What is a Carbuncle?
Page Contents
- 1 What is a Carbuncle?
- 2 Occurrence of Carbuncles
- 3 Comparison between Furuncles (boils) and Carbuncles
- 4 Symptoms of Carbuncles
- 5 Causes for Carbuncles
- 6 Risk factors for Carbuncles
- 7 Complications of Carbuncles
- 8 Diagnosis for Carbuncles
- 9 Treatment for Carbuncles
- 10 Home remedies for treating Carbuncles
- 11 Prevention of Carbuncles
- 12 When to call a doctor?
- 13 Carbuncles Images
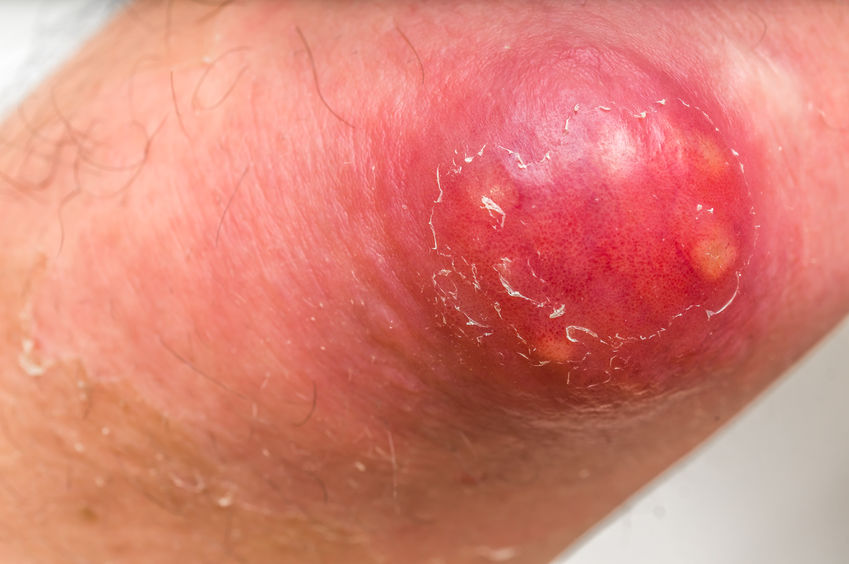
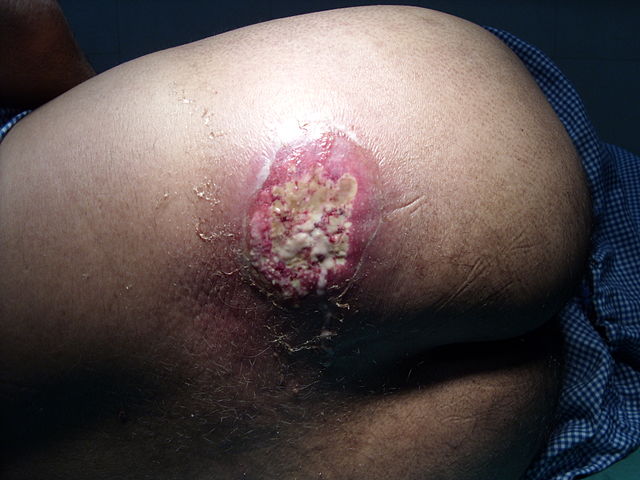
Carbuncle is a skin infection that is characterized by red colored swollen and dome-shaped cluster of boils involving a group of hair follicles. The infection caused under the skin leads to formation of a lump which may damage deep through the skin and contain pus. It is also known as staph skin infection and usually grows to a size varying from 3 to 10 centimeters.
Occurrence of Carbuncles
Carbuncles are likely to occur on hairy areas of the body particularly at the back of the neck. But they may also be found on shoulders, thighs, groin, buttocks, and armpits. This can result in permanent scarring on the skin affected. They may be very painful if grown in closely attached surfaces like nose, fingers or ears. Carbuncles are very infectious too and may spread to other parts of the body and even to other people.
Comparison between Furuncles (boils) and Carbuncles
The staphylococcal infection causes Furuncles or skin abscesses and involves the hair follicles and adjacent tissues. They contain a limited amount of pus and when these furuncles or boils are connected subcutaneously and are clustered together, they cause deeper scars and more pus formation.
These are smaller and more superficial in nature. In comparison to boils, Carbuncles cause deeper and much severe infection accompanied by fever and chills. Carbunculosis is when there is more than one Carbuncle develops.
Symptoms of Carbuncles
- Painful red mass
- Appears as a nodule or a pustule
- Accompanied by fever or prostration
- Swift growth
- Center is white or yellow containing pus
- Weeping, oozing out or crusting of skin
- May spread to other areas
- Looks as small as a pea sized or as large as a golf ball
- Red and irritable on touching
- Fatigue
- Fever with high temperature of 38C (100.4F) or above
- Discomfort or feeling sick
- Itching skin on the affected area
- Swelling in surrounding tissues and lymph nodes
- Body ache
Causes for Carbuncles
- Infection by a notorious bacteria or virus (Primarily staphylococcus aureus bacteria)
- Bacterial infection entering through hair follicles
- Underlying condition of eczema or acne
- Previous amalgamation of boils
- Infection by microorganisms
- Folliculitis
- Rashes caused due to harsh shaves
- Hair pulling
- Poor nutrition
- Immune deficiency
- Poor hygienic conditions
Risk factors for Carbuncles
Although everyone bears the risk of developing Carbuncles, some factors may increase the risks of its occurrence:
- Old age
- Obesity
- Poor hygienic conditions
- Overall poor health
- Chronic skin conditions
- Diabetes mellitus
- Kidney disorders
- Liver problems
- Weak immune system
- Sharing bed linens, towels or clothing of others
- Wearing tight clothes
- Shaving and other activities breaking the skin
- Insect bites on the skin with heavy perspiration
- Acne and eczema patients
- Neutrophil disorders
- Living in crowded quarters
- Contact with virulent strain infected people
- Close contact with Carbuncle affected people
- Dermatitis
- Side effects of Immune modulating agents
Complications of Carbuncles
There might be severe complications related to these boils or Carbuncles. Sometimes, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria cause Carbuncles and the lesions must be drained out properly through high dosage of antibiotics to prevent further damage. Some of the common complications have been discussed below:
- Sepsis
- Infections in different body parts
- Lung infection
- Bone infection such as osteomyelitis and joint damage
- Infections in blood
- Heart disorders like endocarditis
- Effect on central nervous system
- Cellulitis infecting deeper sections of skin
- Permanent scarring
Diagnosis for Carbuncles
- Doctor can easily detect Carbuncles by merely looking at the affected area
- Pus sample is needed for lab analysis
- Span of the Carbuncle if lasts for two weeks
- Lesion culture
- Urine test
- Blood tests
- Clinical evaluation
Treatment for Carbuncles
Usually, Carbuncles or simple boils can be treated with home methods. But if chronic, the doctor’s recommendations are crucial. One must never take the risk to drain a Carbuncle by him as it can lead to infections in the bloodstream. Some common treatments and medicines that doctors might prescribe are:
- Oral Antistaphylococcal antibiotics for healing severe cases
- Trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, and doxycycline or minocycline
- Incision at the tip of the Carbuncle and drain out the pus
- Deep Carbuncles require sterile gauze to soak and get rid of the additional discharge of the pus
- At times, antibiotic ointments rubbed onto the skin also helps to heal
- Painkillers may be used for reducing pain
- In extreme cases for deep and large Carbuncles, they need to be operated after draining it out.
- Antibacterial soaps also prescribed by the doctors to be used daily
Home remedies for treating Carbuncles
- Warm compressing over the Carbuncle
- Soak the Carbuncle in warm water
- Application of clean, warm moist cloth for 20 minutes at frequent intervals in a day
- Apply heating pad or a hot water bottle for 20 minutes many times a day
- After every use clothes and wraps must be washed in hot water to be freed of germs
- Covering the area with sterile bandage
- Medications such as Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen relieve the pain
- Use of over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen to reduce pain
- Cleanse skin with antibacterial soap
- Apply soap and wash your hands with warm water after touching a Carbuncle or the area
- Prevent contamination
- Never squeeze a boil or leave it open
- Bandages worn should be changed at regular intervals and thrown in closed bags
Prevention of Carbuncles
Carbuncles or infected boils cannot always be avoided but some measures must be adopted and proper hygiene must be maintained to reduce the risk of its occurrence:
- Clean the skin using a mild antibacterial soap
- Clean the cuts, wounds and injuries very carefully
- Cover the wounds and cut with sterile bandages until they get entirely healed
- Healthy diet and regular exercise helps to boost the immunity system
- Clean hands before eating and after using the bathroom
- Have frequent showers to free the skin from bacteria
- Avoid squeezing of boils and rubbing of broken skin
- Use of cleansers with chlorhexidine, triclosan, and triclocarban in them
When to call a doctor?
Typically, boils and Carbuncles do not require medical treatment as they tend to burst and heal by themselves. If the Carbuncle is lying somewhere adjacent to the nose, spinal cord or eyes, one must call the doctor immediately or else it can lead to severe problems. But there are certain conditions if noticed and then you must consult a doctor:
- Carbuncles on nose, face or spinal cord
- Carbuncles extremely painful
- Carbuncle which grows bigger when touched feels soft and spongy
- Those which do not heal within two weeks
- High temperature & chills associated with the boils
- Feeling unwell
- Recurrence of the Carbuncles
- Prolonged lasting of the lesions
- Weakness & exhaustion