Calciphylaxis Definition
Page Contents
It is a syndrome that is a combination of vascular calcication, skin necrosis and thrombosis. A rare and serious disorder, it is characterized by systematic medial calcification of the arterioles which leads to ischemia and subcutaneous necrosis. This is a type of extra-osseous calcification which may occur in patients who have developed end-stage renal disease. In medical history, it has traditionally been classified as metastatic calcification which is an indication passive mineralization of serum calcium and phosphate crystals.
This syndrome usually arises in people who have undergone hemodialysis or have received a renal transplant.
Calciphylaxis Symptoms
This fatal disease is caused due to the deposition of calcium from blood vessels into the skin which leads to hypersensitivity. Some signs and symptoms related to Calciphylaxis are:
- Systemic medial calcification of the arteries.
- Formation of red papules, plaques and other nodules.
- Small vessel mural calcification with or without extravascular calcification, endovascular fibrosis and vascular thrombosis, all of which lead to tissue ischemia.
Other Symptoms
Some other problems related to this disease include:
- Painful skin ulcers
- Organ failures
- Bleeding from the scarred area
- Itching and burning sensations
- Purple or red colored lesions on abdomen, stomach or buttocks or thighs.
Calciphylaxis Causes
The cause of this syndrome is still not clearly known. It is not an allergic reaction but there are several additional factors that lead to its development.
Most cases of Calciphylaxis have been found to occur when there is a chronic renal failure, hyperparathyroidism or abnormal calcium-phosphate homeostasis. However, few case reports also suggest that the condition can occur even when there is no renal disease and a patient suffers from rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn disease.
Calciphylaxis mostly occurs in body areas having maximum fat. Fatty areas are at greater risk of developing thrombosis due to low blood flow or due to increased tendency for vascular kinking. Patients who are at risk include those who are obese and those who are exposed to immunosuppressive agents like glucocorticoids. People who are suffering from diabetes mellitus are also at risk of developing this rare disorder.
Know about some disorders associated with the development of Calciphylaxis:
- Systemic inflammation is a pre-disposing factor.
- Speculative associations include iron dextran infusion, aluminum toxicity and coagulation abnormalities.
- Several associations like hypercalcemia, vascular calcification, hyperphosphatemia and elevated calcium-phosphate product.
Calciphylaxis Diagnosis
The diagnosis for this disorder involves considering the medical history of sufferers as well as conducting a few physical exams, which include:
Blood Tests
Blood sample of the patient is taken to measure a variety of substances in the bloodstream, such as:
- Calcium
- Aluminum
- Urea
- Phosphorus
- Albumin
- Parathyroid hormone
- Creatinine
This test helps doctors to assess the functions of the kidney and liver. If creatinine, a chemical waste, does not leave your body through urine it indicates that the kidney is not functioning properly. Also, if there is excess of urea nitrogen found in blood, it is a precursor for this disease. Healthy liver function is detected by the presence of proteins like albumin and clearing the waste product of blood bilirubin. Presence of bilirubin in the blood means the liver is not functioning properly.
Deep Skin Biopsy
A tissue sample from the affected area of the skin is taken by a doctor to confirm whether the underlying condition is Calciphylaxis or any other infection.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies like X-rays show a clear picture of the vascular calcifications that appear like branches is a common phenomenon in Calciphylaxis. Other additional imaging exams include mammograms, bone scans and high resolution CT scans.
Calciphylaxis Treatment
There is no specific treatment for Calciphylaxis. The optimal curative process for this disorder is prevention. However, following treatment approaches are accepted:
Intensive wound treatment
In this method of treatment, damaged tissues are removed surgically and also by other methods. In some situations, the damaged tissues are removed with the help of wet dressings, whirlpool treatments etc. Medications are also prescribed to reduce pain during wound care. Antibiotic treatment is part of treating and preventing wound infection.
Reduction of Calcium Deposits
Reduction of calcium deposits in the arteries can be carried out by the following methods:
Surgery
If a doctor finds out an overactive parathyroid gland as the reason behind over production of calcium, he may decide to remove the entire gland or only a part of it.
Dialysis
A doctor may also recommend continuing kidney dialysis and adjust their frequency along with the medications required with it.
Medications for Reducing Calcium Levels
The doctor will make an evaluation of the current medications and try to remove the potential factors that trigger Calciphylaxis. He may change the dose of calcium and vitamin D supplements and ask you to stop taking corticosteroids or iron. Doctor may also suggest a medication known as cinacalcet which helps control parathyroid hormone. Other medications, which are also recommended, include sodium thiosulfate (to flush out calcium through urine) and medications that improve the balance of calcium and phosphorus in the body.
Restoration of Oxygen and Blood flow
Doctors may suggest a hyperbaric oxygen therapy to maximize the amount of oxygen in the affected parts. Medications that thin out the blood may also be prescribed to prevent additional blood clots from forming. Low-dose tissue plasminogen activator or TPA may also be used by the doctor to help dissolve the blood clots inside the tiny blood vessels of the skin.
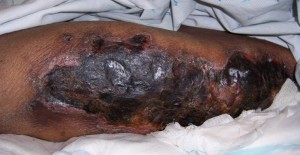
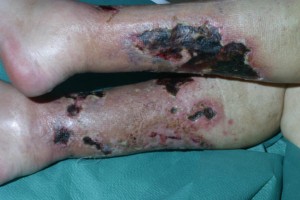
Calciphylaxis Pictures
Here are a few pictures to help you understand the disorder and its effects.
Picture 1 – Calciphylaxis
Picture 2 – Calciphylaxis Image
References:
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/calciphylaxis
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calciphylaxis
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1095481-clinical#a0218
http://www.health-issues.org/skin-disorders/calciphylaxis.htm
http://www.mayoclinic.org/calciphylaxis/treatment.html