Cornelia de lange syndrome Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Cornelia de lange syndrome Definition
- 2 Cornelia de lange syndrome – Epidemiology and Incidence
- 3 Cornelia de lange syndrome Symptoms
- 4 Cornelia de lange syndrome Causes
- 5 Cornelia de lange syndrome Diagnosis
- 6 Cornelia de lange syndrome Treatment
- 7 Cornelia de lange syndrome Management
- 8 Cornelia de lange syndrome Prognosis
- 9 Cornelia de lange syndrome Support Group
- 10 Cornelia de lange syndrome Pictures
- 11 Cornelia de lange syndrome ICD9 Code
Cornelia de lange syndrome (CdLS) is a congenital defect [1] that is not always detected at birth.
It is also known by the names:
- Amsterdam dwarfism
- Bushy Syndrome
Cornelia de lange syndrome – Epidemiology and Incidence
It is estimated to affect 1 out of every 10,000 live births. The exact incidence is unknown, although it is assessed to be 1 in 10,000-30,000 live births.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Symptoms
It is characterized by:
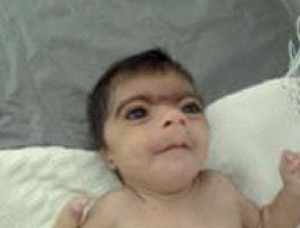
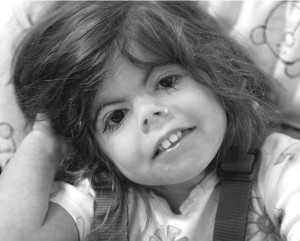
- Distinctive facial appearance [2]
- Difficulties in feeding
- Behavior problems (compulsive behaviors, daily aggression, hyperactivity, sleep disturbance, self-injury, social anxiety)
- Genitourinary problems (cryptorchidism, hydronephrosis, hypogonadism, hypoplasia, renal dysplasia, subcortical renal cysts, impaired renal function, urethral reflux)
- Growth deficiency (prenatal and postnatal), or retarded growth before and after birth
- Psychomotor delay, generally manifested by acute to profound intellectual disability
- Developmental defects (primarily involving the upper extremities – arms and hands)
- Autism (in some patients), marked by impaired social interaction and communication
The facial abnormalities involve:
- Arched eyebrows, often growing together in the centre (synophrys)
- Small, upturned nose and thin lips (downturned)
- Low-set ears
- Long eyelashes
- Dental problems (small, widely spaced teeth)
Additional symptoms include:
- Abnormally small head (microcephaly)
- Cleft palate
- Low birth weight and height (generally less than 2.5 kg/5 pounds)
- Digestive tract problems (Pyloric stenosis, Gastro-esophageal reflux, alimentary canal abnormalities)
- Excessive body hair or Hypertrichosis (hypoplastic nipples and umbilicus, hirsutism on the back, long eyelashes)
- Eye problems (ptosis, myopia and nystagmus)
- Central nervous system issues
- Congenital heart defects (atrial septal defect, Fallot’s tetralogy pulmonary stenosis and ventricular septal defect)
- Hearing problems (Hearing loss, stenosis of the external auditory canals)
- Heat intolerance
- Lack of pain sensation
- Short height
- Seizures
- Skeletal abnormalities (hypoplastic or absent ulna, Oligodactyly, clinodactyly, single palmar crease, syndactyly, proximal placement of thumb/thumbs)
- Respiratory problems (upper respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, bronchopulmonary dysplasia)
Cornelia de lange syndrome Causes
Most cases occur from spontaneous mutations in the genes SMC1A, SMC3 and NIPBL. NIPBL mutations have been spotted in over half of all CdLS sufferers. Cases involving mutations of the two other genes are much less common. [3]
Mutations in the three genes can disrupt gene regulation during critical early developmental phases. As per studies, mutations in the SMC1A and SMC3 genes cause mild cases (milder symptoms) than those in cases of NIPBL mutations. Most cases involving SMC1A mutations arise in people without any family history of the disease.
SMC3 or NIPBL mutations are supposed to be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Only one copy of the mutated gene can cause CdLS. An X-linked inheritance pattern is associated with SMC1A mutations. In other words, the responsible mutated gene is located on X chromosome (one of the two sex chromosomes). X-linked cases of CdLS affect both males and females similarly.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on:
- Symptoms manifested by sufferers
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- Laboratory testing
Recommendation to a genetic specialist can also help in confirmation.
For parents of CdLS sufferers wanting to have more kids, prenatal ultrasound can help assess subsequent pregnancies. In some organizations, ultrasound is deemed as best for prenatal diagnosis.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Differential Diagnosis
It includes isolating the signs of CdLS from those of fetal alcohol syndrome and other rare genetic conditions.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Treatment
Cure involves:
Non-surgical approach
Early medical intervention helps improve:
- Feeding problems
- Urinary system anomalies
- Congenital heart disease
- Visual and hearing impairment
Medical intervention can include:
- Emphasis of perceptual organizational tasks
- Computer programs, to stress visual memory
- Stressing fine motor activities in education
- Tactile stimulation, during indirection
Surgical approach
In some cases, surgery (under anesthesia effects) may be required for correction of:
- Cleft palate
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Hip dislocations
- Intestinal malrotation/volvulus
- Lacrimal duct stenosis
- Nasal polyps
- Pyloric stenosis
- Undescended testis
Consultations
Guardians can consult the following specialists:
- Cardiologists
- Gastroenterologists and nutritionists
- Geneticists
- Hearing specialists
- Nephrologists (for congenital abnormalities, impaired renal functions or recurrent urinary tract infections)
- Neurologists
- Ophthalmologists
Cornelia de lange syndrome Management
Management is primarily based on specialists. General practitioners ensure overall health supervision and regular hospital reviews and recommend genetic counseling. Recurrence risk is reduced for spontaneous mutations.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Prognosis
Most premature deaths occur in acutely affected neonates, within the first 2 years of life [4]. A slightly reduced life span is observed in survivors. Life expectancy depends on the general health as well as the level of care.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Support Group
The Cornelia de lange syndrome (CdLS) Foundation, which is a non-profit Connecticut-based organization, provides support to family members. It helps in early and proper diagnosis of CdLS and encourages research into the causes and symptoms of the disease.
Cornelia de lange syndrome Pictures
The images show the appearance of CdLS sufferers.
Picture 1 – Cornelia de lange syndrome
Picture 2 – Cornelia de lange syndrome Image
Cornelia de lange syndrome ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code for CdLS is 759.89.
References:
- Cornelia de lange syndrome (Wikipedia)
- Cornelia de lange syndrome (Medscape)
- Cornelia de lange syndrome (nlm.nih.gov)
- Cornelia de lange syndrome (Patient.info)