Noonan Syndrome is a complicated condition that is regarded as a type of dwarfism. Read on to know what is Noonan Syndrome as well as its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and cure.
Noonan Syndrome Definition
Page Contents [hide]
- 1 Noonan Syndrome Definition
- 2 Noonan Syndrome ICD9 Code
- 3 Noonan Syndrome Incidence
- 4 Noonan Syndrome History
- 5 Noonan Syndrome Symptoms
- 6 Noonan Syndrome and Learning Disabilities
- 7 What Causes Noonan Syndrome?
- 8 Is Noonan Syndrome Hereditary?
- 9 Noonan Syndrome Diagnosis
- 10 Noonan Syndrome Treatment
- 11 Noonan Syndrome Prognosis
- 12 Noonan Syndrome Complications
- 13 Noonan Syndrome Life Expectancy
- 14 Noonan Syndrome Association (NSA)
- 15 Noonan Syndrome and Hearing Loss
- 16 Noonan Syndrome and Bleeding Disorders
- 17 Noonan Syndrome and Cardiac Defects
- 18 Noonan Syndrome in Babies
- 19 Noonan Syndrome Pictures
- 20 Noonan Syndrome Prevention
It is an acquired genetic disorder that runs down generations of the same family and results in unusual growth in many parts of the human body. The disease was earlier known as “Turner-like Syndrome” or as “Male version of Turner’s Syndrome”.
Noonan Syndrome ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code for Noonan Syndrome is 759.89.
Noonan Syndrome Incidence
This is a rare genetic disorder that is found to affect only 1 out of every 2000 individuals.
Noonan Syndrome History
The disease owes its name to Dr. Jacqueline Noonan, an American child cardiologist. In 1963, Dr. Noonan observed that many children, who were her patients, had similar facial features along with narrow pulmonary valves. The kids were also found to be of similar short stature. Noonan was the first physician who is credited to have discovered this syndrome.
Noonan Syndrome Symptoms
Noonan Syndrome (NS) has a wide range of symptoms, not all of which are exhibited by all patients. Symptoms and their severity differs one patient to another. Generally, however, a patient with NS displays physical abnormalities that include:
Facial irregularities
People with NS typically have large eyes which may either be widely spaced or drooping (downward slanting) in appearance. Sagging eyelids (Ptosis) is one of the common symptoms of Noonan Syndrome. The nasal bridge may appear as flat. The ears may appear abnormal in shape or as if they have been set low on the head.
Cervical abnormalities
The neck (cervix) is often shorter than usual in NS sufferers. There may also be additional folds of skin on either side of the posterior neck region.
Heart defects
As many as 80% children with Noonan syndrome are found to suffer from cardiac defects. These defects may include a hole in the cardiac chambers, a narrowing of the pulmonary valve and thickening of the heart muscles.
Some other prominent signs of this disease are:
- Variable loss of hearing capabilities
- Delayed puberty
- Slight mental retardation, only in about 1/4th of all patients
- Small penis
- Short stature
- Undescended testicles (testicles that fail to move into the scrotum despite development of the male fetus)
- Abnormal shape of chest, generally a sunken chest (Pectus Excavatum)
Noonan Syndrome and Learning Disabilities
It has been suggested that Noonan syndrome is associated with learning disabilities, despite a lack of substantiating
evidence, and parents have suggested that affected children are clumsy and have behavioral problems. In a study of 151 individuals with Noonan syndrome, Sharland et al. (1992) noted that there was a slight delay in the motor milestones and that only 11% of children of school age attended a school for children with learning disabilities, but there was no formal assessment of IQ.
What Causes Noonan Syndrome?
The development of NS is associated to defects in any of the genes that are involved in the formation of many tissues all through the human body. Scientists presently know of seven genes that may give rise to Noonan Syndrome. A mutation in any of these genes can cause NS.
These genes manufacture proteins which play a role in growth and development of humans. Defects in these genes cause hyperactivity of the manufactured proteins which interrupts the normal method of cell growth and division.
In some people, NS develops even without a mutation in any of the seven genes. In such cases, NS seem to be a result of mutations in genes that are yet undiscovered.
Is Noonan Syndrome Hereditary?
This largely appears to be a hereditary condition and is said to be autosomal dominant in nature. In other words, an infant can have this syndrome if it receives the mutated gene from either of its parents. The genetic mutation can occur in any of these ways:
- It can be acquired from a parent who carries the mutated gene, in an autosomal dominant case.
- It may develop due to an altogether new mutation in offspring, even in the absence of any a genetic predisposition for the condition.
Kids having one parent with NS have a 50% chance of suffering from the disorder. In some cases, however, the condition may not be inherited.
Noonan Syndrome Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disease depends on the amount of symptoms displayed by sufferers. If the symptoms are more in number, the condition can be diagnosed earlier. Doctors may also become aware of this disease faster if a heart murmur is found to be caused by an uneven flow of blood. An Echocardiogram (ECG) test can help investigate irregularities in blood flow.
Diagnosis is usually done after a physician observes some of the primary symptoms of the disorder. However, some features are too subtle to be detected through tests. Noonan Syndrome testing is non-specific in nature.
In some cases, the disease is diagnosed only after a person has reached adulthood and given birth to a child with obvious NS symptoms.
If a doctor suspects heart problems, he or she will initially carry out a physical examination. A physical observation helps detect symptoms of Congenital Heart Disease like Pulmonary Stenosis and even ASD in some cases.
Doctors may also recommend other cardiac tests, such as:
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The procedure involves placing electrodes on the chest of patients to assess problems. The technique helps in recording and analyzing the electrical impulses that pass through the heart.
Echocardiogram
The test involves using sound waves to produce a moving diagram of the functioning heart. It allows doctors to view the source of problems in the organ.
These cardiac tests can be used to assess the nature and intensity of the disease. The tests are generally carried out by a physician who specializes in heart ailments (cardiologist).
Some other diagnostic tests for this disease include:
- Chest x-ray
- Molecular genetic testing
- Hearing tests
- Platelet count
- Blood clotting factor test
Noonan Syndrome Treatment
There is no particular treatment for this condition. Doctors usually suggest treatment that helps manage or relieve the symptoms arising from the disease, such as heart complications. Treatment is also required if there is any structural irregularity or an obstruction that prevents normal flow of blood within the body. The approach for cure depends on the type and severity of the disease. Most of the physical problems arising from this disease are cured in a general manner. No specific approach is used.
Some of the main symptomatic treatments, used for curing this condition, may include:
Heart Treatment
Various cardiac problems, associated with this disease, are quite effectively cured with certain drugs. Surgery may be required if any valve involvement is detected.
Low Growth Rate Treatment
In children affected with NS doctors usually examine hormone levels, bone growth and thyroid function as well as blood chemistry. The height of patients should be determined thrice every year until they are 3 years of age. After that, height measurement can be done once every year until adulthood. If the level of growth hormones is found to be insufficient, growth hormone therapy may be used to treat the condition. In some patients with NS, Growth hormone therapy has been found to yield successful results in improving short stature.
Learning Disability Treatment
This includes the correction of various mental as well as behavioral issues. Doctors may also use infant stimulation programs in some cases.
Vision Treatment
Children affected with NS require regular testing of eyesight after every 2 years. Most vision-related problems can be improved simply with the help of glasses.
Genital Treatment
In male infants with undescended testes at birth, surgery is a possibility.
Urinary Tract Treatment
If NS sufferers are diagnosed with urinary tract infection, physicians may use antibiotics as a standard treatment procedure.
Noonan Syndrome Prognosis
The condition has a good prognosis due to the fact that treatment is generally successful. However, it is better to be said that the prognosis largely depends on the severity of the various symptoms, particularly cardiac defects. Sufferers with a severe form of this syndrome can have a much shorter life span than those with mild problems.
Long-term prognosis also depends on whether the patient suffers from mental deficiencies.
Noonan Syndrome Complications
The condition may cause several physical complications, most of which are permanent. These include:
- Structural problems of the heart
- Short stature
- Failure to thrive (especially in infancy)
- Reduced growth of height
- Slow weight gain
- Infertility in males with twin undescended testes
- Hair problems
- Skin irregularities
- Poor muscle tone
- Accumulation of fluids in body tissues (Cystic Hygroma, Lymphedema)
- Tendency to bruise easily
- Eyesight problems, such as short-sightedness
- Ear infections, leading to possible hearing loss
Patients may also suffer from mental problems that include:
- Reduced self-esteem
- Social difficulties (related with physical symptoms)
Noonan Syndrome Life Expectancy
In NS sufferers, life expectancy depends on the associated complications as well as their severity during the lifetime of patients. A few medical studies suggest that lifespan can be reduced by approximately 10 years in sufferers.
Noonan Syndrome Association (NSA)
It is a registered charitable organization in the UK that provides support to patients affected by Noonan Syndrome as well as their families. The establishment extends complete support through research, care-giving and raising awareness about the disease.
The registered address of this organization is:
Noonan Syndrome Association
Newlife Centre
Hemlock Way
Cannock
Staffordshire WS11 7GF
Registerd Charity Number: 1140671
The contact information of this establishment is:
Telephone: 0800 083 2972
Fax: 01543 468999
E-mail: info@noonansyndrome.co.uk
Noonan Syndrome and Hearing Loss
Patients with NS have a higher risk of suffering from certain degree of hearing loss. The type of hearing loss is Sensorineural, which means the hearing defect is experienced in areas like:
- Inner ear
- Auditory nerve
- Auditory centers of the brain
Surgery is used to improve this form of hearing loss, often without any success. In such cases, hearing aids may help cure auditory defects.
Noonan Syndrome and Bleeding Disorders
Several bleeding disorders have been related with this condition. Women with a bleeding disease typically suffer from heavy bleeding during childbirth or menstruation (Menorrhagia). Some individuals may experience other difficulties, such as:
- Bleeding through the nose
- Excessive bruising
- Prolonged bleeding following trauma or surgery
Noonan Syndrome and Cardiac Defects
2/3rd patients with NS are found to suffer from cardiac problems like:
Pulmonary Valvular Stenosis
The condition arises in 50% of NS sufferers. It is characterized by an obstruction of proper blood flow to the lungs from the right lower chamber of the heart (right ventricle). Infants with NS often suffer from a decrease in width of the pulmonary valve, through which blood moves from the heart to the lungs.
Septal defects
These defects may include holes in either of the upper or the lower chambers of the heart. The cardiac muscles may also get thickened.
Heart murmur
It refers to the sound of flowing back of blood through an impaired heart valve. Heart murmur often helps in diagnosing NS in patients.
Cardiomyopathy
The disease involves a weakening or an aberration in the cardiac muscle. The problem often arises due to problems in cardiac functioning or when the heart fails to pump normally. Most patients with Cardiomyopathy suffer from heart failure at a later stage.
Noonan Syndrome in Babies
NS is found to arise in only one out of 1,000 to 2,500 live births. The problem may be detected in babies in infancy due to the presence of
- Abnormal facial characteristics
- Excessive neck skin
- Thin hairline on the back of the neck
- Flat nose
- Larger head than body
- Reduced growth in stature
- Decreased weight gain
Noonan Syndrome Pictures
Here are some assistive Noonan Syndrome photos that will give you an idea about the physical appearance of sufferers of this condition. You may find these Noonan Syndrome images quite useful for reference.
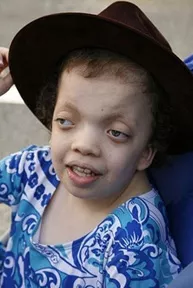
Picture 1 – Noonan Syndrome Image
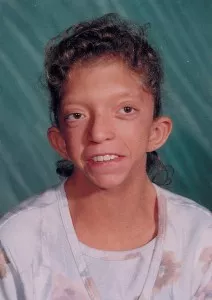
Picture 2 – Noonan Syndrome Photo
Noonan Syndrome Prevention
There is no definite way to prevent this condition. However, married couples who wish to give birth and have a family history of NS should consider genetic counseling before having children. Those who have just delivered babies should perform early evaluation. Early examination in infants can help detect this condition. Often, assessment by an experienced geneticist is required to diagnose Noonan Syndrome.
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002621/
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/noonan-syndrome/DS00857
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/947504-overview
http://www.experts123.com/q/what-is-noonan-syndrome.html
