Are you finding it increasingly difficult to stare at light, even dim bulbs? Are you also suffering from extreme dryness in your eyes? You could be having Ocular rosacea, a discomforting eye disorder. Read and know more about this ophthalmologic condition including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment.
Ocular rosacea Definition
Page Contents
It is an inflammatory condition of the eye and eyelids that is associated with rosacea, a dermatological (skin-related) disorder characterized by chronic redness of the face. It is manifested by small lesions that can cause persistent burning or lumpy feeling in the eyes.
Ocular rosacea Incidence
It occurs more frequently in women but in some cases, men are also prone to this condition. It is estimated that nearly 50 percent of the population with rosacea have ocular symptoms. It primarily affects adults between the ages of 30 and 60. It is more common in people with light eye color.
Ocular rosacea Symptoms
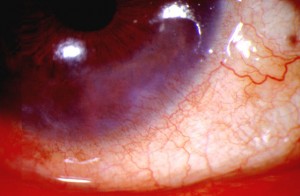
Picture 1 – Ocular rosacea
In 20% of all cases of the disease, ocular problems occur prior to rosacea symptoms. Normally, however, the skin symptoms appear first. Complications of this condition are not always related to the severity of rosacea and are dependent on the degree of the ailment.
Some of the main problems experienced by individuals affected with this disorder include:
Dry eye syndrome
Generally, tears keep the conjunctiva (mucous membrane of the eye) moist and combat any infection in it. In people with this condition, the eye is unable to have a coating of a layer of tears. Patients often complain of minor irritation in the eye, which is frequently accompanied by itchiness.
Grittiness
Dryness in the eyes leads to a sandy-gritty sensation. Patients always get a feeling of having a foreign body or object in the eye manifested by blurred vision.
Photophobia
Patients may develop extreme sensitivity to any form of light, including dim light. During exposure to light, irritability and discomfort are experienced in the eye.
Bloodshot eyes
In affected people, there is dilation of the small blood vessels present on the lining of the conjunctiva. This leads to red eye, which can be contagious.
Blepharitis
It is an inflammation of the eyelash follicles, along the edge of the eyelid, which results in redness and itchy sensations. It is characterized by swollen eyelids, caused by accumulation of debris and flaky skin along the margin.
Chalazion
It is a lump caused by obstruction of the drainage duct of an oil gland within the upper or lower eyelid. It tends to increase in size within a few weeks. Occasionally, it turns red and painful.
Stye
It is a red, swollen bump arising on the edge of the eyelid due to an infected eyelash follicle. It is usually painless and tender, often mistaken for Chalazion.
Corneal ulcer
Patients may exhibit erosion or open sore on the cornea of the eye. This normally happens in severe cases where there is mild to severe discharge and partial loss of vision.
Dehydration
Affected eyes may often be in a state of dehydration, causing inflammation. In affected individuals, water tends to evaporate faster from the eye causing extreme dryness.
Ocular rosacea Causes
The exact causes of this condition are not very clear. However, certain environmental factors are suspected to be responsible for the ocular inflammation that characterizes this disorder. Some other possible causes include:
Flushing
It is an involuntary response of the nervous system, which leads to dilation of the capillaries inside the eye. Frequent flushing can disturb the tear film of the eye and result in inflammation. Consumption of alcohol, hot beverages, spicy foods and vasodilators like niacin may give rise to burning sensations in the eyes. Smoking is also said to cause widening of the ocular blood vessels.
UV sunlight
Regular exposure to the sun may contribute to this inflammatory condition of the eye. Levels of UV radiation from the sun are particularly very high during summer that can cause damage by burning the eye surface. These burns, although very painful, are usually temporary. Long-term exposure to UV light may even affect the internal structures such as lens and retina.
Heat
Taking hot baths or staying in hot tubs, steam rooms or saunas for a longer period may also cause grittiness and swelling of the eyes. In this case, inflammation occurs as a result of substantial damage to the blood vessels of the eyelids.
Abnormal oil secretion
Hypersecretion or excessive secretion from the oil glands of the eyelids can cause inflammation of the eye. On the other hand, reduced secretion of the oil due to blockage of the glands also has an adverse effect. The water layer beneath the thin oil layer evaporates rapidly, leaving the eyes in a dehydrated state. In the absence of a normal oil layer, the tear film of the cornea can lose water at a faster rate.
Cold temperature
Chilled conditions and cold wind exposure can cause watery discharge and scaly patches around the eyelids as seen in Dry Eye Syndrome.
Stress
Emotional stress or anxiety increases flushing that may damage the tear glands of the eye.
Bacterial Infection
Helicobacter pylorus is sometimes regarded as an undetermined factor that may cause inflammation of the eye. However, no direct link has been established between the two.
Genetics
Some medical experts believe that ocular rosacea is an inherited condition and could be passed on from generation to generation.
Ocular rosacea Diagnosis
It is usually diagnosed when the symptoms of rosacea are visible. However, skin symptoms are not always prerequisite to the diagnosis and may occur before the appearance of the cutaneous features.
There are no specific diagnostic tests or procedures that can detect this ocular disorder. Physicians do the initial diagnosis by assessing the signs and symptoms in patients. Sufferers may even be asked about their medical history in order to determine the origin of the disorder. It is usually followed by a routine eye exam to check any sort of abnormality in and around the eye such as Conjunctivitis, dryness, or grittiness. Appropriate treatment is suggested by physicians on the basis of the results obtained from the physical exam.
Ocular rosacea Treatment
In severe cases, untreated corneal infection may lead to perforation of the eye thus leading to permanent loss of vision. Although this disorder cannot be cured completely, some medications may help in managing its symptoms.
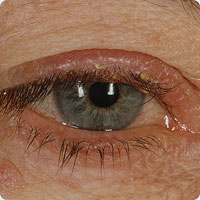
Picture 2 – Ocular rosacea Image
Some of the primary treatment options for this disorder include:
Artificial tears
These are synthetic and water-based solutions used for treating Dry Eye Syndrome. They lubricate the eye to eliminate dryness and irritation.
Humidifier
Patients having chronic dry eye can opt for this home device that emits water into the air to increase moisture levels. It can reduce the dryness in eyes and is quite beneficial during cold conditions.
Silicone plugs
These are soft and malleable plugs that can be inserted temporarily in the tear drainage ducts at the inner corner of the eyelid. These can help prevent continuous drainage of tears and retain them in the eye, thus improving the vision. Permanent ones are also available that can be inserted painlessly and quickly, and can be removed if required.
Punctal cautery
It is a very popular ocular treatment where the punctal or tear drainage ducts are closed permanently by the application of heat.
Warm compress
Blepharitis, stye, or chalazion can be controlled by keeping the eyelids and eye lashes clean. A clean wash cloth is usually soaked in hot water and placed on the closed eyelids for sometimes. This is followed by gentle scrubbing of the eyelids with a cotton swab soaked in soap water and rinsing with warm water. Patients are required to follow this procedure several times in a day in order to reduce the inflammation.
Eye drops
Minor corneal infections are generally treated with anti-bacterial or anti-fungal eye drops. In severe cases, patients are administered with steroid eye drops to reduce inflammation.
Oral antibiotics
Antibiotic medications like Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Erythromycin or Minocycline have very good anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Lower doses of these drugs may aid in suppressing the symptoms. In mild cases, these are not usually prescribed by physicians and can be managed with antibiotic drops or ointments.
Ocular rosacea natural treatment
Natural remedies that mainly comprise of herbal supplements are usually opted for when other treatment options prove to be ineffective. Some of the main natural substances used for remedying this disorder include:
Ginger
A popular ingredient in various dishes, it can be used in treating Ocular rosacea. Ginger supplements may help in reducing inflammation of the eyes if used for a prolonged duration.
Turmeric
Components of this herb have many medicinal properties, such as anti-inflammatory that can be used to treat this condition.
Ocular rosacea Diet
An overall balanced diet can ease the discomfort in the eye caused by the disorder and prevent the occurrence of any further complications. Sometimes, patients may show negative response towards some types of foods that may worsen the condition. It is therefore essential to consult a good physician who can suggest a proper diet for patients. Doctors typically recommend inclusion of:
Omega-3 fatty acids
Foods that contain omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation associated with dry eye. Salmon and other fatty fish as well as flaxseed and walnuts, containing omega-3 can be consumed by patients. Although these do not provide quick relief, these may help in controlling inflammation.
Fruits and vegetables
Plenty of raw or steamed vegetables like potato, spinach, or carrots and whole grains that are rich in fiber should be eaten. Fruits like blueberries, strawberries, raspberries and cucumber containing antioxidants are very essential for treating this ophthalmologic condition.
Water
Drinking more water can reduce dehydration and discomfort of dry eyes. This is usually done during hot and dry conditions. Physicians normally recommend patient to have nearly 8-10 glasses of water every day. Sufficient amount of water is vital for the eyes to produce tears and keep it moist for clarity of vision.
Ocular rosacea is neither contagious nor serious. However, an early diagnosis of the condition should be done in time to prevent its symptoms from worsening. Patients must also make sure that they get enough essential nutrients for proper functioning of their eyes.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ocular_rosacea
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1197341-overview
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/ocular-rosacea/DS01177/DSECTION=symptoms
http://www.allaboutvision.com/conditions/ocular-rosacea.htm