Dracunculiasis Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Dracunculiasis Definition
- 2 Dracunculiasis ICD9 Code
- 3 Dracunculiasis Synonyms
- 4 Dracunculiasis Incidence
- 5 Dracunculiasis Eradication
- 6 Dracunculiasis Causes
- 7 Dracunculiasis Symptoms
- 8 Dracunculiasis Diagnosis
- 9 Dracunculiasis Treatment
- 10 Dracunculiasis Prognosis
- 11 Dracunculiasis Prevention
- 12 Dracunculiasis Complications
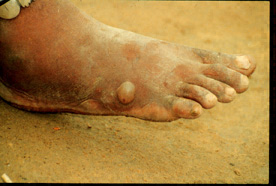
It is a type of highly contagious infection that results from a parasitic roundworm and manifests as a discomforting and painful sore. The parasite moves through the deep connective and subcutaneous tissues of the skin and gives rise to pain, especially near the joints. This nematode infection generally emerges from the feet and leads to blisters and ulcers. It has tremendous socio-economic influence, since it results in short-term disability.
This is quite common in Africa affecting dogs, cats and horses. It can even pass on to human beings.
Dracunculiasis ICD9 Code
The ICD9 code for this medical condition is 125.7.
Dracunculiasis Synonyms
This disorder is also referred to by various other names like:
Picture 1 – Dracunculiasis
- Guinea-worm disease (GWD)
- Dracunculosis
- Serpent worm
- Dracontiasis
- Pharoah worm
- Medina worm
- Filariosis medinensis
- Avicenna worm
Dracunculiasis Incidence
Dracunculiasis is rarely a fatal disorder. However, its patients become non-active for several months. This disaese is prevalent in poor rural area and remote communities who are dependent on open water sources, such as ponds. This disorder rarely occurs in the US. However, two cases have been reported ever since 1995, among the immigrants from Sudan.
Guinea-worm disease is prevalent among young individuals and can affect other mammals of North America and Central Asia. Till 2007, a total of 9585 cases of GWD have been have been reported. However, the number of affected people decreased to 1100 in 2011. 97% of the affected patients belonged to South Sudan and the rest from Ghana.
Dracunculiasis Eradication
Since 1989, 99% reduction of GWD has been reported worldwide. 187 nations have been certified GWD- free. Efforts have been made by WHO to exterminate the disorder completely, especially in African countries. GWD can be eradicated since:
- The transitional host is limited to dormant water bodies
- It has seasonal transmission and is restricted to geographical distribution
- Several Middle East and Asian countries has eradicated the disorder
- Definite and easy detection
- Less expensive control interventions
Dracunculiasis Causes
This disorder is caused by an infection known as Dracunculus medinensis, commonly known as Guinea worm disease. People get infected after drinking the water containing the Guinea worm larvae. Though the digestive acids present inside the stomach can absorb the water fleas, the worm endures as larva. An adult female worm travels to different parts of the body via the subcutaneous tissues and emerges from the feet and lower limbs. With the discharge of larvae, blisters appear on the skin. Such blisters are often accompanied by burning and itching sensation.
Dracunculiasis Symptoms
Patients affected with GWD do not usually display warning signs until one year. Before the infection emerges, a patient displays a number of symptoms including:
- Nausea
- Blisters
- Pain in the joints
- Pruritus
- Ulcers
- Secondary infections
- Eosinophilia
Dracunculiasis Diagnosis
The diagnosis of GWD begins with visual classification of the female worm emerging out of the skin. To confirm the diagnosis, doctors recommend a number of tests to detect the syndrome. These include:
Serum immunoglobulin levels
Immunoglobulin G4, Immunoglobulin E and Immunoglobulin G1 levels are high depending on the stage of the disease. Plain infections give rise to the GI and G4 sublevels which helps doctors to diagnose the syndrome.
CBC
Slight elevation of the WBC count indicates the presence of the Guinea-worm disease in the body of the patient.
Radiological examination
Radiological inspection of the lower extremity is often used to determine the presence of calcified worms in the skin.
Dracunculiasis Treatment
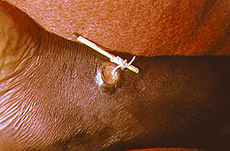
Guinea worm disease cannot be treated with any vaccine or drug. When the worm emerges from the infection, it should be pulled out to each centimeter per day and wrapped against a small stick. In a few cases, the worm is dragged out completely within one day, after being treated for months. The swelling and pain can be minimized with the help of few analgesics namely ibuprofen or aspirin. Regular use of antibiotic ointment can prevent the occurrence of any bacterial infection. Before the worm takes the shape of an ulcer, it should be removed surgically by a qualified surgeon in a well equipped medical center.
Dracunculiasis Prognosis
The prognosis of GWD is considered to be very good with a low death rate and mandatory disability. Patients experience incapacitation due to pain and the complications arising due to secondary bacterial infections. During worm-removal, patients become unable to carry out daily activities like tending animals, working in the fields and caring for families. Such form of disability persists for 8.5 weeks. In rare cases, the disability can become permanent.
Dracunculiasis Prevention
Medical researchers have not recommended any vaccine or medicine to treat the syndrome. However, various preventive measures can be adapted to restrict the occurrence of the infection and eradicate it completely. Such strategies include:
- Avoiding the transmission of the worms with the help of proper treatment, bandaging and cleaning the affected skin until the larva is removed from the body completely.
- To prevent infection, access to safe drinking water should be ensured.
- Applying vector control with the help of larvicide temephos.
- Enhancing the surveillance in order to identify each and every GWD case within 24 hours.
- Prevent the contamination of drinking water by counseling people to avoid swimming through it, as in case of pools.
- Ensuring filtering of water from all open water body sources before drinking.
- Encouraging health education and behavioral change.
Dracunculiasis Complications
Blisters occurring in GWD patients are quite painful. If the wound gets infected due to bacteria, it can give rise to series if complications including:
Picture 2 – Dracunculiasis Image
- Abscesses
- Sepsis
- Cellulitis
The worm removal process is considered to be a very painful process. If the worm breaks while removing due to any uncertainty, it gives rise to acute inflammation. This is because the rest of the dead worm causes degeneration inside the body of the patient. This leads to swelling, pain and cellulitis.
Dracunculiasis is a transmittable infection. If you notice blisters on your skin or experience pain in the joints, consult your health care provider immediately. Do not neglect the infection for it can give rise to complications and permanent disability.
References:
http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/HTML/Dracunculiasis.htm
http://www.stanford.edu/class/humbio103/ParaSites2001/dracunculiasis/DRACUNCULIASIS.html
http://cmr.asm.org/content/15/2/223.full