Campomelic dysplasia (CD) is a rare genetic disorder that is characterized by bent limb. Find out more about the condition including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
Campomelic dysplasia Definition
Page Contents
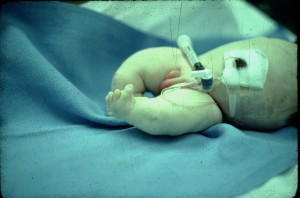
It is a severe congenital defect that hinders the development of the skeletal and reproductive system. The symptoms of this disease get apparent prenatally, or just after birth. In Greek, the term “campomelic” refers to bent limb. The condition is known to give rise to fatal consequences in newborns.
Campomelic dysplasia Synonyms
The various other names used for denoting the disorder are:
Picture 1 – Campomelic dysplasia
- Campomelic syndrome
- Camptomelic dysplasia
- Campomelic dwarfism
Campomelic dysplasia Incidence
This distressing syndrome affects 1 in 40,000 to 200,000 live births.
Campomelic dysplasia Symptoms
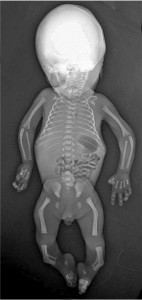
The disorder is typically characterized by angular bowing as well as shortening of the long bones in the legs, and arms. The congenital condition is called Acampomelic campomelic dysplasia in individuals who do not display any significant bowing of the bones. Skin dimples form over the curved bone, especially on the lower legs. The condition is also present with an array of orthopedic, facial and reproductive features like:
- Short legs
- Dislocated hips
- Underdeveloped shoulder blades
- Absence of the 12th pair of ribs
- Small, narrow, bell-shaped chest
- Anomalies in the neck bone
- Redundant skin at the back of the neck
- Protuberant abdomen
- Decreased muscle tone
- Clubfeet/Twisted feet
- Ambiguous genitalia
- Small chin
- Flat face with depressed nasal bridge
- Prominent eyes and forehead
- Cleft palate
- Congenital heart defects
- Abnormal downward displacement of the tongue
- Undersized jaw
- Weakened cartilages surrounding the trachea/windpipe
- Respiratory distress
- Abnormal curvature of the spine
- Short stature
- Hearing impairment
- Unusually large head
Campomelic dysplasia Causes
The syndrome is inherited in a sporadic, autosomal dominant manner, in which an affected individual has one copy of a mutant gene and one normal gene on a pair of autosomal chromosomes. This means that only one copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In fact, individuals with no history of the disorder in their family are also at a risk of undergoing genetic transformation. However, such cases are reported only on rare occasions. The mutation occurs in or near the SOX9 gene located on chromosome 17. The gene encodes for a protein called SOX-9 that regulates the transcription of Type 2 collagen and proteoglycan aggrecan, responsible for the normal development of cartilages. The transcription factor also plays a crucial role in the fetal genital development. Mutation within the SOX9 gene can either block the production of the protein or result in a protein with impaired function. Chromosomal anomalies that occur around the SOX9 gene account for 5% of all cases of CD. In this disease, the region of DNA that controls the activity of the gene gets destructed. Approximately 75% of affected individuals with a typical male chromosome pattern (XY) possess normal female genitalia as SOX9 fails to assist in the development of testis. In this disorder, the internal development of the reproductive organs shares no relation with the formation of the external genitalia. The resulting effects of these genetic changes are seen in the form of maldevelopment of the vital tissues and organs during the fetal period.
Campomelic dysplasia Diagnosis
The characteristic bowing of the limbs is the most important clinical finding of the disorder. The external features, including the facial abnormalities are more obvious during a physical examination. Irregularities in the bones can be confirmed with an X-ray. The identification of the chromosomal abnormality can be done with genetic testing. A small sample of blood is required for the clinicians to determine the alteration in the SOX9 gene. The sophisticated technique can also be used for carrier screening, prenatal testing, and newborn screening. Sex determination can be either done by morphological or chromosomal examination. Some of these tests include:
- Chromosome analysis
- Hormone stimulation test
- Electrolyte test
- Specific molecular testing
- Endoscopic examination to verify the absence or presence of a vagina or cervix
- Ultrasound or MRI to evaluate the type of internal sex organs present
Functional deficits in cardiac performance can be diagnosed with some of the most common diagnostic tools like:
Picture 2 – Campomelic dysplasia Image
- Cardiac Catheterization
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- MRI
- CT
- Myocardial Biopsy
Campomelic dysplasia Treatment
As of now, there is no specific cure for this congenital syndrome. The orthopedic manifestations such as clubfeet and bowed limbs can be corrected to some extent with the aid of braces as well as specially-designed footwear to relieve discomfort. Ponseti method or a variety of surgical interventions can repair the deformed feet. A cleft lip may require one or two surgeries depending on the extent of the repair needed. The initial surgery, which involves creation of a functional palate, is usually performed by the time a baby is 3 months old. Additional surgeries may be performed to improve the appearance of the lip and nose. The hormonal imbalance associated with ambiguous genitalia could be treated with medications as well as hormone replacement therapy. Corrective surgery to remove or create reproductive organs appropriate for the gender of the child is highly needed, owing to the increased risk for tumors in the gonads. There is no effective treatment available to expand the size of the chest. Early intervention therapy services are provided by occupational therapists to the infants and toddlers who have a myriad of feeding issues. Breathing problems may necessitate the use of continuous positive airway pressure. This is a form of respiratory ventilation where patients are made to wear a face mask connected to a pump that forces air into the lungs at pressures high enough to overcome obstructions in the airway and stimulate normal breathing. The pressure in the upper airway is continuous during both inhalation and exhalation. The method is safe and effective in children as it prevents the lungs from collapsing. Complex cardiac abnormalities may need special care for an indefinite amount of time.
Campomelic dysplasia Prognosis
Only a small proportion of individuals with CD can survive past infancy. However, most long-term survivors require annual monitoring of growth and spinal curvature.
Campomelic dysplasia Complications
In the majority of cases, the condition becomes fatal during early infancy due to the wide range of physical anomalies. The ones who survive into adulthood may develop additional problems such as hypoxic brain injury due to reduced supply of oxygen.
As discussed earlier, Campomelic dysplasia is a highly fatal disorder that does not have any standard treatment. Emergency life support measures can only prolong the life of the affected patient. Individuals who happen to be the carriers of the disorder may consult a genetic counselor before planning a baby. The option of pregnancy termination should be offered if the condition is detected in the fetus during prenatal diagnosis.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Campomelic_dysplasia
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/campomelic-dysplasia
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1760/
http://www.healthline.com/galecontent/campomelic-dysplasia-1#1