Are you suffering from an inflamed and painful shoulder and finding it increasingly difficult to move the affected arm? If you have recently injured the region, there is every possibility that you are having a dislocated shoulder. Get to know about this condition in detail, including its causes and treatment options, before seeking medical assistance.
What is Dislocated shoulder?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Dislocated shoulder?
- 2 Dislocated shoulder ICD 9 Code
- 3 Dislocated shoulder Symptoms
- 4 Dislocated shoulder Causes
- 5 Dislocated shoulder Pathophysiology
- 6 Dislocated shoulder Diagnosis
- 7 Dislocated shoulder Treatment
- 8 Home Remedies for Dislocated shoulder
- 9 Dislocated shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises
- 10 Dislocated shoulder Prognosis
- 11 Dislocated shoulder Complications
- 12 Dislocated shoulder Risk Factors
- 13 Dislocated shoulder Prevention
It refers to an injurious condition characterized by the protuberance of the upper arm bone from the cup-like socket that is a part of the shoulder blade.
Dislocated shoulder ICD 9 Code
The ICD 9 Code for this condition is 831.
Dislocated shoulder Symptoms
People affected by this condition usually suffer from problems like:
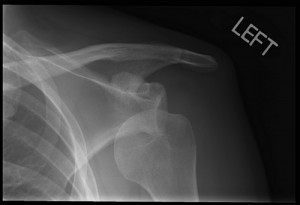
Picture 1 – Dislocated shoulder
- Acute pain
- Inflammation or bruising
- An out of place or visibly deformed spot on the shoulder
- Inability to move the shoulder joint
Dislocation of the shoulder may also lead to other problems like weakness, numbness or tingling sensations close to the site of injury such as down the arm or in the neck. There can be spasms in the muscle due to disruption which often increases the intensity of pain.
The shoulder can move in various directions. As a result, you may suffer from dislocation downward, forward or backward. The dislocation can be complete or partial. The fibrous tissues that attach the ligaments (shoulder bones) can get torn or stretched, often complicating the condition.
Dislocated shoulder Causes
The shoulder joint commonly suffers from dislocation due to repetitive stress. Some of the common reasons for shoulder dislocation are:
Sports injuries
Indulging in contact sports, such as martial arts, hockey or football, commonly results in this type of injury. Dislocation may also occur due to participation in sports activities like volleyball and gymnastics that involve falling down.
Non-sports related injury
A severe blow to the shoulder during an activity or an accident commonly gives rise to this problem.
Falls
Falling down from a ladder or tripping on a rope or rug may also injure the shoulder joint and result in dislocation.
Dislocated shoulder Pathophysiology
A sudden impact to the shoulder causes its bones to be pulled by a strong force, thus resulting in a dislocation. Excessive rotation of the shoulder joint can make the humerus (upper arm bone) project out of the glenoid (shoulder socket) that is a part of the scapula (shoulder blade). This is complete dislocation. Affected individuals may also suffer from partial dislocation (subluxation), in which the bone of the upper arm remains partly inside and partly outside the glenoid.
Dislocated shoulder Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disorder is initially conducted through a physical examination of the shoulder. Thereafter, depending on the condition, a physician may use one or more of the following medical exams:
X ray
An X ray examination of the shoulder joint displays the type and extent of dislocation as well as broken bones or any other damage to the shoulder joint.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
This imaging exam employs a magnetic field to produce cross-sectional images of the affected section. The images help physicians to assess the nature of damage to the soft tissue structures in the region surrounding the shoulder joint.
Electromyography (EMG)
The process measures the electrical charges produced in the muscles of sufferers, at the time of rest as well as during contraction, with the aid of a special apparatus. Physicians analyze the electrical signals in the area to assess the damage to the nerve caused by repeated or severe dislocation.
Dislocated shoulder Treatment
The treatment of this condition may include one or more of the following curative options:
Rest
Patients are advised to provide their injured joint with as much rest as possible. They are asked to avoid all sports and non-sports activities that might cause stress to the joint.
Immobilization
In some severe cases, doctors use a sling or special splint to immobilize the shoulder of patients for some time ranging from a few days to a few weeks. The time span for immobilization depends on the type of the dislocation and how soon the shoulder is immobilized with a splint after dislocation.
Medications
Physicians might prescribe a muscle relaxant or an analgesic (pain relieving medicine) to provide comfort to patients while they are recuperating from a shoulder injury.
Closed reduction
Physicians may also use some gentle other tactics to help the shoulder bone slide back to its actual position, which involves a maneuver known as “Closed Reduction”. Sufferers might require a sedative or muscle relaxant for support, depending on the amount of inflammation and pain that they are found to be suffering from. In rare cases, a general anesthetic is injected into the shoulder before manipulating the humerus (shoulder bones). When the bones snap back into place, any pain or inflammation is likely to improve almost instantly.
Surgery
If you are suffering from weakened ligaments or bones in the shoulder area, you may require a surgical cure. Operative treatment is also necessary for those who tend to suffer from shoulder instability or shoulder dislocations, even after proper strengthening and rehabilitation. In rare cases, affected individuals may require operative remedy to reverse any damage to the blood vessels or nerves due to dislocation.
Rehabilitation
Once the sling or shoulder splint has been removed, patients are often advised to gradually begin a rehabilitation program that is designed to restore strength and range of motion to the shoulder joint.
Home Remedies for Dislocated shoulder
Minor cases of the condition can be healed with the help of home remedies. Such measures may also be used for supportive treatment of the disease, along with medical procedures.
Rest
This involves limiting or negating all movements and activities that can worsen the problem, or might have led to the condition in the first place. Restrict lifting heavy stuff or raising arms over head until the shoulder has healed completely.
Ice application
Applying ice onto the injured area helps decrease pain and inflammation associated with the condition. It is necessary to place a thin strip of cloth over the region and apply ice over it. This would help you avoid risks of ice burn. Use ice treatment for 15-20 minutes, every few hours hence, during the first few days.
Heat application
When the shoulder improves a little with ice treatment, apply hot compresses over the injured spot with heating pads or hot packs to ease soreness and tightness of muscles in the region. Reduce application of heat to 20 minutes.
OTC pain relievers
Over-the-counter (OTC) analgesics like Ibuprofen (Motrin or Advil), Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Aspirin or Naproxen (Aleve) may provide patients with relief from painful symptoms. It is necessary to read the label for dosage instructions and stop taking the medications when the pain subsides.
Exercises
Practice some gentle exercises a day or two after visiting your physician. This would help maintain the range of motion of your shoulder joint.
Continue exercising when your injury has healed and the range of motion has improved. Performing a balanced strengthening program and stretching exercises on a daily basis can help you prevent the condition from recurring. Ask your physician, or a physical therapist, for an appropriate workout program for yourself.
Dislocated shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises
Leaving the joint completely inactive can make it stiff and further complicate the problem by leading to Frozen shoulder – a condition that makes you unable to even move your shoulder. Consult your doctor and begin rehab exercises as soon as you are advised to perform them.
Isometric shoulder external rotation
The steps for performing this exercise are as follows:
- Stand in a doorway.
- Bend your elbow to a right angle.
- Press the back of your wrist against the frame of the door.
- Try pressing your hand toward the outside into the frame.
- Hold the position for 5 seconds.
- Repeat the process. Stop after 3 sets (10 repetitions in each set).
Isometric shoulder internal rotation
Follow these stepwise directions to perform this workout:
- Stand in a doorway.
- Bend your elbow to a right angle.
- Press the front of your wrist against the frame of the door.
- Try pressing your palm into the frame.
- Hold the position for 5 seconds.
- Repeat the process. Stop after 3 sets (10 repetitions in each set).
Isometric shoulder adduction
Follow these steps to practice this exercise:
- Place a pillow between your arms and your chest.
- Squeeze the pillow with the help of both arms.
- Hold the count for 5 seconds.
Repeat the process. Stop after you have performed 3 sets (10 repetitions in each set).
Isometric shoulder flexion
Practice the steps given below to perform this exercise:
- Stand upright, facing a wall.
- Bend your elbow at a right angle and keep it positioned close to your body.
- Extend your fist forward and press it against the wall.
- Hold the stance for 5 seconds, before taking rest.
- Perform the steps for a total of 10 times. This completes one set. Perform two more sets, and 30 repetitions in total.
Dislocated shoulder Prognosis
An affected shoulder usually takes a few weeks to heal after proper treatment. Following reduction, patients are advised to keep their arm rested in a sling for several weeks. It usually takes anywhere from 12-16 weeks to recover completely from a dislocated shoulder. Generally, sufferers can resume most activities within a couple of weeks. However, they should avoid heavy lifting and sports activities that demand using the shoulder for 6 to 36 weeks. F you have a job that is physically strenuous, discuss the issue with your doctor and ask for proper advice.
In case of a broken arm, sufferers need to wear a sling for up to 6 weeks. The time for recovery is likely to be greater in such cases.
Dislocated shoulder Complications
The condition may give rise to complications like:
- Damage of the blood vessels or nerves
- Rupture (tear) of the ligaments, tendons and muscles that reinforce the shoulder joint
- Susceptibility to shoulder instability, in case of repeated or a severe dislocation
In case of such complications, patients might require a surgical cure for repairing the problems.
Dislocated shoulder Risk Factors
The susceptibility to this condition might be increased due to certain factors, like:
Being male
Males tend to suffer more from this condition than females.
Being young
Young people are naturally more inclined to increased physical activities, such as sports, which increases the risk of having the problem for them.
Dislocated shoulder Prevention
It is usually difficult to prevent this condition. However, adopting certain measures can reduce the risk of this problem for you. These involve:
Picture 2 – Dislocated shoulder Image
- Wearing protective gear while taking part in sports activities that involve contact and falls.
- Taking precautions to avoid falls and wearing joint guards while venturing on rough surfaces.
- Exercising on a regular basis to maintain flexibility and strength in the muscles and joints.
If you suspect yourself to have suffered a shoulder dislocation, adopt the following measures while you are still waiting for medical help:
Providing rest to the joint
It is necessary for you to keep the affected joint as much immobilized as you can. Use a sling or splint to prevent worsening of the problem. Do not attempt by yourself to move or force the joint back into its place. This can cause you much pain and damage your shoulder as well as the adjoining nerves, muscles blood vessels or ligaments.
Applying ice over the spot
Press ice over the affected shoulder area to control any internal bleeding as well as accumulation of fluids in and around the impaired joint. Ice application would also help decrease pain and inflammation in the region.
If you suspect yourself to be suffering from a dislocated shoulder, seek medical help on an immediate basis. Early medical detection and treatment would help you avoid all possible complications and make a quicker recovery from the condition.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/dislocated-shoulder/DS00597
http://www.medicinenet.com/dislocated_shoulder/article.htm
ACSM Fitness Book”; American College of Sports Medicine; 1998
Stretching Anatomy”; Arnold G. Nelson, Ph.D. et al; 2005