Are you suffering from a swollen lump at the back of your testicle? If you are, you may be having a condition called Epididymitis. Read on and know what is Epididymitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and cure.
Epididymitis Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Epididymitis Definition
- 2 Symptoms of Epididymitis
- 3 Causes of Epididymitis
- 4 Epididymitis Risk Factors
- 5 Epididymitis Diagnosis
- 6 Epididymitis Treatment
- 7 Epididymitis Drugs
- 8 Natural Treatment for Epididymitis
- 9 Epididymitis Diet
- 10 When Is Epididymitis Chronic?
- 11 Is Epididymitis Contagious?
- 12 Epididymitis Complications
- 13 Epididymitis Prognosis
- 14 Does Epididymitis Go Away Permanently?
- 15 Epididymitis Pictures
Epididymitis medical definition is given as an inflammation or infection of the Epididymis, a coiled tubular structure at the back of the testicles that stores and carries the male sperm. This tube-like thing connects the testis with the vas deferens. Sperms mature in the Epididymis and are transferred to the Vas Deferens, the epithelial duct. It is the Vas Deferens that takes the sperms out of the Epididymis during ejaculation.
An inflammation in the Epididymis is called Epididymitis. In some people, the swelling spreads to the testicles. The condition is then known as Epididymo-orchitis.
Epididymitis is pronounced as “Ap-ee-did-i-mee-tis”.
Symptoms of Epididymitis
Epididymitis is mainly characterized by inflammation. However, it gives to other symptoms as well such as
Pain
In sufferers of Epididymitis groin pain is a major complaint. In Epididymitis abdominal pain and pelvic discomforts are also quite common.
Painful Ejaculation
Victims of this disease also suffer from pain during ejaculation. This impacts the overall health of sufferers and affects their sex life as well.
Bloody Ejaculation
Epididymitis patients often find blood being ejaculated in their semen. Blood in semen is one of the most common signs of Epididymitis.
Burning Sensation
In sufferers of Epididymitis burning or painful sensation while urinating is also common.
Urethral Discharge
Epididymitis patients also suffer from discharge through the urethra or the aperture at the end of their penis.
Fever
Higher body temperature often accompanies groin pain and inflammation. The entire inflamed area becomes tender to touch. Fever comes with fatigue that may affect the daily lives of patients.
Bloody Urine
In some sufferers of Epididymitis blood in urine is also a major complaint. Bloody urine along with penile discharge is extremely discomforting and disturbing for the patient.
Causes of Epididymitis
Epididymitis arises due to a variety of reasons. Some of the major Epididymitis causes are
Bacterial Infection
In sufferers of Epididymitis bacterial infection of the urinary tract has been found to be the main cause. This kind of infection usually arises after an improper surgery of the urinary tract or a swelling of the Prostate gland (Prostatitis) that spreads to the testis. Bacteria of genus Ureaplasma and Mycobacterium tuberculosis are the main causes of this disorder. Serious cases of Epididymitis infection are often the result of E. Coli bacteria.
Retrograde Urine Flow
If the bladder is full of urine and violent pressure forces it along the Vas Deferens, Epididymitis can arise. This is a common problem in bodybuilders who rush into the gym and start exercising on a full bladder to save time.
Pumping iron with a full bladder can push urine into the testis through the Vas Deferens. The more the amount, the worse is the Epididymitis. The problem especially happens in cases where the urine contains bacteria. It gives rise to bacterial infection.
STD
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD) like Chlamydia or Gonorrhoea can also give rise to Epididymitis.
Amiodarone
In some cases, Epididymitis arises as a side-effect of the drug Amiodarone that is used to reduce heart rate abnormalities.
Epididymitis Risk Factors
As can be guessed, you can only find Epididymitis in men. It is primarily seen to affect men in the age group 20-40. It is seen more in sexually active males. Men having unprotected sex with multiple sexual partners are at increased risk of contracting diseases like Chlamydia and Gonorrhea which raises susceptibility of suffering from this condition.
Other people who can suffer from this disease include individuals who are uncircumcised, have structural defects in their urinary tract or regularly use urethral catheter. People who have recently had a urinary tract surgery can also suffer from this disorder.
Epididymitis Diagnosis
Initial Epididymitis examination usually begins with physical tests that show a swollen red, tender lump on the affected edge of the scrotum. An experienced physician checks whether inflammation is a result of localized swelling of lymph nodes in the groin region.
In sufferers of Epididymitis tests like Testicular Scan, Complete Blood Count, and Urinalysis are carried out to differentiate the disease from other similar conditions. A Rectal examination may be performed to see whether a tender or enlarged prostate is the cause of swelling. A Doppler Ultrasound Test may also be carried out to see whether there is an increased flow of blood to the affected Epididymis.
Epididymitis Treatment
Epididymitis cure actually depends on the causative factor of the condition as well as the symptoms.
Antibiotics
If sexually-transmitted infections are found to cause Epididymitis antibiotics are necessary for cure. In Epididymitis treatment antibiotics should be administered to the patient as well as his sexual partners.
Lowering Medicinal Dose
Epididymitis cases found to be resulting as a side effect of Amidarone should be treated simply by lowering the dosage of the medicine.
Analgesics
Acute pain in the groin should be treated by analgesic drugs. Over-the-counter analgesics provide Epididymitis pain relief in a short time but should be taken as per doctors’ recommendation.
Epididymitis Drugs
Epididymitis medicines usually prescribed by doctors include Azithromycin, Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone, Cefixime, Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin and Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim.
If sexually transmitted diseases like Chlamydia and Gonorrhea are found to cause Epididymitis medication treatment should be done with drugs like Azithromycin and Cefixime. Epididymitis E. Coli cases are treated with Levofloxacin and Ofloxacin. In sufferers of Epididymitis Doxycycline is used as alternative for Azithromycin.
Natural Treatment for Epididymitis
Epididymitis natural cure is possible through various methods. The following ways are quite popular for natural Epididymitis home treatment.
Rest
Physical activity increases inflammation which can be reduced by rest. As a natural cure for Epididymitis bed rest is very effective.
Ice
Application of ice to mildly swollen Epididymis can help reduce inflammation. Doing this at least for two times every day can be quite effective.
Elevation
As aforesaid, Epididymitis can occur due to increased blood flow to the testicles. Keeping the groin raised over other body regions can reduce the extent of swelling by natural means.
Epididymitis Diet
Epididymitis sufferers should make some dietary modifications along with medicinal treatment to get rid of this discomforting disease. If you are having Epididymitis, it is advisable that you stay away from beverages like tea, coffee alcohol and carbonated drinks which irritate the urinary system. Foods that act as natural laxatives such as fresh fruits, nuts, whole-grain cereals and dried plum (prunes) are also recommended.
When Is Epididymitis Chronic?
When Epididymitis lasts for over six weeks, it is termed as Chronic Epididymitis. Chronic Epididymitis is believed to be a result of hypersensitivity of nerves and muscles. It occurs even in the absence of infection of any kind.
Chronic Epididymitis gives rise to symptoms like persistent scrotal pain and scrotal inflammation. For diagnosis of Chronic Epididymitis Ultrasound and other tests may be performed to rule out other conditions like Epididymis Cyst, Testicular Veins and Swollen Scrotal Veins.
Chronic Epididymitis treatment is usually treated by injecting a combination of anti-inflammatory medicines, analgesics and steroids into the scrotal nerve. This medication can cure pain for nearly 3 months though the duration of respite may vary from person to person. If the scrotal pain refuses to disappear despite this treatment, a process known as ‘Cord block’ may be used for cure. In acute cases, doctors may go for a complete Epididymis removal. This is done through a careful Epididymitis surgery by expert surgeons.
Is Epididymitis Contagious?
The University of Illinois Medical Center holds that Epididymitis is not a contagious disease. However, it may accompany any contagious condition that is sexually transmitted.
Epididymitis Complications
If treated well, Epididymitis does not usually give rise to any complications. With proper treatment of Epididymitis infertility does not occur as feared by many. However, in case of Epididymitis left untreated, problems like Chronic Epididymitis can arise. This is an Epididymitis long term complication. It can also cause permanent destruction or damage of the testicles or epididymis resulting in Hypogonadism or infertility.
In some cases, infection may spread to other systems or organs of the body.
Epididymitis Prognosis
Epididymitis recovery time is generally 1-3 days. With proper treatment pain subsides in a couple of days. However, an Epididymitis swelling may take several weeks or months to heal. Chronic Epididymitis lasts for three months or more while Acute Epididymitis persists for around six weeks.
Does Epididymitis Go Away Permanently?
With proper treatment, Epididymitis goes away in most cases. However, the condition may turn chronic in some cases even with treatment. Epididymitis recurrence can also happen in a few cases.
Epididymitis Pictures
Epididymitis is quite a complex condition that may be mistaken with other disorders that give rise to scrotal swelling. Here are some useful Epididymitis photos to help you out. Check out these Epididymitis images to make sure whether you are actually having this condition.
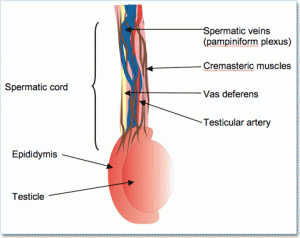
Picture 1 – Chronic Epididymitis
Source – findmeacure.com
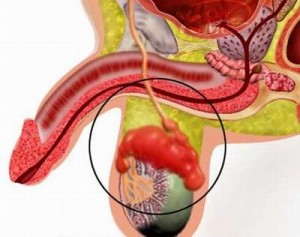
Picture 2 – Epididymitis Image
Source – medicalook.com
If you are having a swollen and painful scrotum, you may be suffering from Epididymitis. A swollen Epididymis can be very discomforting and lead to much embarrassment. The faster you begin treatment for this condition, the better it will be for you.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epididymitis
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/testicle_infection_epididymitis/article_em.htm
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/777181-overview
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001279.htm
https://health.google.com/health/ref/Epididymitis
http://www.rxmed.com/b.main/b1.illness/b1.1.illnesses/EPIDIDYMITIS.htm
http://www.drugs.com/cg/epididymitis-inpatient-care.html

suffering from acute epididymitis for how long away from sexual intercourse and giving advice for me taking diet for which food.
The recently developed Chronic Epididymitis Symptom Index is presented, . The job of the epididymis is to transport the sperm to the tube that . Epididymitis in adults is most often caused by gonorrhea or chlamydia, while . How are the causes of testicular pain diagnosed? Treatment and symptoms of orchitis. FashionWesley Cosmetic. Learn about epididymitis symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Read on and know what is Epididymitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and . The differential diagnosis of chronic non-infectious epididymitis. In acute epididymitis, symptoms are present for less then six weeks and are. If you are, you may be having a condition called Epididymitis. Testicular torsion is the most important differential diagnosis. Scrotal pain can be caused by a number of conditions, and some of them require . Located near the back of each testicle lies the epididymis, a coiled tubular structure which . Department of Health. Herbal Treatment for Epididymitis. A Practical Approach to Understanding and. This common clinical entity is diagnosed and treated by practicing urologists. Behcet’s disease develop epididymo-orchitis. Escherichia.