What is Esophageal Varices?
Page Contents
Esophageal varices is a medical condition characterized by enlarged and abnormal veins which appears in the lower part of a person’s esophagus, the tube which connects the stomach and the throat. This is one of the common esophageal disorders experienced by people with severe liver disease and develops when the normal blood flow of an individual towards the liver slows down. This results to backed-up blood flow in the smaller blood vessels like that of the esophagus which leads to the swelling of your blood vessels.
Esophageal Varices Symptoms
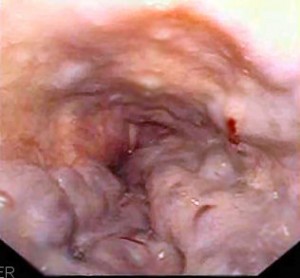
Picture 1 – Esophageal Varices Image
One of the most unfortunate things about esophageal varices is the fact that it does not show any visible esophageal symptoms unless bleeding actually occurs. The bad thing about this incident is when it happens it entails a medical emergency. The patient has to be rushed immediately to the hospital if he or she starts vomiting blood, discharges black, blood or tarry stools, esophageal spasms and experiences shock while experiencing these bodily events.
Other symptoms include esophageal pain, light headedness, paleness, decreased urine output and excessive thirstiness.
Esophageal Varices Causes
Aside from the earlier mentioned esophageal varices causes, the following conditions may also result to this rare yet dangerous condition.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis or severe liver scarring is one of the major causes of esophageal varices associated with alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis infection and bile duct disorder referred to as primary biliary cirrhosis.
Thrombosis
Thrombosis or blood clot is another cause of esophageal varices which occurs in the portal vein or the splenic vein of an individual. This is the result of the slow transportation of blood to the liver which leads to increased pressure in the portal vein forcing blood to proceed to other blood vessels. Unfortunately, this escape mechanism of the blood leads to ballooned veins which eventually ruptures and creates internal bleeding.
Schistosomiasis
This is a parasitic infection which is common in South America, Africa, Middle East, Southeast Asia and the Caribbean. The parasite which causes this infection lingers in the liver, lungs, intestine and bladder which results to esophageal varices.
Budd-Chai Syndrome
This is a very rare condition which causes blood to back-up in your liver. This results to blood clotting which soon blocks the blood flow into your river.
Esphageal varices Grading
Esophageal varices classification as Grade I, Grade II and Grade III is depending on the esophageal varices size.
Risk Factors of Esophageal Varices
Not all patients who suffer from liver disease will experience bleeding but the following conditions increases the risk of it.
High portal vein pressure
Individuals with high blood pressure have higher possibility of suffering from esophageal varices especially if he or she is also inflicted with liver problems.
Large Varices
Genetics also play an important role in distinguishing individuals who are most likely to suffer from esophageal varices and individuals who have large varices are the most likely candidate for this disorder.
Red Marks on the Varices
Appearance of abnormal red marks on the varices are already warning signs that an individual may soon suffer from esophageal varices. So if you notice these red marks appearing on your neck, it is best to see your doctor about this matter so your condition can be properly evaluated.
Severe Cirrhosis
Patients who suffer from severe cirrhosis are more likely to suffer from esophageal varices so make sure you regularly visit your dentist to check your condition.
Continued Alcohol Use
If the cause of your liver disease is associated with alcoholism, then you should get rid of this bad habit. Otherwise, you should be prepared of the consequence of this habit because your risk of suffering from this condition becomes greater so it is best that you stop from drinking alcohol.
Esophageal Varices Complications
The only serious complication associated with esophageal varices is the occurrence of bleeding or the actual rapture of the portal veins. This is extremely dangerous because it will lead to a person’s death. Do not think twice and immediately call 911 so proper treatment can be applied to the patient. Never attempt to touch the ruptured area nor move the body of the patient because this may only lead to more complications.
Esophagus varices Diagnosis
It is very typical for doctors to diagnose all patients with serious liver disease for possible esophageal problems like varices. This is done through an endoscopic examination wherein the doctor inserts a thin, flexible and very light tube through your mouth reaching through your esophagus. If the physician sees any dilated veins then it will be further evaluated to see if it contains any red streaks, a significant indicator that a patient may be suffering from esophageal varices.
Aside from endoscopic, patients have the option to choose computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help diagnose if a patient is suffering from esophageal varices. Moreover, this test will also allow your doctor to check and examine the condition of liver and the blood circulation of your portal veins.
Esophageal Varices Treatment
There are two ways of esophageal varices treatments depending on the intensity of the condition.
Treatment to prevent bleeding varices
Patients who wish to avoid postal vein bleeding due to esophageal varices symptoms are normally asked to take beta blocker medications. This helps reduce blood pressure in your portal vein while reducing the possibility of bleeding. Drug medications include nadolol and propranolol.
Treatment to stop bleeding esophageal varices
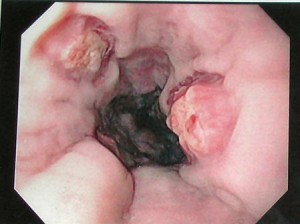
Picture 2 – Esophageal Varices
If esophageal variceal bleeding occurs, esophageal varices banding may be used to help stop the bleeding of the veins. At times, physician also use injectible solutions to the vein through endoscopic injection therapy to help shrink the veins nevertheless, this is prone to dysphagia so it must be done only by highly skilled physicians.
Other esophageal varices treatment methods include the use of drug medication like octreotide; transjugular intrahepatic portosytemics shunt (TIPS); and liver transplant.
Reference:
http://www.turkgastro.org/pdf/310.pdf
http://www.wjes.org/content/3/1/24

No Responses