Pancreatic Pseudocysts are the most common types of pancreatic cystic lesions that account for around 75-80% of all abnormal masses arising in the pancreas. Read and know what a pseudocyst is as well as all about its causes, symptoms, management and treatment options.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Definition
- 2 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prevalence
- 3 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Classification
- 4 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Pathophysiology
- 5 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Causes
- 6 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Risk Factors
- 7 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Signs and Symptoms
- 8 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prevention
- 9 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Diagnosis
- 10 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Differential Diagnosis
- 11 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Treatment and Management
- 12 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prognosis
- 13 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Complications
- 14 Pancreatic Pseudocyst Recurrence
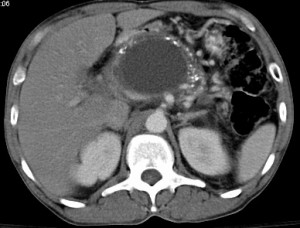
It is a condition marked by the development of a fluid-filled sac within the abdomen. It is generally located in the lesser sac of the abdomen and contains pancreatic enzymes, necrotic tissues and blood. It commonly develops in children after some type of abdominal trauma.
The prefix “pseudo” (meaning “false” in Greek) in the name of this disorder distinguishes these lumps from true cysts that are lined by epithelium. Pseudocysts are surrounded by granulation tissues.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prevalence
Picture 1 – Pancreatic Pseudocyst
The exact prevalence of this condition is not known. According to medical research, however, 60 to 85% of these cases occur due to alcohol abuse and gallstones. Men are 5 to 10 times more prone to the condition compared to women.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Classification
There is much confusion regarding “chronic” and “acute” pseudocysts. According to experts, acute Pancreatic Pseudocysts are sacs containing pancreatic juice and lined by a granulation tissue wall. These cysts arise due to pancreatic trauma or Acute Pancreatitis. Chronic Pseudocysts are sacs filled with pancreatic juice and lined by fibrous tissues. These mainly arise due to Chronic Pancreatitis.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Pathophysiology
Acute Pancreatitis is caused by disturbances in the functioning of the pancreatic parenchyma and ductal system. Due to this, the pancreatic enzymes are extravasated leading to the digestion of the adjoining tissues. It results in the development of fluid sacs around the pancreas that comprise of pancreatic enzymes, necrotic debris and hemolysed blood. The fluids generally accumulate in the lesser sac and form pseudocysts in the pancreas. This is known as ‘Acute Pancreatic Collection’. Some of these pancreatic collections are cured automatically as an affected individual recovers from the condition. However, many of them organize themselves and get surrounded by a solid wall of fibrosis and granulation tissue. This process continues for several weeks, finally leading to the development of Pancreatic Pseudocysts.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Causes
Know about some of the main factors that lead to this condition:
- A severe episode of acute Pancreatitis, characterized by a sudden swelling of the pancreas, is the most common cause of this disorder.
- Swelling and inflammation, occurring due to Pancreatitis, generally damages the pancreatic ducts. This may give rise to a pseudocyst.
- Some kind of abdominal trauma, especially in children, may also result in the development of such sacs.
- Individuals suffering from Chronic Pancreatitis may also develop this condition.
- An episode of acute Pancreatitis sometimes leads to pseudocysts, especially in case of people who have experienced some penetrating trauma.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Risk Factors
The risk factors of this condition include
- Underlying Chronic Pancreatitis
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Abdominal trauma
- Alcohol abuse
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of the disorder tend to vary from one patient to another. The main signs and symptoms of the condition include:
- Abdominal Bloating
- Severe abdominal pain
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice or yellowing of the eyes and skin
- Tender mass in the abdomen
- Development of fluid in abdominal cavity
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prevention
Avoiding Pancreatitis is the only way to prevent the development of these sacs. If gallstones are causing Pancreatitis, it is necessary to remove the gallbladder with an appropriate surgery (Cholecystectomy). It is important to give up drinking alcohol if alcohol abuse is the main reason behind Pancreatitis. This helps prevent future occurrence of Pseudocysts.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Diagnosis
The chief objective of diagnosis is to determine the location, size and number of pseudocysts in the pancreas. Draining these kinds of pseudocysts increases the possibility of development of pancreatic fistula. Due to this reason, it is important to find out if the pseudocysts have any connection with the pancreatic ductal system.
Some of the diagnostic imaging tools that are commonly used for this disorder include:
Ultrasonography
It is an ultrasound based imaging technique used for detecting various diseases. In this case, however, the usefulness of Ultrasonography for understanding the state of the pancreas is often limited due to the health of patients and the experience of the operator.
Computerized Tomography
This test is perfect for both the initial assessment and the follow-up treatment of this disorder.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
This test helps understand the relationship between the pseudocysts and the pancreatic ducts.
Blood Tests
The amount of different substances present in the blood can be measured by a blood test. Blood test is commonly done during the diagnosis of these cysts.
X-Ray
An X-ray examination produces images of the internal structures of the body by electromagnetic energy beams. This helps check whether any pseudocysts are present in the pancreas.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for this disorder includes ruling out presence of other associated conditions, such as:
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Pancreatic Pseudoaneurysm
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Chronic Pancreatitis
- Pancreatic Necrosis
- Pancreatic Abscess
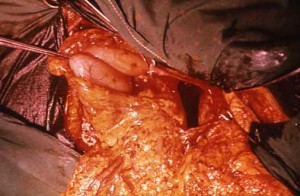
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Treatment and Management
Pseudocysts do not always require treatment as some of them heal on their own. However, an advanced stage of this pancreatic disorder requires professional medical treatment which involves surgery, gastroenterology and radiology.
Picture 2 – Pancreatic Pseudocyst Image
The condition rarely occurs during pregnancy. Its management depends on various factors.
Surgical Treatment of Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Surgery is the most common treatment option used for curing this condition. The various surgeries used for curing this disease include:
Cystgastrostomy
It connects the back wall of the stomach and the pseudocyst in such a way that the fluid in the pseudocyst can drain into the stomach.
Cystjejunostomy
In this surgery, the small intestine and the pseudocyst are connected so that the pseudocyst fluid can flow directly into the small intestine.
Cystduodenostomy
In this procedure, surgeons make a connection between the pseudocyst and the duodenum to make the fluid drain directly into the latter organ.
Drainage of Pancreatic Pseudocyst by Radiology
In this process, a radiologist inserts a thin needle into the pseudocyst with the aid of a CT X-ray to drain the fluid. This technique can successfully cure the condition. In many cases, however, it gives rise to various complications including constant leakage from the surgically created drainage spot and infection of the Pancreatic Pseudocyst. Due to such risks, this surgery is generally not used for treatment of the condition.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Prognosis
Generally, the outcome of this pancreatic disorder is good after a successful surgery. However, the condition can become much more serious if left untreated.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Complications
The condition may lead to various complications, such as:
- Rupture
- Infection
- Hemorrhage
- Obstruction
The obstruction or blockage can cause GI tract compression from stomach to colon as well as compressions in the biliary system, urinary system and arteriovenous system. Leaving the condition untreated for a long time may also lead to severe health problems.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst Recurrence
The chances of recurrence of these abnormal vesicles are very low. It is believed that surgical treatment reduces the risks of recurrence more than percutaneous treatment options.
Pancreatic Pseudocyst is a highly painful abdominal condition. Without proper treatment, it may also lead to various acute health disorders. However, there are numerous surgical procedures that can cure the problem, allowing an affected individual to live a long and normal life. If you have a family member having symptoms of this disorder, get in touch with a healthcare professional as fast as you can. Timely treatment will help cure the condition faster and allow preventing unnecessary complications.
References:
http://health.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/pancreatic-pseudocyst/overview.html
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001317/
http://www.mdainternet.com/MDA4/topics/p/pancreatic_pseudocyst.asp
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000272.htm
http://health.yahoo.net/adamcontent/pancreatic-pseudocyst