Nemaline Myopathy Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Nemaline Myopathy Definition
- 2 Nemaline Myopathy Incidence
- 3 Nemaline Myopathy Types
- 4 Nemaline Myopathy Causes
- 5 Nemaline Myopathy Symptoms
- 6 Nemaline Myopathy Pathophysiology
- 7 Nemaline Myopathy Inheritance
- 8 Nemaline Myopathy Diagnosis
- 9 Nemaline Myopathy Differential Diagnosis
- 10 Nemaline Myopathy Treatment
- 11 Nemaline Myopathy Prognosis
- 12 Nemaline Myopathy Life Expectancy
- 13 Nemaline Myopathy Prevention
- 14 Nemaline Myopathy Support Groups
- 15 Nemaline Myopathy Pictures
Nemaline myopathy (NM) is an inherited congenital neuromuscular condition characterized by skeletal muscle weakness in various parts of the body.
The condition is also known by other names like:
- Nemaline Rod Myopathy
- Congenital Rod Disease
- Rod Myopathy
The disorder causes various physical deformities and makes it difficult for patients to move due to the muscle weakness and delayed motor development. It is counted among the relatively common congenital Myopathies.
The brain development is not hampered by this condition. NM patients have normal intelligence level and are believed to have a higher Malignant Hyperthermia susceptibility. The disorder is sometimes associated with other health conditions like monoclonal gammopathy and Early HIV infection.
Nemaline Myopathy Incidence
According to its incidence statistics, 2 out of every 100,000 individuals inherit this condition. It can occur in people from all ethnic groups, but is believed to be more prevalent in Ashkenazi Jewish populations. Its carrier frequency is approximately 1:108 in Ashkenazi Jewish people.
Nemaline Myopathy Types
NM is clinically classified into various groups, including the following:
- Mild (Typical) Nemaline Rod Myopathy
- Intermediate Nemaline Rod Myopathy
- Severe Nemaline Rod Myopathy
- Adult-onset Nemaline Rod Myopathy
However, the classification is somewhat ambiguous as the categories often overlap with each other.
Nemaline Myopathy Causes
The exact etiology of this condition is still not known. Researchers have shown certain genetic mutations to be responsible for its occurrence. Mutations in the genes controlling the creation of some specific sarcomere proteins may lead to Rod Myopathy. Five separate genes have been identified as being involved with the disorder:
- ACTA1 (controlling the production of the protein skeletal muscle alpha actin)
- TPM2 (coding for the beta tropomyosin protein)
- TPM3 (regulating the production of alpha tropomyosin slow)
- NEB (controlling the nebulin production)
- TNNT1 (coding for the troponin protein)
Nemaline Myopathy Symptoms
The symptoms of NM and their severity may vary, depending upon the seriousness of the disorder and the age of onset. Muscle weakness and low muscle tone are among the most common symptoms occurring in all patients. The symptoms of NM are mentioned below:
- Weakness – mainly in the upper arms and legs, face, neck, trunk muscles as well as the respiratory muscles
- Hypotonia or low muscle tone
- Respiratory problems
- Difficulty swallowing
- Speech problems
- Joint deformities
- Developmental delay which hampers the walking and mobility of children
- Scoliosis or abnormal spinal curvature which tends to worsen during puberty of the patient
Cardiac involvement has also been reported in some very rare cases where a patient develops dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Nemaline Myopathy Pathophysiology
It results from the abnormal accumulation of the nemaline rods in muscle fibres, disturbing the sarcomere function. Sarcomeres, the smallest of all contractile units in the muscle, consist of thick myosin and thin actin filaments. These units contract when the tick and the thin filaments slide past one another. These coordinated contractions and elongations of numerous sarcomeres produce muscular activity.
In NM, the functioning of the sarcomeres is distracted which hampers muscle activity and causes muscle weakness.
Nemaline Myopathy Inheritance
Rod Myopathy can be inherited in either the autosomal dominant or the autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. In the autosomal dominant pattern, the child gets the disease from only one parent. But in the autosomal recessive pattern, the child has to receive one copy of the abnormal gene from each parent in order to develop NM.
Nemaline Myopathy Diagnosis
Doctors investigating this disorder perform a thorough physical examination and ask patients various questions about their symptoms to diagnose this type of muscular dystrophy. The sufferer is also asked questions regarding any family history of NM.
Performing a neurophysiological evaluation can be helpful for making the diagnosis. It includes analyses of the muscle functions (EMG), peripheral nerve conduction and blood concentration of the creatine kinase. Patients with NM will have normal results for peripheral nerve conduction. However, the electromyogram (EMG) test results will show abnormalities.
A muscle biopsy is done to confirm the diagnosis. In this test, a diagnostician removes a small tissue sample from the affected muscle under local anesthesia. The sample is then examined for traces of nemaline bodies.
Genetic testing can also be used for confirming the diagnosis in some cases.
Nemaline Myopathy Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosticians should eliminate the possibilities of the following disorders while diagnosing NM:
- Idiopathic Polyhydramnios
- Steinert Myotony
- CNS Anomaly
- Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Zellweger Syndrome
- Non-Immune Fetal Hydrops
Nemaline Myopathy Treatment
There is no cure for this muscular disorder. The principal objective of the treatment is to relieve the symptoms and increase the mobility and independence of patients.
Respiratory assistance
Neonates born with severe NM usually need respiratory assistance and nutrition support. The breathing problems should be treated properly; otherwise, they may lead to respiratory tract infections. Tracheostomy ventilation may also be necessary along with breathing aids in some serious cases. The infants should also be given vaccinations for viral and bacterial pneumonia.
Occupational therapy
Patients should remain under the care of various medical specialists, such as an orthopedist and a pediatric neurologist. Occupational therapy is very important as it helps affected children to take part in the normal social activities despite the physical deformities.
Feeding tubes
The feeding difficulties due to throat (bulbar) muscle weakness may be solved by using feeding tubes. Individuals with mild NM may not need feeding assistance. Patients suffering from difficulty in speaking properly should be treated with speech therapy as it helps them to improve the communication skills. Oral prosthetic devices and augmentative communication can also be helpful for overcoming speech problems. Surgical intervention may be necessary in some severe cases.
Supportive devices
Many children with this disorder are eventually able to walk without any assistance. Devices to enhance mobility, such as wheelchairs, can be used by those who are unable to move independently.
Tyrosine supplementation
Current research shows that dietary tyrosine supplementation may be useful for improving activity levels and bulbar function in NM patients. Stem cell therapy is being considered as a possible treatment option for adult-onset NM as some patients have responded well to this treatment.
Physical Therapy
Physiotherapy is a very useful treatment option for NM as it helps to increase the mobility of the patient and prevent scoliosis (curvature of spine). It also keeps the relatively inactive muscles from contracting. The physiotherapist evaluates the patient’s ability to physical activities like standing and walking. This helps him or her to prescribe the suitable exercises for the treatment. The physical therapy sessions generally include the following:
- Exercises, for improving or maintaining the strength and functional level of the muscles
- Stretching exercises, for improving and maintaining the range of movement of the joints
- Exercises, for increasing the ability to move independently and to improve the movement quality
Nemaline Myopathy Prognosis
The prognosis depends on the severity of the disorder and the age of onset. Mild cases of NM can be treated successfully, restoring the muscle function of the patient. But, the outcome may be negative in more severe cases. The decreased muscle function can lead to serious physical inability and the patient may become permanently wheelchair-bound. The disorder may even turn fatal due to the complications arising from it.
Nemaline Myopathy Life Expectancy
The neonatal onset Rod Myopathy has a poor life expectancy and the patients often do not live more than 2 to 3 years. However, individuals suffering from less severe forms can have a normal lifespan with regular treatment.
Nemaline Myopathy Prevention
It is not possible to prevent NM as it is a hereditary condition. Genetic counseling can help couples with a family history of the disorder to find out their chances of having a child with the syndrome. Gene reviews can help couples planning a child to find out if they are carrying the defective gene.
Nemaline Myopathy Support Groups
A number of foundations and associations have been established to spread awareness about this form of Myopathy. Some of these are:
March of Dimes Birth Defects Foundation
1275 Mamaroneck Avenue
White Plains, New York State 10605
Tel: (914)997-4488
Fax: (914)997-4763
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.marchofdimes.com
Nemaline Myopathy Support Group
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.davidmcd.btinternet.co.uk/
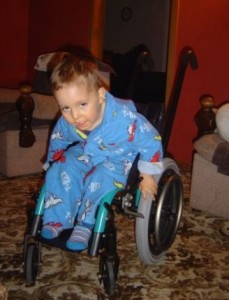
Nemaline Myopathy Pictures
The following images show how NM affects the physical appearance of its patients.
Picture 1 – Nemaline Myopathy
Picture 2 – Nemaline Myopathy Image
Nemaline Myopathy is a congenital muscular disorder which required early diagnosis and prompt treatment. The patients have to remain in contact with doctors and receive regular treatment to be able to lead a normal life.