What is Cryptococcal Meningitis
Page Contents
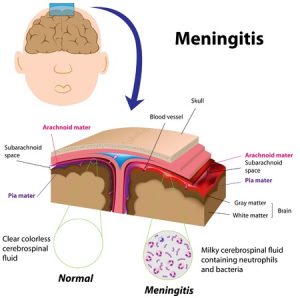
Cryptococcal meningitis is a non-contagious, opportunistic infection that occurs when the meninges tissue covering the brain and spinal cord get infected by certain fungus. Other body parts, such as the lungs, kidney, bone marrow, urinary tract, lymph nodes and skin, may also be affected.
Causes
The disease is usually caused by the fungus, Cryptococcus neoformans, (present in the wastes of birds such as pigeons, as well as in soil), and rarely by Cryptococcus gatti (commonly found around eucalyptus trees). The mode of transmission of C. neoformans is through inhaling dust particles contaminated with dried bird droppings, with the fungus mostly affecting individuals having a weak immune system. The C. gatti fungus, on the other hand, may infect anyone.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms are slow and may take a few days to a few weeks to appear, generally including:
- Headache
- Hallucinations
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Behavioral changes suggesting mental confusion
- Irritability to light
- Eye problems such as impaired vision
- Seizures
Rare symptoms may include:
- Moderate to high fever
- Stiffness and pain in neck
- Fatigue
Risk factors of C. neoformans-Induced CM
It is more likely to affect people with:
- CD4 cell counts below 100
- Aids
- Cirrhosis
- Diabetes
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Sarcoidosis
- An organ transplant
- Long term steroid therapy
- Renal failure
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- After renal transplant (rarely)
Possible Complications
- Deafness
- Brain damage
- Coma
- Hydrocephalus
- Critical skull swelling leading to pressure on brain
- Blindness from optic neuritis
- Decreased mental capacity
- Meningoencephalitis
- Permanent cranial nerve palsies
- Hydrocephalous
- Vasculitis
- Ischemic stroke
Diagnosis and Tests
- A complete physical examination concerning the symptoms associated with the ailment
- A lumbar puncture test or spinal tap to examine a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Chest x-ray
- CT scan of the head
- Examination of CSF to find out cell count, glucose, and protein
- CRAG test to look for cryptococcal antigen in CSF or blood
- Gram stains
- Blood culture
- Culture of CSF
- Sometimes a diagnostic test using a dye called India ink
Differential Diagnosis
- Tuberculous meningitis
- Lymphomatous meningitis
- Hyponatraemia
Treatment and Management
Medication
Antifungal medicines such as amphotericin B, along with flucytosine may be prescribed, with the dosage continuing for two or more weeks, as necessary. Close monitoring by the doctor is often necessary to check for any toxic effects on the kidney (nephrotoxicity).
Amphotericin B may be replaced by fluconazole, if spinal fluid tests (for CM) taken in two consecutive weeks show negative results. Fluconazole may be substituted with other alternative antifungal agents such as Itraconazole or Voriconazole.
Intravenous Therapy
In case of IV therapy, amphotericin B is combined with an antifungal medicine called 5-flucytosine and inserted intravenously.
Lumbar Drainage
Some patients with raised intracranial pressure may undergo a lumbar puncture to drain excess spinal fluid to reduce the opening pressure. However, more research needs to be done in this area.
Adjunctive Treatment
Glucocorticoids, such as dexamethasone, may reduce the possibility of blindness associated with the disease.
Treatment of CM during Pregnancy
For pregnant women who have CM, the usual drug of choice is amphotericin B as it is safer than the azole drugs, like fluconazole, itraconazole and ketoconazole, which may induce birth defects.
Can CM be Prevented
Although it is not possible to prevent initial exposure to the fungus, taking a few measures may help people more at risk of developing the infection. The drug, fluconazole reduce the chances of CM for those with CD4+ counts less than 50, but long-term use can have side effects, like thrush, vaginitis or candida infections since these yeast infections are resistant to fluconazole.
Incidence and Prevalence
With AIDS patients, its incidence lies between 2-7 cases per 1000 people, while amidst non-HIV-infected people, it occurs in 0.4 to 1.3 cases per 100,000 people. The ailment is more prevalent with adults and adolescents than children (found in less than 1% of all HIV-affected children).
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
Most patients improve with adequate treatment. Recurrence may be prevented by continuing the antifungal drugs. It has a mortality rate of around 10% and chiefly with those with HIV. In Sub-Saharan Africa, the death rate of AIDS patients having the disease is around 50-70%. Research is being done to develop a vaccine to prevent the ailment.
ICD-9-CM and ICD-CM-10 Codes
The ICD‑CM‑9 code of cryptococcal meningitis is 321.0, while its ICD-CM-10 code is B45.1.