What is Endophthalmitis?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Endophthalmitis?
- 2 Types
- 3 Tissue Advancement in Endophthalmitis
- 4 Acute infectious post operative Endophthalmitis
- 5 Delayed Onset Infectious Endophthalmitis
- 6 Bleb Associated Endophthalmitis
- 7 Complications associated with Endophthalmitis
- 8 Causes
- 9 Magnitude of Post Operative Endophthalmitis
- 10 Signs and Symptoms
- 11 Diagnosis
- 12 Prognosis
- 13 Prevention
- 14 Treatment
- 15 Surgical Management
Endophthalmitis is a condition where intraocular cavities become inflamed usually due to infections.
Types
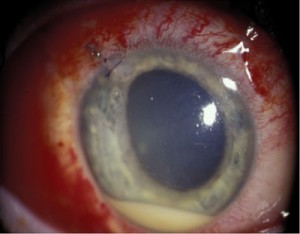
Picture 1 – Endophthalmitis
Source – odlarmed
Endophthalmitis can be either endogenous or exogenous.
Endogenous endophthalmitis or metastatic endophthalmitis is caused by the organisms’ hematogenous spread from far-flung infection sources. In this case, organisms that are blood borne penetrate the blood ocular barrier through direct invasion.
Alternatively, it could be by variations in the vascular endothelium resulting from substrates that are released in infections.
Destruction of the intraocular tissues could be as a result of organism’s direct invasion or the immune response’s inflammatory mediators.
Exogenous Endophthalmitis: Ocular surgery complications, foreign bodies or blunt ocular trauma cause exogenous endophthalmitis. In this case, the disruption of the globe’s integrity by surgical procedures would result to exogenous endophthalmitis. Normally, the eye is protected from invading organisms by the blood ocular barrier.
Tissue Advancement in Endophthalmitis
It is important to acknowledge that endophthalmitis can incorporate various levels. You may have all ocular tissues becoming inflamed or just the iris, choroids, retina or the lens capsule bearing white nodules. The inflammation would also extend to the soft tissue of the orbit.
Panophthalmitis- In this case, all the coats of eyes become inflamed including the intraocular structures.
Non-infectious endophthalmitis- This condition may have numerous causes like toxic agents. It could also result from the material making the native lens of the eye being retained
Acute infectious post operative Endophthalmitis
Generally occurs within 6 weeks of surgery.
Delayed Onset Infectious Endophthalmitis
This kind of endophthalmitis occurs after 6 weeks of surgery. The organisms involved are Propionibacterium acnes and S.epidermidis
Bleb Associated Endophthalmitis
Occurs post operatively after glaucoma filtering procedure
Complications associated with Endophthalmitis
There are several complications associated with endophthalmitis. To start with, the patient may actually experience decrease vision or lose it completely. This may necessitate enucleating in order to eliminate the blind or painful eye.
On very rare cases will the patient die from the condition. However, the patient may die from the medical problems underlying the condition. This is especially in endogenous endophthalmitis where the infections are from inside the body and therefore may be spreading hematogenously.
Causes
Various conditions would result to endophthalmitis post operatively. These include-:
- Retention of the lens material– In cases where crystalline lens does not get fully removed during cataract surgery, intraocular inflammation would be caused by the remaining piece. This is actually an immune reaction of the eye to the lens protein that is exposed. Actually, using a slit lam, one would be in a position to see the remaining lens material if the patient moves their eyes. It would be floating on the vitreous or aqueous but settles down once the patient stills their eyes.
- Increased intraocular pressure due to undergoing the procedure.
- Allergic reactions– As a response to substances used in the cataract surgery, inflammatory reactions would occur. Substances that are used in the sterilization of intra-ocular lens.
- Surgical complications-If the tissue is excessively manipulated after prolonged surgical procedures, aseptic endophthalmitis would occur though with mild signs and symptoms.
- Bacterial and fungal infection– Surgical site may be infected by bacteria or fungus leading to bacterial endophthalmitis or fungal endophthalmitis.
It is important to acknowledge that trauma or postoperative patients can develop endophthalmitis due to other problems that are not related to surgery.
Magnitude of Post Operative Endophthalmitis
With the improved surgical techniques and instrumentation, the magnitude of post operative infectious endophthalmitis is decreased over the past few years. Improved sterility measures play an important role in this decline.
Signs and Symptoms
Endophthalmitis incorporates various signs and symptoms including
- Loss of vision
- The eye could also incorporate discharge especially after surgery
- The eye could also become red or swell
- Fibrin clot of the eye’s interior chamber.
- Visibility of abscess or vitreous cells.
Other associated symptoms include lid edema and conjunctival hyperemia.
In cases where the signs are very pronounced, there would be no doubt in the diagnosis. However, many are the times when inflammation of relatively low grade is experienced. Nevertheless, when there can be no logical explanation as to the inflammations or in cases where the conditions are doubted, treatment should be administered as if the eye was infected.
Diagnosis
When one has a red eye, initial diagnosis would incorporate slight lamp examination.
Ultrasound scan may also be carried out easily as well as painlessly in outpatient clinics. These would just be the basis of the hypothesis as to the condition.
However, conclusive diagnosis could only be based on the vitreous samples being taken for microbiological culture. This is mainly conducted in theaters. It would also incorporate therapeutic procedures in cases where the vitreous gets completely removed thus cutting down on the load that is infectious. At this time, intraocular antibiotics may be administered.
However, in cases where the patient has endogenous endophthalmitis, it would necessitate screening of the full infection as well as looking for likely immunocompromise. There are procedures that are used in the differentiation of bacterial and fungal infections. Ophthalmic conditions may be ruled out using MRI scans.
Prognosis
You will acknowledge that the prognosis carried after endophthalmitis for visual recovery varies with the type. When carried out early, the patient may actually do well as the organisms may be less virulent. In cases where the organisms are virulent or even after the eyes has suffered traumatic injury, it may be a bit difficult to regain the vision. There will be constant monitoring of the patient by the doctor to ensure that the infection is undergoing some improvement.
Severe inflammation of the eye may take quite some time before clearing up sometimes even months. It would be important that the doctor is consulted early to ensure that injection of antibiotics is done promptly.
Prevention
It is important to acknowledge that there is no preventive measure that can be taken in regard to endophthalmitis with the exception of giving endogenous infections and trauma a wide berth.
Treatment
Non Surgical Management of Endophthalmitis
Medications are prescribed depending upon the causes and symptoms of endophthalmitis.
Treatment for Bacterial Endophthalmitis
As pertaining to the treatment of the bacterial endophthalmitis, it would be necessary that intravitreal antibioticts be administered into the eye. Example of these antibiotics is ceftazidime or vancomycin.
Treatment for Fungal Endophthalmitis
For candida endophthalmitis infections, the doctor would administer amphotericin.
Steroids are prescribed when fungal or bacterial infections are not present.
Surgical Management
Endophthamlitis surgery can be done if there is no infection. Careful Endopthalmitis surgery reduces the wound abnormalities and loss of vitreous humor.
Ocular surgery is done using sterile technique. This technique usually incorporates the rinsing of conjunctiva, eyelashes and periocular skin with betadine.
In some cases, patients with eyelash inflammation that is severe may be asked to make use of lid scrubs some days preceding the surgery. The importance of following the instructions of the physicians as pertaining to using the antibiotic drops both prior to and after the surgery.
References:
http://www.improveyourvision.com/retina-center/endophthalmitis.html
