What is Macular Degeneration?
Page Contents
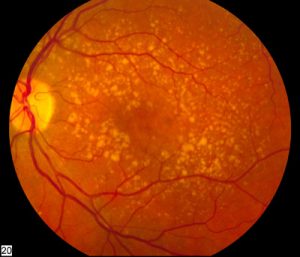
Macular degeneration is an age-related problem in the central part of the retina known as macula which gets destroyed causing chronic vision impairment. Disease is irreparable but can be managed with laser therapy, vitamin intake, vision aids and medication.
The disease is also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). It loses or minimizes the sharp central vision, and one cannot see the details correctly. AMD does not hurt but allows the macula cells to die. It is the leading source of vision impairment in aged Americans. Random eye tests can help in detecting the disease before it results in vision loss.
Types
Dry AMD
It is the early stage of the illness when light-sensitive macula cells gradually break down. Dry AMD results from reduction of macular tissues or pigment deposition in macula due to age, sometimes a combination of both processes. Dry AMD is diagnosed once yellowish spots also called as drusen accumulate inside or around the macula. These spots are presumed to be the trash from the decaying tissue. Depending upon the accumulation of debris, dry AMD is differentiated in three stages, early, intermediate and advance. It is a gradual vision loss, but not chronic as wet AMD.
However, slow degeneration of the retinal cells can cause severe vision loss, but eating a healthy diet rich in vitamins and protecting eyes from direct UV rays and dust can help to prevent it.
Wet AMD
Not similar to Dry AMD, it is more chronic. New blood vessels are known as Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) that develops below the retina and leaks fluid and blood. This discharge results in persistent damage to fragile retinal cells which end up making spots in focal vision. People suffering from dry AMD are at high risk of developing wet AMD. Wet AMD has two categories:
- Occult: Causes severe vision loss due to new blood vessels
- Classic: Has clear outlines below the retina, also known as classic CNV, making vision loss more severe.
Stages
- Early AMD: This stage does not experience vision loss, and eye checkups are essential. Medium sized drusen help in recognition.
- Intermediate AMD: Vision loss with noticeable symptoms. Eye exams and tests will check for pigment changes and larger drusen.
- Late AMD: Complete vision loss.
Causes
Macular degeneration is connected to aging, but genetic component also contributes to the disease. However, other factors are found to be responsible according to the research.
Genetic Component
Deficiency of gene complement factor H (CFH) and Complement factor B is related with most of the AMD cases. Individual variants play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, and maximum examples have been found to be responsible for vision impairment.
Vascular endothelial growth factor
Oxygen divested cells produce (VEGF) vascular endothelial growth factor. The normal function of (VEGF) is to develop new blood vessels at the time of embryonic development. But excessive production of VEGF increases development of new blood vessels in the retina which opens and breaks quickly damaging the macula.
Symptoms
- Blurriness
- Distortion
- Painless vision loss
- Shadowy central vision
Risk Factors
- Aging: AMD is an age-related disease and its commonness increases with age.
- Inactivity &Obesity: Inactive people double the risk of AMD. Researches have proved that vigorous activity reduces the risk.
- Hereditary: Variants of genes present and ancestral disease plays a crucial role in the severity of AMD.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Might be involved indirectly.
- Smoking: Major factor in almost 50% of the cases resulting in vision loss. It was reported patients living with smokers increased the risks of AMD.
- Lighter Eye Color: People with darker eyes have extra pigment which acts as a protective shield and people with the lighter eye are more prone to the disease.
- Side Effects of Drug: Sometimes AMD is induced from toxic drug effects like phenothiazine, Aralen, Mellaril, profilin, trillion, etc.
Treatments
There is no specific cure for macular degeneration, but some changes in lifestyle can lower the risk and slow the development. Patients should pursue some changes like proper exercising, avoiding smoking, adequate dieting, protecting eyes from UV rays, etc.
Also, there is no particular medication for macular degeneration, but some medication can improve the vision and reduce the development. However, it entirely depends on the disease stage, advanced, dry form or wet form.
There are FDA approved medicines for wet AMD treatments that reduce the abnormal growth of blood vessels. Medications like Eylea, Lucentis, Visudyne, Macugen with PDT or Photodynamic therapy. Lucentis has shown improvement of vision in a considerable number of people suffering from AMD.
Nutrition
Diet
Dietary modifications reduce risks of vision loss. Diet with abundant cold water fish and salmon fish which are high in omega-3 fatty acids reduces AMD symptoms or prevents the disease. Additionally, green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamins and proteins helpful in keeping eye diseases at bay.
Supplements
Supplements like zeaxanthin and lutein are known to increase pigment density in the macula which are directly associated with AMD.
Complications
Progression of wet AMD development from dry macular degeneration is the main complexity. It increases the severity of the disease or complete vision impairment. However, there is no accurate way to anticipate that patient with dry AMD will progress or not. Eye diseases like glaucoma, cataracts, dry eyes or retinal detachment are not the direct complexities of AMD but can develop from abnormal eye health. People can develop AMD and other eye problems simultaneously.
Prognosis
With improper care, it can worsen with time, but proper care helps to reduce the symptoms. Hence, the time duration of the disease is not apparent yet. The disease affects the central vision, and the peripheral vision is retained. Therefore, people can see enough to visit familiar surroundings. Additionally, utilization of magnifying glasses can help to improve vision while reading or watching.
Prevention
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in inducing or reducing the risk of macular degeneration. Eating a diet rich in vegetables, fish and adopting healthy lifestyles without smoking, retaining weight and blood pressure to an average level and involving in regular moderate exercise will be helpful to prevent AMD.