Is your child vomiting right after being fed every time or at certain times? He or she could be suffering from gastric outlet obstruction, a bothersome condition of the abdomen. Read on to know more about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment of this disorder.
Gastric outlet obstruction Definition
Page Contents
It is a clinical condition of the pylorus or pyloric canal of the stomach that causes blocks the entry of food particles from the stomach to the duodenum (first section of the small intestine). Pyloric canal is a narrow tubular passage that forms an opening between the stomach and small intestine. It is generally not considered as a separate clinical entity and is usually a physiological consequence of other abdominal disorders.
The condition is usually abbreviated as GOO. It is known by various names like:
- Pyloric obstruction
- Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
- Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Gastric outlet obstruction Incidence
The prevalence of GOO has not been clearly estimated. However, less than 5% of the patients with peptic ulcer disease are believed to be suffering from this abdominal condition. 15 to 25 % of patients with pancreatic cancer are known to have GOO.
Gastric outlet obstruction Symptoms
Some of the common symptoms of this condition are:
Picture 1 – Gastric outlet obstruction
Projectile vomiting
Patients are found to forcibly eject the contents of the stomach through the mouth, owing to pyloric obstruction.
Constipation
While emptying the bowels, patients may face difficulties and acute discomfort that usually occur infrequently. In this condition hard, dry and small stools are passed. Eliminating these can be quite painful.
Weight loss
Loss of fluids and reduced appetite may result in sudden decrease in weight.
Epigastric pain
It is one of the most common symptoms of this stomach disorder. It is generally associated with acute pain arising in the upper middle part of the abdomen.
Dehydration
Persistent vomiting may lead to significant loss of body fluids, primarily causing excessive water deficiency.
Electrolyte imbalance
Hypochloremia, a deficiency of chloride ion in bloodstream due to prolonged vomiting, is a common symptom observed during this condition. Excessive loss of potassium (Hypokalemia) and Hydrochloric acid (Metabolic alkalosis), which occurs as a consequence of dehydration, highly contributes to this sudden reduction in body chlorides.
Wasting
Continuous degeneration of the body muscle and fat tissues may occur in the affected individuals, owing to low intake and high loss of nutrients (especially that of proteins). Malignant conditions of the stomach could be the primary factor, causing this gradual deterioration of the muscle tissues.
Gastric outlet obstruction Causes
The condition is generally divided into two categories, where each group is manifested by a specific array of symptoms. The causes of this condition differ, depending on the type of the disorder that one is suffering from.
Benign GOO
As the name signifies, it does not involve any cancerous complication. A wide number of abdominal infections fall under this category. These include:
Peptic ulcer
Mucosal erosions in the duodenum can be attributed to the obstruction of ingested food from the stomach which may aggravate the intake of more food.
Pyloric stenosis
This is generally a congenital condition that causes narrowing of the pylorus due to enlargement of the muscle surrounding it.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria responsible for causing TB, may often spread from the lungs to the stomach causing stomach tuberculosis. In this condition, a sudden and sharp ache or a dull, persistent abdominal pain may occur. This can be associated with the formation of inflammatory lesions. This may restrict normal emptying of the stomach contents.
Amyloidosis
In this condition Amyloid proteins, that constitute the insoluble fibrous protein in the body, may get abnormally deposited in the stomach. This might result in massive obstruction near the pyloric canal.
Bouveret’s syndrome
Gastric outlet obstruction is often a consequence of a large gallstone present in the duodenum or pylorus. This is generally a rare cause of this condition.
Malignant GOO
Several types of cancers of the stomach or of the pancreas or duodenum usually fall under this category.
Gastric adenocarcinoma
It is a cancer of the glandular epithelium of the gastric mucosa, mucous membrane layer of the stomach, containing the gastric glands. In this condition, the tumor cells secrete large pools of mucus that may cause pyloric obstruction.
Gastric Lymphoma
It is a form of lymphoma that originates in the stomach and is typically a cancer of the lymphocytes, a group of cells that is an essential part of the immune system. When lymphomas occur in some other organ of the body, Gastrointestinal tract is the most common site of occurrence.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
It is a type of tumor occurring in the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) of the gastrointestinal (GI) or digestive tract. These cells are responsible for sending signals to the GI tract that enable movement of food and fluids through the entire digestive system. In most cases, these tumors are malignant and prevent entry of food into the duodenum. This may turn fatal.
Gastric outlet obstruction in adults
Majority of cases of GOO are seen in the adult population, which is due to some benign conditions with peptic ulcer disease being the most common cause. Several infants are also known to suffer from this condition due to some congenital abnormalities in the abdomen, such as Pyloric stenosis.
Gastric outlet obstruction Diagnosis
During diagnosis of GOO, physicians generally perform a physical examination of the stomach to reveal signs of dehydration. Affected patients may have a swollen stomach. This is generally followed by few diagnostic tests.
X-ray
An abdominal x-ray usually shows a stomach filled with gastric fluids and a distended or swollen small bowel, owing to the blockage at the level of the pylorus.
Barium meal
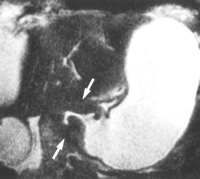
In this process, affected patients are made to ingest Barium sulfate. This is followed by x-ray imaging of the stomach and duodenum. X-ray images generally reveal distension of abdomen and narrowing of the pyloric canal due to Pyloric stenosis.
Endoscopy/ Gastroscopy
In this non-invasive technique, an endoscope is inserted through mouth into the upper gastrointestinal tract that includes esophagus, stomach and duodenum. This technique can help detect any tumor or ulcer in the stomach.
Imaging studies
Ultrasound examination, computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may aid in detecting abnormal enlargement of the abdomen, or presence of any form of tumor.
Electrolyte panel
It is a blood test that measures the levels of electrolytes and carbon dioxide. Abnormal levels of chloride, potassium and hydrochloric acid may indicate electrolyte imbalance in the body due to pyloric obstruction.
Gastric outlet obstruction Treatment
On the basis of the cause of the disorder, physicians generally recommend an appropriate cure for affected patients. Treatment can be primarily classified into two groups.
Picture 2 – Gastric outlet obstruction Image
Medical Treatment
Some of the commonly applied methods include:
Nasogastric suction
It is a medical process where a plastic tube called nasogastric tube is inserted into the stomach through the nose and throat to drain the gastric contents. If continuous drainage of the contents is required then a collector bag is attached to the tube and placed below the level of the stomach. However, constant suction can be damaging to the lining of the stomach and must only be used in emergency situations.
Electrolyte treatment
Sodium chloride solution is generally administered to patients for curing chloride deficiency in the body. Potassium supplementation is required and the mineral should be taken along with zinc and magnesium.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
This is a group of drugs that are most often used to reduce gastric acid production in the stomach that causes peptic ulcers. Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole and Dexlansoprazole are some of the commonly used drugs.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical procedures are usually opted for when patients show least or no response towards any form of medical therapy.
Antrectomy
In this procedure, the lower section of the stomach called antrum is surgically excised to inhibit the effects of peptic ulcers which might lead to Pyloric obstruction.
Vagotomy
Acid secretion in the stomach can also be reduced by surgically removing the vagus nerve. This particular nerve plays a central role in the production and regulation of acid secretion. The removal of this nerve can cure ulcer complications.
Billroth I
In this surgical technique, the pylorus is entirely removed followed by direct reconnection or anastomosis of the upper portion of the stomach to the duodenum. Patients suffering from gastric tumors or peptic ulcer disorder are greatly benefitted from this method.
Gastrojejunostomy
It is a surgical procedure that directly connects the stomach to the jejunum, second portion of the small intestine with the help of a small tube. In this way, the contents of the stomach bypass the duodenum and enter straight into the jejunum to enable normal absorption of the ingested food.
When benign, Gastric outlet obstruction is not a life-threatening condition. Its symptoms can be treated with appropriate medication and surgery. Timely diagnosis is essential, especially if the cause is malignant. If cancerous developments are suspected, medical assistance should be availed instantly.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastric_outlet_obstruction
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/gastric-outlet-obstruction-in-adults
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/190621-overview
http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=39900