnosis
In most cases of this condition, treatment is not necessary. This is mainly due to the fact that patients do not experience any adverse symptoms that require immediate redressing. Mild topical steroid creams and moisturizers are usually enough to treat the symptoms. If the white spots remain unaffected by moisturizers, patients should visit a dermatologist. A dermatologist conducts a thorough examination to diagnose the condition. Diagnosis usually begins with a physical examination. If a skin cancer or some more acute disease is suspected, a biopsy of skin tissue may be performed.
If doctors or physicians suspect an yeast infection, they may scrape some of the abnormal scales onto a slide and examine them under a microscope. The process is known as KOH (potassium hydroxide) preparation and helps ascertain the presence of fungus or yeast.
Pityriasis alba Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this condition involves distinguishing it from other disorders that produce similar symptoms. These include:
Postinflammatory hypopigmentation
This involves partial loss of skin pigment and often follows an inflammatory skin disorder. It leads to the development of white patches which have irregular borders. The condition is especially noticeable in those with a darker skin tone.
Atopic dermatitis
It is an inflammatory, non-contagious skin disorder that is characterized by extremely itchy symmetrical patches which are red in appearance. The condition often arises due to other disorders, such as Allergic Conjunctivitis, Asthma and Hay fever. It responds well to topical steroids.
Psoriasis
This chronic skin condition is marked by the occurrence dry, symmetrical red patches that are covered with scales. These arise on various regions of the body, particularly over the scalp, ears and genitals. These also develop on the skin over bony protrusions.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
It is an acute inflammatory disorder of the skin. It is usually found to affect people with oily skin and is characterized by the occurrence of scales. Patients also suffer from yellow patches, over which crusts develop. Itching symptoms are also experienced by many sufferers. However, it is uncommon in children between 2 and12 years of age.
Pityriasis versicolor
It is a common skin disorder that leads to the occurrence of brow or pale-red patches over the skin. It is mainly caused by yeast fungus and arises on the chest and upper back. Rarely, it also results in the development of patches over the genital and scalp.
Tinea corporis
It is a fungal infection of non-hairy regions of the skin and affects various parts of the body, primarily the arms and the legs.
Nummular dermatitis
It is characterized by the formation of oval or round-shaped itchy lesions over the body, particularly on the legs and buttocks.
Vitiligo
It is an inherited skin disorder marked by patches of unpigmented skin that are often outlined by a heavy pigmented border.
Hypopigmented mycosis fungoides
It is a rare lymphoma of the skin, which may restrict itself for 10 years or more before diffusing to internal organs and leading to death.
Pityriasis alba Treatment
Most patients of this condition do not suffer from any adverse symptoms and hence, require no treatment. With time, the abnormal patches can resolve without any artificial cure. Simple emollients and in some cases, Hydrocortisone (a weak steroid) can effectively manage redness, scales and itchy symptoms.
Patients with very dry skin can use over-the-counter skin moisturizers or lotions to reduce dryness and improve the appearance of their skin. It is essential for such people to keep their skin hydrated and free from oily substances. This can encourage faster healing and make the spots disappear more quickly.
Terrasil (Tacrolimus) has been found to speed up resolution of this condition. In extremely acute cases, doctors may consider using PUVA therapy. Patients with severe skin patches may need cosmetic camouflage.
It must be remembered that discolored patches of Pityriasis alba darken on prolonged exposure to sunlight. To counter this, patients should use effective sun protection that helps reduce the difference between the colors of the patches with those of the surrounding skin.
Pityriasis Alba Creams
For facial lesions, over-the-counter moisturizing creams can be enough for cure. If scales develop over the spots or the lesions fail to disappear even months after moisturizer application, patients should visit a dermatologist who can prescribe topical corticosteroids for remedy. Topical hydrocortisone creams are also prescribed to many patients. These should be daily applied on the patches until they resolve entirely.
Applying 1% hydrocortisone cream over the affected region can relieve itchiness; reduce redness and help the patches fade more rapidly quickly. Other effective ointments involve:
- Pragmatar
- Lac-Hydrin
- Zetron
- Cordran Cream (consisting of 2% Zetra)
Proper treatment can make the disease resolve within a few months or a year.
Pityriasis alba Natural Treatment
Like most skin conditions, Pityriasis alba may also be treated by natural methods. Here are a few natural remedies that patients of this skin disease can use to reduce the rash.
Cabbage leaves
Take a handful of cabbage leaves. Blend them well to extract juice. Use a clean cotton cloth to strain the juice out of the cabbage pulp. Apply a generous dose of this juice over the affected region. Let the area dry itself naturally.
Black gram paste
Use a handful of black grams and form them into a thick paste. Apply a liberal amount of this paste on the patches or spots. Allow the mixture to persist for at least 15 minutes over the rashes. Wash the region and rinse off the paste with cool water.
Healthy diet
A nourishing diet comprising of essential vitamins and minerals can help in faster resolution of this disease. A healthy diet can supply important nutrients to the body, develop a stronger immune system and significantly improve the appearance of the skin.
Pityriasis alba Prognosis
The condition generally lasts for a short span. Patches arising due to this disease usually take anywhere from one to six months to fade away. However, some children and adolescents suffer from acute cases of the disorder that last for several years at a time.
Patches arising on the face may take about a year to go away.
Pityriasis alba Recurrence
The recurrence of this disease is uncommon. Very few patients over the age of 20 suffer from reappearance of this disorder. Some severe cases are found to recur frequently.
Pityriasis alba Complications
Some of the primary complications of this disease are:
Pruritus
It refers to any of the different skin diseases, such as scabies, that is characterized by itchiness and extreme irritation. It may be caused by allergies, infection, jaundice or lymphoma.
Hypopigmentation
This condition is marked by an abnormal lack of skin color. It is caused diminished pigmentation, particularly of the skin.
Prolonged application of steroid-based creams, such as Hydrocortisone, on the face can give rise to side-effects and cause additional skin problems.
Pityriasis alba Prevention
It is not possible to prevent this disease as its cause is unknown. However, those already suffering from this disorder can use sunscreen lotions on a daily basis to prevent worsening of the skin condition. Creams with a sun protection factor of around 15 can be enough to avoid aggravation of the skin patches due to exposure to sunlight.
Pityriasis alba Pictures
Take a look at these Pityriasis alba photos to get an idea about the skin appearance of those affected by this syndrome. You may find these Pityriasis alba images quite useful for reference.
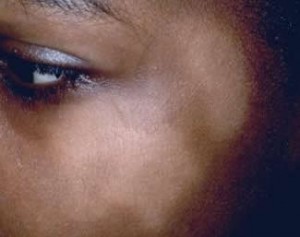
Picture 2 – Pityriasis alba Image
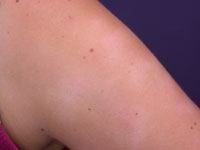
Picture 3 – Pityriasis alba Photo
If you suspect yourself or anyone in your family to be suffering from this disease, immediately get in touch with a doctor or experienced dermatologist. Faster diagnosis and treatment will help resolve the condition faster and help achieve a quicker recovery.
References:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001463.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1068868-overview
http://dermnetnz.org/doctors/dermatitis/pityriasis-alba.html#dd
http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/p/pityriasis_alba/intro.htm