Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a severe form of pharyngeal cancer that accounts for approximately 1% of all malignancies. Read and learn all about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Definition
- 2 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Types
- 3 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Stages
- 4 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Incidence
- 5 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Symptoms
- 6 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Causes
- 7 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Diagnosis
- 8 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Treatment
- 9 Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Prognosis
The condition is marked by an abnormal proliferation of malignant/cancerous cells in the tissues of the nasopharynx, the upper section of the pharynx or throat behind the nose.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Types
This cancerous condition of the nasopharynx has been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) into the following three types:
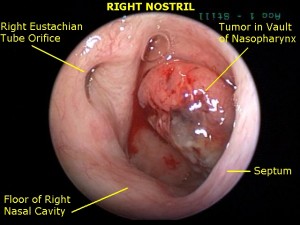
Picture 1 – Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
In this type, the condition usually originates in the squamous cells that line the middle part of the pharynx called oropharynx.
Keratinizing undifferentiated carcinoma
The keratinizing cells that arise from the epithelial basal layer of the nasopharynx become cancerous in this condition.
Non-keratinizing undifferentiated carcinoma
This form is represented by malignancy arising in the non-keratinized squamous epithelium and observed in most number of patients.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Stages
NPC can spread within the nasopharynx as well as to other parts of the body through the following stages:
Stage 0
The malignant condition starts with the formation of abnormal cells found in the lining of the nasopharynx. These cells may unknowingly become cancerous and advance to the nearby normal tissues. This stage is also called carcinoma in situ.
Stage 1
Tumor cells develop and are found only in the nasopharynx at this stage.
Stage 2
This particular stage of NPC can be subdivided into the following:
Stage 2A
The malignant cells undergo rapid proliferation and gradually reach the oropharynx, affecting the soft palate, tongue and tonsils. In a few instances, the cancer can spread to the nasal cavity.
Stage 2B
The cancerous cells can be found in the lymph nodes on one side of the neck, besides the nasopharynx. In other cases, the cancer may spread to the area surrounding the nasopharynx as well as to the lymph nodes in a unilateral direction.
Stage 3
The malignant condition can spread from the nasopharynx to any of the following:
- Lymph nodes on both sides of the neck, resulting in their abnormal growth
- Soft tissues of the oropharynx and nasal cavity
- Regions around the pharynx
- Nearby bones or sinuses
Stage 4
This stage is classified into the following three sub-stages:
Stage 4A
On further multiplication, the cancer cells spread beyond the primary site to the cranial nerves, posterior throat, ocular bone, and areas surrounding the skull or jawbone.
Stage 4B
The cancer extensively spreads to lymph nodes above the collar bone, which is located between the ribcage and shoulder blade. At this stage, the probability of metastatic cancer of the lungs is very high.
Stage 4C
The condition spreads to various tissues beyond the lymph nodes.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Incidence
It is highly prevalent in the southern regions of China. About 18% of cases are reported from Guangdong, a province on the south sea coast of the People’s Republic of China. It also occurs commonly in Taiwan. The incidence of NPC is moderately high in Asia and some parts of Africa.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Symptoms
In the preliminary stages, the size of the tumor is small and the affected patients are normally present with symptoms like:
- A small lump in the nose or neck
- Difficulty breathing or speaking
- Painful inflammation of the ears
- Sore throat
- Difficulty hearing
- Severe headaches
- Reflux of fluids into the nasopharynx and nasal cavity
The later stages of the condition may give rise to serious health issues like:
- Nosebleeds
- Nasal congestion
- Blood in the saliva
- Intense bone pain
- Joint disorders
- Malfunctioning of the associated organs
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Causes
The pharynx starts behind the nose and ends at the top of the trachea, a membranous tube which makes its entry directly into the lungs. The upper pharynx, also called nasopharynx leads into the nostrils and ears. This could be the chief reason for the cancer to easily spread to these regions. The life-threatening disorder has been attributed to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which belongs to the herpes family. This commonly found infectious agent generally causes a host of malignant ailments, including Burkitt’s lymphoma and NPC. Pathological studies of type 2 and 3 of the disease have shown that the virus can severely infect the epithelial cells by undergoing multiple transformations. The manner in which the virus enters the body has not been determined because the natural reservoir of this minute living particle is still unknown. Many medical investigators agree that NPC follows a complex process and apart from its ethnic susceptibility, the involvement of several carcinogens triggers the formation of the malignant cells. Some of the common ones are:
- Radiation
- Radioactive gases
- Poisonous chemicals
- Polluted water
- Food chemicals
The possibility of a genetic mutation as well as intake of food contaminated with carcinogenic nitrosamines in causing cancer of the nasopharynx cannot be entirely ruled out.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Diagnosis
Proper diagnostic information can be obtained from the process of staging, which helps healthcare providers to know the current stage of the disorder. This can be done through the following tests and exams:
Physical inspection
Physicians should palpate the neck for swollen lymph nodes. A small, long-handled mirror is used to examine the throat for any lump.
Nasoscopy
In this procedure, nasoscope, a thin, lighted tube-like instrument fitted with a lens, is inserted into the nasal cavity to look for abnormal areas. It is often installed with a tool to conduct a biopsy of the nasal mucosa. The tissue samples can be closely examined for any abnormal cell growth.
Blood test
Affected patients can be checked for antibodies produced against the nuclear antigens associated with EBV. Abnormal count of white blood cells is a warning sign of a possible malignant condition in the body.
Lymph node biopsy
A small piece of lymph node can be removed for examination under a microscope. The method is useful to check for signs of cancer.
Neurological assessment
The method does not involve any deeper investigation of the neurological system, but includes a superficial determination of the sensory neurons and motor reflexes. For this, a plain physical examination and evaluation of a patient’s medical history is needed to identify problems related to the brain, coordination of muscles and movement.
Skull X-ray
Radiographic studies of the head produce a series of images of the nose, sinuses, and facial bones for detecting both minor and minor growths in the respective regions.
Chest X-ray
Nasopharyngeal tumors can occur in the severe stages of the condition. An X-ray of the chest can help in the determination of such abnormalities.
MRI and CT scan
The imaging techniques are the ideal modalities to detect the disorders of the bone and other organs as well. Careful assessment of the lymph nodes and skull is crucial for the diagnosis of large/aggressive tumors.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
This highly specialized imaging technique is normally used to find the presence of malignant cells in the bones. The procedure involves intravenous administration of a small quantity of radioactive glucose. A scanner is made to revolve around the body to produce three-dimensional images of organs that have utilized the maximum amount of glucose. Since cancer cells are highly active, the rate of metabolic process in the affected areas of the body is rapid.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Treatment
Treatment of NPC varies according to the stage of the disorder. These are:
Chemotherapy
It is a form of drug therapy that blocks or delays the growth of cancerous cells. Some anticancer drugs are orally administered to the patients while the remaining ones are given through the vein or muscle. The chemotherapeutic agents are usually given in cycles on an outpatient basis.
Radiation therapy
In this process, the malignant cells are subjected to high-energy x-rays in order to destroy or delay its growth. The method can either be done with radioactive materials sealed in needles/wires/ catheters or an external radiation machine.
Biological treatment
NPC patients have a weak immune system to fight against the cancer cells. The method uses laboratory-prepared substances that may boost or restore the body’s natural defense system and negate the effects of cancer.
Surgery
Operative techniques are normally performed when other treatments turn futile. This is more often seen in the advanced stages of the disorder where the lymph nodes and other tissues of the neck get involved. Surgical removal of these diseased tissues may prevent the cancer from spreading to the other regions.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Prognosis
The long-term outlook for NPC depends on certain factors like:
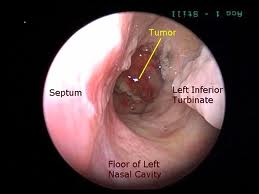
Picture 2 – Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Image
- Type of the disorder
- Stage of the cancer
- Size of the tumor
- Age and health status of the concerned patient
Younger patients as well females seem to respond better to the treatment than the older population. The prognosis of NPC is not good in the case of large tumor growths. NPC has a 5-year survival rate, which means that affected patients live for at least 5 years after the diagnosis of the disorder.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma could turn lethal in the later stages due to metastasis. Prompt screening and treatment is essential to avoid a fatal outcome. The risk factors associated with the condition must be kept at bay to prevent it from occurring.
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nasopharyngeal_carcinoma
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/nasopharyngeal-carcinoma/DS00756
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/988165-overview
http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/nasopharyngeal-cancer