Cherubism Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Cherubism Definition
- 2 Cherubism Incidence
- 3 Cherubism Causes
- 4 Cherubism Genetics
- 5 Cherubism Inheritance Pattern
- 6 Cherubism Symptoms
- 7 Cherubism Prevention
- 8 Cherubism Diagnosis
- 9 Cherubism Differential Diagnosis
- 10 Cherubism Treatment and Surgery
- 11 Cherubism Prognosis
- 12 Cherubism Support Groups
- 13 Cherubism Pictures
Cherubism is a rare genetic condition that leads to the prominence of the lower part of the face. The name of the disorder is derived from the fact that the chubby-cheeked appearance of the patients resembles the putti, frequently confused with the cherubs, represented in the Renaissance paintings.
Cherubism Incidence
Around 200 people have been reported to be affected by this condition by various medical journals. Majority of the patients were males. This indicates that males may be more likely to develop the disorder compared to women. However, there is lack of enough evidence to prove this.
Cherubism Causes
SH3BP2 gene mutation is the principal cause for this hereditary disorder. Mutations in this specific gene have been found in around 80% of Cherubism patients. The SH3BP2 gene is responsible for providing the commands for producing a type of protein. It is believed that the lack of this protein causes this disease.
Its histology consists of giant cells, blood vessels having hyaline deposits and granulation tissue stroma.
Cherubism Genetics
The exact functioning of the protein produced by the command of the SH3BP2 gene is still unknown. However, it is known to help in the transmission of chemical signals within various cells, especially those helping in replacing old bone tissues with new ones (a process known as bone remodeling) and the cells of certain immune systems.
The overactivity of the protein probably causes jaw bone irritation which produces osteoclasts, cells responsible for breaking down the bone tissues during remodeling. Excessive production of these bone eating cells destroys the bones in the lower and upper jaws.
Cherubism Inheritance Pattern
The inheritance pattern of this condition is autosomal dominant, meaning one copy of the mutated gene in every cell can cause the disorder.
Sometimes, a child inherits the abnormal gene from one parent with the condition. However, it is also possible for an individual with no family history of Cherubism to develop the disorder due to new gene mutations.
Cherubism Symptoms
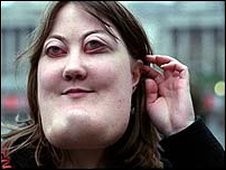
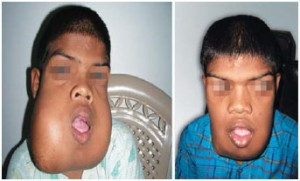
People affected by this condition suffer facial distortion. The gene mutations result in the destruction of bones in the mandible area that are replaced by the body with lots of fibrous tissues. These abnormal bone tissues give the upper and lower jaw (the mandible and maxilla) an enlarged swollen appearance which is the main characteristic of this disorder. The age of onset of the symptoms is between 6 years and 10 years. In majority of the cases, the advancement of the disease stops with the growth of the affected child so that he or she has a relatively normal facial appearance. However, in some very rare instances, the facial deformation of the patient continues even when he or she enters puberty. The osteoclastic and osteoblastic bone remodeling is responsible for replacing the normal bones with fibrous tissues as well as the cyst formation. As the name suggests, the atypical bone formation and fibrous tissues cause enlargement and disproportion of the face of an affected individual.
Premature primary teeth loss and un-eruption of permanent teeth are other manifestations of Cherubism. The abnormal bone formation causes permanent problems with timely tooth eruption. The orbital area of the individual is also affected by the disease which results in an upturned appearance of the eyes. The normal jaw motion of the patients during actions like speaking and eating are also disrupted by it.
Cherubism does not generally cause any pain or discomfort in the patients. However, severe cases of the disorder may lead to symptoms like:
- Breathing difficulty
- Renal failure
- Vision problems
- Speech disability
- Difficulty in swallowing
Cherubism Prevention
Couples with a family history of this disease should consider genetic counseling before deciding having a child. This helps to understand the chances of giving birth to a baby with the disorder. In many cases, it does not result in noticeable symptoms. Due to this reason, parents may have the genetic disorder with no knowledge of having it. Naturally, genetic testing is the only way of prevention. However, the gene responsible for it is sometimes known to undergo spontaneous mutation. In these cases, there is no way of preventing the disorder.
Cherubism Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests are performed to detect any mutations in the SH3BP2 gene when a child shows the dental and oral abnormalities. The analysis of the SH3BP2 gene sequence is the only way in which the condition can be diagnosed correctly. Research has shown this gene to have mutation in the exon 9. Initially, tests like CT scan and x-ray are done for detecting the disease. In some cases, Cherubism may be accompanied by another similar condition called Neurofibromatosis. Its radiographic features are similar to Fibrous dysplasia, a disease that causes bone thinning and lesions in bones. The ultimate diagnostic tool available for detecting the presence of Cherubism in an individual is genetic testing.
Cherubism Differential Diagnosis
The following disorders are characterized by symptoms similar to that of Cherubism. The differential diagnosis should aim at ensuring the absence of these conditions in a patient:
- Central Giant-Cell Granuloma
- Noonan Syndrome
- Multiple giant-cell lesion syndrome
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Fibrous dysplasia of jaw
Cherubism Treatment and Surgery
Treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms. This is among the few genetic disorders which may stop progressing itself. In these cases, the bone formation becomes normal again and the patient does not have symptoms of facial deformity and delayed dental growth. However, severe cases require proper treatment. Removing the affected tissues and bones by surgery is the only treatment option available at present.
The change and improvement of Cherubism over time follows dissimilar patterns in different patients. Due to this reason, the treatment options are individually determined. Usually, moderate cases of the condition are studied closely to check whether it is progressing to a level where surgical treatment may be necessary.
Severe cases may be treated with surgery for removing the bulk cysts as well as the fibrous growth of mandible and maxilla. Bone grafting of cranial facial bones by surgery can successfully cure some individuals. Surgery is the favored treatment option for patients aged between 5 year and 15 years. Plastic surgery of the face is also done to correct the disfigurement due to this disorder. While performing the operation on the face, a surgeon should take special care not to harm the zygomatic branch and marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve of a patient. Any type of damage to these nerves may result in decreased facial muscle strength in the affected person.
Dental Surgery
Patients require orthodontic treatment to avoid any permanent dental problems that may result from malocclusive bite as well as un-erupted and misplaced permanent teeth. Tooth extraction is the ideal treatment option if the teeth of the patient are ectopically impacted or severely affected by the lesions associated with Cherubism. Children may need prostheses in extremely severe cases. The prostheses require to be adjusted with the child’s growth or with the changing pattern of swelling within oral cavity. A dental prosthesis can be helpful for boosting the child’s self-esteem by improving his or her ability to chew. The ideal time for orthodontic treatment is after the growth of the child is completed and once Cherubism starts regressing.
Cherubism Prognosis
Most cases of this disorder regress without any treatment. Affected individuals have mild or no symptoms of the condition when they grow up. In severe cases, prognosis is generally positive with proper treatment. The surgeries conducted for correcting the facial deformities usually succeed in restoring most of the abnormal features which significantly increases the confidence and self esteem of a sufferer.
Cherubism Support Groups
Many foundations and support groups are there to provide proper guidelines to help affected individuals and their families to cope with the disorder. These include:
The Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center
P. O. Box 8126
Gaithersburg, Maryland 20898-8126
Phone: (888) 205-2311
Fax: (301) 251-4911
Website: http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/GARD/Default.aspx
National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) (NIH)
6701 Democracy Boulevard
Suite No. 1001, MSC 4874
Bethesda, Maryland 20892
Phone: (301) 402-4336
Fax: (301) 480-9655
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/Default.aspx
Cherubism Pictures
The following pictures show how the condition affects the appearance of the face of humans suffering from the disease.
Picture 1 – Cherubism
Picture 2 – Cherubism Image
References:
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition=cherubism
http://www.fdssuk.org.uk/cherubism.html
http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/c/cherubism/causes.htm
http://www.fibrousdysplasia.org/index.php?page=25