Periapical abscess is a highly discomforting dental condition that accounts for 4-7% of all teeth-related problems. Read and know all about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this disorder.
Periapical Abscess Definition
Page Contents
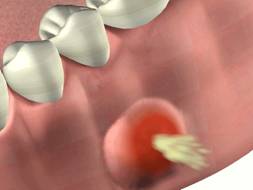
It is a condition marked by accumulation of pus in the centre of a tooth, caused by a localized bacterial infection. In this case, the tip of an infected root develops and encloses pus resulting in a dull and throbbing pain that makes it quite impossible for patients to eat.
The condition is also referred to by many other names like tooth abscess and dental abscess.
Types of Periapical Abscess
There are two main classifications for this disorder:
Picture 1 – Periapical abscess
Acute Periapical Abscess
This condition results from an acute periapical periodontitis. It cannot easily be distinguished during its early states but the through radiographic tools, dentists can identify if the condition has worsened and has developed into acute periapical abscess.
Chronic Periapical Abscess
This condition may be painless in comparison to the swelling and fever symptoms exhibited by acute Periapical abscess. The individual may not even be aware of its presence as it continues to develop inside the jawbone. Nevertheless, the area of infection may already be housed by a fibrous sac that forms a granuloma containing non-infectious sterile tissue. Although this is not pus, it is still important for dentists to learn about this condition because of the brain complications it may produce. The brain and mouth are very close to one another. It would not be difficult for bacteria to infect it and cause abnormalities to an individual.
Periapical Abscess Symptoms
Know about the main symptoms of this disease:
- Widened periodontal ligament space
- Soft tissue swelling on the adjacent teeth can be seen
- Extremely tender tooth
- Gnawing and continuous dental pain, especially when the affected tooth is tapped
- Difficulties in closing teeth, due to the pain and discomfort experienced during its contact with another teeth
- Increased pain in tooth, while consuming hot foods
- Sensation of having a longer tooth in comparison with other teeth
- Gumboil
- Localized swelling
- Gingival fistulas
- Halitosis
- Enlarged local lymph nodes
- Bitter taste in the mouth, especially after draining procedure
These signs are quite evident in acute types of the condition. However, the above mentioned list may not include all the problems experienced by chronic sufferers. Moreover, there are some reported cases wherein the alveolar bone gets affected by the condition causing inflammation to spread even to the surrounding facial tissues. This may reveal an inflammation even in the facial area.
If you are experiencing one or more of the aforementioned symptoms, get in touch with a dentist at the earliest. You may have a high risk of suffering from Periapical abscess.
Periapical Abscess Causes
The main cause of this disorder is poor dental hygiene, resulting in an untreated dental decay. Other causes include:
Failed root canal treatment
An unsuccessful treatment of the root canal results in a breakdown of the bone surrounding the root of the tooth. This fosters the development of an abscess or a cavity loaded with pus.
Injuries to the affected tooth
If the tooth experiences trauma, it may be left with an infected dental nerve or dead pulp. This may lead to a breakdown of the bone and complete insufficiency of the primary function of the tooth.
Dental caries
Dental caries destroys the enamel and the dentin. When this happens, the bacteria have easier access to reach the pulp of the tooth. Once it has gained access to the mouth, the pulp can be infected and destroyed by these microorganisms.
Periodontitis
This is another relative factor for the condition. At times, gum damage not caused by the disorder may also be seen as one of its major causes.
Periapical Abscess Diagnosis
Before treatment is applied on the tooth, dentists will conduct a thorough oral examination of the infected tooth. If blood or pus is seen oozing from the pulpal exposure and large carious lesions are also displayed then the dentist will recommend an emergency treatment plan.
Periapical Abscess Treatment
The curative process for this dental ailment involves:
- Drying the cavity from the fluid using cotton pellets
- Maintaining its dryness by slightly moistening the cotton pellets and packing the cavity with eugenol
- Carefully removing loose debris from the cavity
- Stuffing the cavity with temporary materials for filling
- Re-evaluating the occlusion
- Re-evaluation of emergency treatment for the teeth
Many patients have reported about relief the moment pus is drained out of their tooth. This is probably due to the easing of pressure put on the tooth by the accumulated pus.
Some of the common treatment options used for this dental disorder include:
Root canal treatment
Root canal therapy is often conducted to save affected tooth. It requires removing diseases tissues from the center of the mouth, such as the decayed portions of the tooth, the nerve, and the vascular tissue or the pulp. After this, it is filled with gutta percha and covered with filling or crown. This is a popular way of saving a tooth from possible extraction. It is regarded as a very effective way of treating Periapical abscess.
Picture 2 – Periapical abscess Image
Tooth Extraction
In cases where the pulp is extremely damaged by the pus, extraction is regarded as the only remedy. This is done when the jaw itself is badly damaged and even root canal procedure will not do it good. This is the last option dentists recommend and is not to be considered as an alternative for Root Canal Therapy. The only way you can gain a tooth back using this approach is to request for a bridge or an implant. However, this very expensive procedure is not open to all patients. Furthermore, dentists wish to preserve the natural teeth of their clients and use extraction only when other curative options fail to bring about an improvement in the condition.
Tooth Scaling and Root Planning
The aim of tooth planning is to avoid occurrence of the same condition. Since it often involves damage to the gum brought by Periodontitis, Periodontal surgery may be conducted to lessen the risk of experiencing the same pain and discomfort in your other teeth in the future.
As periapical abscess treatment can be quite expensive, several dental offices are offering financial assistance to their patients these days. Patients are put in a more comfortable position if they purchase dental insurance. If this is not available it is best to discuss alternative financial plans with dentists.
Periapical Abscess Home Remedies
Mothers may try giving their children oil of cloves that has Eugenol. Place it on the infected tooth and it will give your kids a short-term relief. However, it is essential to follow this up with a visit to the dentist for a more effective treatment.
How to Prevent Periapical Abscess Complications?
Since the condition has been found to affect other tooth and the brain functions, the following remedies are highly recommended to prevent occurrence of unwanted discomforts.
Saltwater Rinse
This may be considered a traditional way of getting rid of bacteria in the mouth, but is still one of the cheapest ways to disinfect the mouth from possible infection. Rinse the mouth with warm saltwater solution to help maintain the cleanliness of the mouth, encourage draining, and relieve it of the pain. It may be done several times in a day to help relieve the patient of the pain.
Ice Pack Treatment
Instead of placing unnecessary ointment on the gum, and triggering possible complications, mothers may simply apply ice pack outside the cheek of their children to help reduce facial inflammation. If this is unbearable, medical attention must be sought immediately from dentists.
Medication
Expect medications from your dentist after dental treatment is applied on your tooth. Follow the prescription accordingly even if you do not experience any pain. This will safeguard you against possible complications and infection in the future. Medicines are to be consumed in a few days. However, if there is re-emergence of pain it is better to call a good dentist for immediate action.
Follow-up X-rays
After treatment, patients need to return after six months so the condition of the gum and the bones can be re-evaluated. A re-evaluation confirms whether the bone and the tissues have positively regenerated without complications. If required, endodontic treatment may be deemed as necessary and performed once again.
If you or any of your family members is experiencing a constant, throbbing toothache you must get in touch with your dentist. Teeth are one of the greatest assets of the body and a timely treatment will help prevent development of complications in it.
References:
http://medical.tpub.com/14274/css/14274_99.htm
http://www.fpnotebook.com/den/teeth/prpclabscs.htm
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002055/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Periapical_abscess

Thank you that was very informative.