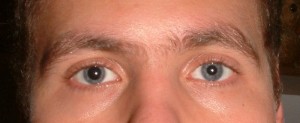
Anisocoria definition
Page Contents
- 1 Anisocoria definition
- 2 Pupil and Iris
- 3 Normal pupil reaction to light
- 4 What is anisocoria?
- 5 Considerations
- 6 Are there instances when anisocoria is normal?
- 7 Anisocoria Causes
- 8 Anisocoria in infants or congenital anisocoria
- 9 Anisocoria Symptoms
- 10 How to determine that the pupil is too small or too big?
- 11 How would one determine whether the anisocoria is resulting from underlying medical disorders?
- 12 Treatment for anisocoria
- 13 Can anisocoria be prevented?
Anisocoria is a condition where the pupils of individual’s eyes are of unequal size.
Pupil and Iris
The part of the eye that is colored is known as the iris. This is actually a circular muscle whose shape is similar to that of a donut. At its center, you have an empty hole that allows for the passage of light into the eye. This empty hole is known as the pupil.
Normal pupil reaction to light
Normally, when an individual is in a well-lit or bright room or even outdoors, this pupil is supposed to constrict. The opposite is supposed to happen when the individual enters a dark room. The pupil would dilate in order to allow for the entry of more light into the eye.
What is anisocoria?
In normal cases, the pupils should be of the same size in both eyes. In this case, they should be constricting and dilating simultaneously. In the case of anisocoria however, the size of the pupils would be varied at the same time. It is important to acknowledge that anisocoria as a condition may be normal. There are instances however when it will be signaling at an underlying or predisposing medical condition. It this case, it is always important
Considerations
There are minute variations in the size of pupils in about twenty percent of healthy people. In most cases, the variations in diameter is lower than 0.5 mm. the difference can however be even 0.05 inches (1 mm). Individuals who are born with variations in the sizes of their pupils may not necessarily have any underlying or predisposing disorder. In fact, if other members of the family have a similar condition, then the variations in the size of pupil could possibly be genetic therefore one should not worry much about it.
On the same note, there are instances when the size of pupils temporarily differs for whatever reason. In case no other indications come up and the normal size of the pupils is regained after some time, then you should not worry much about it.
However, when the variations in the size of pupils is beyond 1 mm and develop at a later stage in life without returning to the equal sizes, then it could be signaling at more serious disorders such as nerve, blood vessels, brain, or eye disorders and therefore necessitating medical attention.
Are there instances when anisocoria is normal?
It is estimated that a fifth of the population suffers from anisocoria. The severity of the condition may be different from one day to another sometimes even switching eyes. When this condition does not emanate from predisposing medical conditions, it is known as physiologic anisocoria. In such instances, the variations in the size of pupils would not be more than a millimeter.
Anisocoria Causes
When this condition is not normal or physiologic, it definitely would be pathologic. There are a number of reasons why the condition may occur. You need to note that unless you can say with certainty that the condition is physiologic, you must always have it evaluated. In cases where third cranial nerve palsy is suspected, brain imaging should be done immediately.
- Damage to the iris sphincter : the iris sphincter may be inflamed or have undergone trauma. The pupil would have an irregular shape with magnified examination indicating that the iris muscles have been damaged.
- Horner’s syndrome : this is a relatively rare disorder which occurs when particular nerves travelling from the eyes to the brain and the face get damaged. You need to acknowledge that Horner’s syndrome in itself is not a disease but rather an indication of other medical problems like injury of the spinal cord, tumor, or stroke. There are instances however when the underlying causes cannot be found. In most cases, Horner’s syndrome will only affect one side of the face. Some of the symptoms of the Horner’s syndrome include reduced size of the pupil, drooping eyelid, and reduced sweating on the side of the face that is affected. The affected pupil will therefore be smaller although both pupils will react rapidly to light.
- Chemical blockade : anisocoria may occur in instances where parasympatholytic chemicals accidentally come into contact with conjunctiva. This deactivates the sphincter muscle of the iris therefore causing the pupils to dilate sometime becoming very wide. This is mostly common with individuals whoa are exposed to plants containing atropine or even hospital personnel.
- Failure of the Parasympathetic innervations : this results in comparatively dilated pupil which will react slowly when direct light faces it. In such instances, one would be concerned about third nerve palsy more so one resulting from aneurysm. However, in no case would the anisocoria be caused by third nerve palsy not unless you have other indications of third cranial nerve palsy, ocular misalignment and less ocular movements. In some isolated cases, anisocoria may be caused by viral infection affecting ciliary ganglion which is orbital structure known to receive parasympathetic part of third cranial nerve.
Other common Anisocoria causes:
There are instances when anisocoria is caused by rather common and harmless factors. For example eye-drops and other drugs getting into your eyes such as chemicals from the asthma inhalers may alter the size of the pupil.
Other common causes of anisocoria include abscess or brain tumor, aneurysm, bleeding in the skull resulting from head injury, infection of the membranes surrounding the brain resulting from encephalitis or meningitis, excess pressure on one eye resulting from glaucoma as well as pressure on the lymph node or tumor of the chest which may be followed by drooping eyelid, small pupil and decreased sweating on the side that is affected.
Anisocoria in infants or congenital anisocoria
Congenital anisocoria or Anisocoria in infants is a normal condition. If the father or mother is with differently sized pupils, the baby has chances of anisocoria from birth itself.
Anisocoria Symptoms
Common anisocoria symptoms include,
- Headache
- Blurred and double vision
- Loss of vision
- Fever, nausea, vomiting
- Eye pain and irritation when exposed to light
- Neck pain
How to determine that the pupil is too small or too big?
It is often important that as anisocoria is evaluated, that the doctor determines which of the pupils is actually abnormal. In cases where the variations in the size of the pupils increases when one is in the dark, the miotic or smaller pupil would not be dilating properly and therefore may be abnormal. In addition, in case the variations in the size of the pupil increases when one is in a room with bright lighting, the mydriatic or larger pupil would be abnormal since it would not be constricting as normally as it should.
How would one determine whether the anisocoria is resulting from underlying medical disorders?
In an effort to determine whether the anisocoria is resulting from pathological reasons or it is just a physiological condition, the doctor will ask questions such as when the condition was first noticed, if there was any preceding events that may be related to the condition such as neck surgery, birth process, or even recent trauma. There will also be questions as to whether the condition is noticed more when in dim or bright illumination.
An examination would also be done where the position of the eyelid is evaluated, the health conditions of the back and /or the front part of both eyes as well as the movement of the eyes. Also examined are the pupil’s size and their reaction to dim and bright illumination. With this evaluation, the medical practitioner may want to perform radiological or laboratory testing or even use eye-drops.
The doctors may also perform blood studies like blood differential and CBC, Lumbar puncture (studies of the cerebrospinal fluid), EEG, CT and MRI scan of one’s head, Tonometry where glaucoma is thought to be the cause and scans of both the neck and the skull.
When does anisocoria necessitate attention of medical providers?
Generally, anisocoria as a condition occurring once in a while should not trigger your alarm bells. However, in cases where the variations in the size of the pupil are sudden, unexplained and persistent, then it could be a sign of serious medical conditions and therefore you need to seek medical attention immediately. It would also be important that you seek medical attention if the variations are occurring after an injury of the head or eyes.
In cases where the variations occur alongside double vision, blurred vision, sensitivity of the eye to light, headaches, loss or impaired vision, fever, vomiting and nausea, stiff neck and intense pain of the eye, immediate attention should be sought.
Treatment for anisocoria
There are various ways of managing the variations in the size of the pupil. Here are some tips on how to do it
- Determine what has caused the condition- as you may acknowledge, there is a wide range of conditions that may cause the condition. It may be resulting from oculo-motor nerve palsy, mild mechanical problems or even Horner’s Syndrome. It is not until the key cause of the condition can be established that the management techniques and therapies would stand a chance at succeeding. In any other case, the techniques may worsen the situation especially if they are not on the mark. When an inappropriate cause is treated, the treatment of major problem may be delayed.
- In cases where the condition is caused by particular pharmacological drugs like asthma inhalers or eyedrop, it may be possible that doing away with the medication will remedy the condition.
- When anisocoria is suspected to be resulting from Horner’s syndrome, the medical practitioners or ophthalmologists will search for this disorder using a ten percent cocaine solution. If detected, a number of treatment pathways would be suggested depending on what caused the syndrome. In case the condition is resulting from a recent stroke, then its cause has to be treated. In addition, prevention of more neurological damage must be taken. In case there is a tumor either along one’s cervical spine or in your lung, consulting an oncological specialist would be important.
- Diagnosing and repairing the mechanical damage of the iris- anisocoria may result from traumatized, torn or inflamed iris especially in case you have undergone surgery in the recent times. The inflammation may be taken care of by taking medication if the cause is a mechanical issue. In cases where traumatic damage is the cause, the medical practitioner may advice you to give it some time to heal.
- Treating the oculomotor nerve palsy- the medical practitioners would device as well as execute a therapy plan.
- Treating swelling of the brain tissue or the brain- cortisone shots may be recommended for in on your face or other areas. This reduces the inflammation thereby causing the normal size of the pupils to be regained.
Can anisocoria be prevented?
Prevention of anisocoria pertains to looking at the causes and devising strategies to prevent the occurrence. In cases where you are using drugs such as marijuana and cocaine base, it would be important that you cease taking them. These drugs affect one’s vision and mind causing rapid dilation of the eyes. In some instances, the eyes may not return to their normal sizes until the drugs are completely out of the system.
References:
http://www.nanosweb.org/files/public/Anisocor.pdf
http://www.iovs.org/content/32/3/501.full.pdf