Are you failing to experience heat and touch sensations after a spinal cord injury? If yes, you might be suffering from Brown Sequard Syndrome (BSS). Read on to find out about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this disorder.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Brown Sequard Syndrome Definition
- 2 Brown Sequard Syndrome Synonyms
- 3 Brown Sequard Syndrome ICD-9 Code
- 4 Brown Sequard Syndrome Epidemiology
- 5 Brown Sequard Syndrome Causes
- 6 Brown Sequard Syndrome Pathophysiology
- 7 Brown Sequard Syndrome Symptoms
- 8 Brown Sequard Syndrome Diagnosis
- 9 Brown Sequard Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
- 10 Brown Sequard Syndrome Treatment
- 11 Brown Sequard Syndrome Complications
- 12 Brown Sequard Syndrome Prognosis
- 13 Brown Sequard Syndrome Images
It is a condition characterized by a loss of motor function and sensation that results from a cutting or lateral hemisection of spinal cord.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Synonyms
BSS is known by various other names, such as:
- Brown-Séquard syndrome
- Brown-Séquard’s paralysis
- Brown-Séquard’s hemiplegia
- Crossed hemiplegia
- Hemiplegia et hemiparaplegia spinalis
- Hemiparaplegic syndrome
- Spinal hemiparaplegia
Brown Sequard Syndrome ICD-9 Code
The ICD-9 Code for BSS is 344.89.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Epidemiology
This syndrome is rare as a traumatic injury usually damages the nerve fibers around just one end of the spinal cord.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Causes
A penetrating or blunt trauma to the back or neck is the most common cause of BSS. The condition can also result from neoplasia or spinal cord tumor. The already present symptoms of BSS can be aggravated by rollercoaster riding or chiropractic manipulation.
The various possible causes of this syndrome have been presented below:
- Syphilis
- Ischemia
- Empyema
- Meningitis
- Tuberculosis
- Herpes zoster
- Herpes simplex
- Gnathostomiasis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Herniation of discs
- Cervical spondylosis
- Idiopathic spinal cord herniation
- Tropical spastic paraplegia (HTLV-1)
- Formation of cysts and cystic disorders
- Hemorrhage, such as in Haematomyelia and spinal subdural or epidural hemorrhage
Brown Sequard Syndrome Pathophysiology
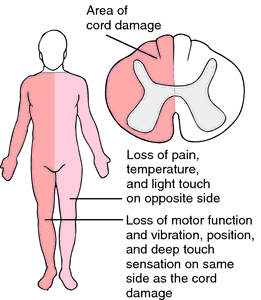
Pure BSS with hemisection of the spinal cord is very rarely seen. On the other hand, a clinical picture with some features of the disorder is more commonly found. Hemisection syndrome, having additional signs and symptoms, can also be seen. Interruption of lateral corticospinal tracts, lateral spinothalamic tract and in some occasions the posterior columns can generally lead to a spastically weak leg with brisk reflexes as well as a strong leg having no sensation of pain or temperature. Hyperactive reflexes and spasticity may not be there in case of an acute lesion. Corticospinal lesion leads to spastic paralysis on same side of the body below the level of the lesion. Here, the muscles are supplied by the nerves of this level and will experience a flaccid paralysis. Lesion in fasciculus cuneatus or fasciculus gracilis leads to ipsilateral loss of proprioception, vibration and loss of all sensations of fine touch.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Symptoms
The various symptoms of BSS are listed below:
- Clonus
- Babinski sign
- Hemiparaplegia
- Hemianesthesia
- Loss of vibration
- Abnormal reflexes
- Horner’s syndrome
- Loss of position sense
- Ipsilateral hemiplagia
- Increased deep reflexes
- Sphincteral disturbances
- Thermanesthesia below lesion
- Sensory loss at the level of lesion
- Reduced tactile discrimination abilities
- Segmental atrophy at the level of lesion
- Contralateral analgesia below the lesion
- Increased muscle tone around the side of the lesion
- Paralysis of the voluntary muscles below the level of lesion
Brown Sequard Syndrome Diagnosis
An expert physician is likely to perform several tests and examine the medical history of a patient for the diagnosis of BSS. The various tests conducted for diagnosing this syndrome are mentioned below:
- Physical Examination
- Ultrasonography tests
- Radiographs for measuring the extent of the syndrome
- CT scans, if MRI scans show contraindications
- Lumbar puncture, in patients having tuberculosis
- Motor examination, which reveals signs of spastic weakness or paralysis
- Laboratory tests, if an infectious disease is the cause
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans, for determining the extent of the injury
Brown Sequard Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
In most cases, BSS is associated with trauma. When there are no signs of trauma, a differential diagnosis of this syndrome need to be conducted. This includes ensuring the absence of conditions such as strokes, multiple sclerosis and spinal cord infections.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Treatment
Treatment of BSS is carried out by firstly understanding the pathology of the paralysis. If the syndrome develops due to some knife injury or a gunshot, other serious conditions such as organ damage or bleeding may crop up. This may even lead to the death of the patient. Due to this reason, the condition needs to be dealt with as soon as possible. If spinal fracture is the main cause behind this syndrome, it should be detected and cured properly. It is advisable that the patient be immobilized in these cases to let them avoid further pain. Corticosteroid medications can be used to reduce inflammations and swelling of the cord. In some cases, such as Spinal Cord Herniation, surgical intervention may allow having a better outcome.
Other forms of treatment for this syndrome include:
- Recreational therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Physical therapy
Brown Sequard Syndrome Complications
The various complications associated with this syndrome include the following:
- Fracture
- Infection
- Depression
- Hypotension
- Fibromyalgia
- Osteoporosis
- Hypercalcemia
- Pressure ulcers
- Disk herniation
- Bowel impaction
- Spinal cord spasm
- Pulmonary embolism
- Vertebral artery dissection
Brown Sequard Syndrome Prognosis
Prognosis for this syndrome is commonly poor, although it is better than in the case of other forms of spinal cord injury. Sometimes, patients may have low life-expectancy. The underlying factors of this syndrome also have an influence on the overall outcome of treatment. In some cases, patients who are treated early with high dosage of steroids also show better results.
Brown Sequard Syndrome Images
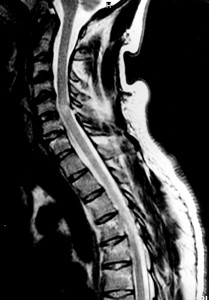
Here are some images that display the areas affected by BSS.
Picture 1 – Brown Sequard Syndrome
Picture 2 – Brown Sequard Syndrome Image
Brown Sequard Syndrome is a paralyzing condition. Early treatment of the condition is necessary to ensure greater chance for a healthy prognosis.
References:
http://syndromespedia.com/brown-sequard-syndrome.html
http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/b/brown_sequard_syndrome/prognosis.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brown%E2%80%93S%C3%A9quard_syndrome
http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Brown-Sequard-Syndrome.htm
http://www.apparelyzed.com/spinal-cord-injury/brown-sequard-syndrome.html