Have you been lately suffering from a reduced sex drive and an absence of menstrual periods? If yes, you are probably suffering from Hyperprolactinemia, a condition characterized by high protein levels. Read and know more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
What is Hyperprolactinemia?
Page Contents
It is a medical condition characterized by the presence of Prolactin (a Gonadotropic hormone) in higher than the normal amounts in the body. Normally, the amount of Prolactin secreted in women is 500 mIU/L. In men, it is lower than 450 mIU per liter. This increases in a number of situations such as use of medications or presence of tumor.
The condition is more common in women than men.
Causes of Hyperprolactinemia
The causes of the disorder can be summarized as under:
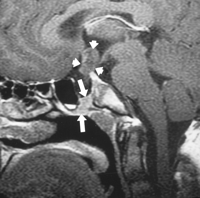
Picture 1 – Hyperprolactinemia
Physiological changes
Physiological changes are those that occur due to disruption of the normal body functioning. The physiological causes for the condition include pregnancy, breastfeeding, mental stress and hypothyroidism.
Prolactinoma tumors
The development of Prolactinoma, a tumor or growth on the pituitary gland, is a common cause of this condition. Prolactinoma produces high amounts of Prolactin. These tumors can be small or large in size. They are usually benign, i.e. non-cancerous. Large-sized tumors can also lead to vision problems, headaches, or both.
Prescription drugs
The use of prescription drugs is one of the most common causes of this disorder. The secretion of Prolactin is controlled in the body by a chemical Dopamine. As can be expected, any drug which inhibits Dopamine also affects this process of control and results in Hyperprolactinemia. Some of the medications associated with this problem include antipsychotic drugs, tranquilizers, anti-hypertensive drugs and the medicines used for nausea.
Diseases
People suffering from conditions like chronic renal failure, hypothyroidism, bronchogenic carcinoma and sarcoidosis are more prone to this disorder.
Symptoms of Hyperprolactinemia
The signs and symptoms of this disease differ in both men and women. Although several symptoms may vary from one person to another, some of the general problems may be the same in all affected individuals. Know about some of these general symptoms in women and men:
Symptoms in Women
Some of the common symptoms of this disorder in women are:
Amenorrhea or skipping of menstruation
Most of the women are not able to find the reasons behind missing menstruation and take it lightly. In case you notice skipping menstruation, you should contact your doctor for diagnosis.
Breast pain
In the initial stages, when the prolactin levels increase all of sudden, pain in the breast may be experienced.
Abnormal production of milk
In some cases, affected women are found to produce milk even in the absence of a pregnancy.
Dry vagina
This condition can result in dry vagina making the sexual intercourse painful.
Loss of sexual urge
In some women the interest in sex has also been reported to diminish.
Symptoms in Men
Some of the reported signs of this disorder in men involve:
Gynecomastia
It is the most common symptom and involves the sudden appearance of breasts in a man.
Reduced libido
A decrease in sex drive or libido is also observed in men, as in women.
Infertility
In extreme cases it can result into infertility or erectile dysfunction.
Diagnosis of Hyperprolactinemia
The systematic procedure for diagnosis of the condition is as follows:
- Firstly, doctors check the prolactin levels in suspected people. The prolactin levels are checked in cases where a patient reports of skipped menstruation or breast pain (as in women) or Gynecomastia and decrease in libido (as in men).
- If the prolactin levels are found to be higher, the thyroid levels are checked. Doctors also enquire about the use of other medications that might be responsible for the increase in prolactin levels.
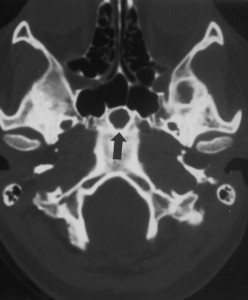
- Next, MRI is used to diagnose the problems associated with pituitary. Alternatively, CT- scan may be used to detect the tumors of pituitary. However, the latter technique is not as effective as MRI.
- In later stages, MRI may be performed at regular intervals for analyzing the development of tumor.
Treatment of Hyperprolactinemia
The mode of treatment of the condition depends on a number of factors, such as:
Picture 2 – Hyperprolactinemia Image
- Age of the patient
- Intensity of the disease
- Medical history of the affected person
One of the important parts of the treatment is regular monitoring of the progress related to decrease in size of the tumor. All the methods of treatment are aimed to control the tumor size only. Treatment involves the use of following methods:
Medications
The most commonly used drugs for this condition are dopamine agonsits. A common drug is bromocriptine mesylate and it helps by reducing the size of prolactinomas. Another popular drug for this condition is carbergoline which has lesser side effects.
Radiation therapy
It is used to keep the size of tumor in check.
Surgery
Surgery is required in cases where a patient does not respond to the drugs. However, surgery is associated with risks as the pituitary gland is located near the hypothalamus.
If you are experiencing the symptoms of Hyperprolactinaemia yourself or noticing them in any family member, seek medical attention on an immediate basis. Timely medical assistance will help you avoid further complications and make a quick recovery.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperprolactinaemia
http://ehealthwall.com/hyperprolactinemia-symptoms-causes-and-treatment/
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/121784-overview