Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a bacterial infection that manifests itself in the form of fever and shock in patients. It is a potentially fatal disorder that you should know all about, including its various causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Toxic Shock Syndrome Definition
- 2 Toxic Shock Syndrome ICD9 Code
- 3 Toxic Shock Syndrome Incidence
- 4 Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms
- 5 Toxic Shock Syndrome Causes
- 6 Toxic Shock Syndrome Risk Factors
- 7 Toxic Shock Syndrome Diagnosis
- 8 Toxic Shock Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Toxic Shock Syndrome Treatment
- 10 Toxic Shock Syndrome Rehabilitation
- 11 Toxic Shock Syndrome Prognosis
- 12 Toxic Shock Syndrome Complications
- 13 Toxic Shock Syndrome Prevention
- 14 Toxic Shock Syndrome Recovery Time
- 15 Toxic Shock Syndrome Pictures
It is an acute disorder that is characterized by shock, fever and problems with the functioning of various organs of the body.
This disorder is also referred to as Staphylococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome.
Toxic Shock Syndrome ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code of this disorder is 040.82.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Incidence
The rate of prevalence of Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome has been estimated to range between 1.2 and 7.3 in every one million patients. The incidence of Staphylococcal TSS is reportedly one in every 100,000 women who are menstruating.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Symptoms
The typical signs and symptoms of this disease include:
- Headaches
- Diarrhea
- Muscle aches
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Low blood pressure
- Nausea and vomiting
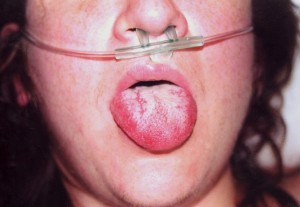
- Redness of eyes, mouth, throat
- Malaise or general or ill-feeling
- High fever, sometimes accompanied by chills
- Organ failure (usually failure of the liver and kidneys)
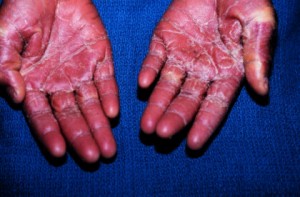
The condition is also characterized by the development of widespread red rash that appear as a sunburn. There is peeling of the skin of patients which occurs 1 or 2 weeks after the development of the rashes, especially on the bottom of the feet or palms of the hand.
Patients should call a doctor immediately in case of the development of any of the above mentioned symptoms of TSS. This is particularly significant if suffering women are menstruating or have just completed menstruating and have been using tampons or having a wound or skin infection. Sufferers should inform doctors about the symptoms and the duration of their persistence.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Causes
The disorder may affect any individual. Around half of all cases of TSS arise in patients who are not menstruating, including men, older women and children.
The condition results from a toxin that is produced by some forms of Staphylococcus bacteria. Toxic Shock-Like Syndrome, which is a similar syndrome, can result from Streptococcal bacteria. However, TSS may not arise due to all strep or staph infections.
The earliest cases of TSS occurred in women who used tampons during menstruation. Today, less than half of all cases of the disease are related with the usage of tampons. TSS can also occur after operations or in case of burns or skin infections.
TSS has been associated with:
- Use of superabsorbent tampons
- Wearing a contraceptive sponge or a diaphragm
- Presence of a strep or staph infection, particularly in case of healing surgical incisions or skin wounds
Medical researchers are yet in the dark regarding the exact way in which tampons are possibly responsible for the occurrence of TSS. Some doctors and researchers are of the opinion that tampons may be conducive for breeding of bacteria when superabsorbent tampons are left in position for a long duration. Others suggest that the fibers in the superabsorbent tampons can scratch the vaginal surface, making it possible for entry of bacteria or their toxins into the bloodstream.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Risk Factors
The factors that increase susceptibility to this condition include:
- Menstruation
- Having a baby recently
- Undergoing a surgery recently
- Wound infection after surgery
- Foreign bodies or packings (as used to stop nosebleeds)
- Use of tampon (especially in case of leave one inside for a long time)
- Infection by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), commonly referred to as Staph infection
Toxic Shock Syndrome Diagnosis
There is no particular diagnostic exam for the detection of this condition. This is due to the fact that no single exam can help establish the presence of TSS.
Patients may need to provide physicians with samples of their urine and blood to help them check for the presence of a strep or staph infection.
For laboratory analysis, samples from the throat, cervix or vagina may also be used.
The diagnosis depends on the following criteria:
- Low blood pressure
- Fever
- Rash, that peels after one to two weeks
- Problems with the functioning of a minimum of three organs
In certain cases, blood cultures may test positive for the growth of S. aureus.
The rapid streptococcal test can be carried out within 10 – 15 minutes. The results are positive in over 85% of sufferers with TSS resulting from Streptococcus infections. In the majority of cases, medical treatment is initiated on an emergency basis before laboratory results are available. Blood tests should be negative for rheumatologic conditions and viral infections. If the heart is involved, Electrocardiogram results may be abnormal.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Differential Diagnosis
At the time of diagnosis, physicians should ensure that patients are actually complaining of symptoms occurring due to TSS and not of any similar disorder such as:
- Cellulitis
- Drug reaction
- Gas gangrene
- Heat stroke
- Bacterial sepsis
- Bacterial pharyngitis
- Bacterial pneumonia
- Leptospirosis
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Kawasaki’s disease
- Meningococcal infections
- Hemorrhagic shock
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Other staphylococcal infections
- Other streptococcal infections
Doctors are likely to carry out necessary tests and medical exams to ensure the absence of the above problems in sufferers and confirm the presence of TSS.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Treatment
Patients who develop TSS are likely to be hospitalized and require antibiotic drugs. Doctors try to detect the source of infection in sufferers.
The aim of treatment is to maintain the vital functions of the body. This may involve:
- Fluid administration through a vein (IV)
- Medications to control blood pressure
- Dialysis (in case of presence of acute kidney problems)
- Intravenous gamma globulin, in acute cases
- Antibiotics for any infection (may be administered through an IV)
- Staying in the hospital intensive care unit (ICU) for monitoring
Along with antibiotics, patients are likely to receive supportive care. This would help treat the signs and symptoms of TSS. If the blood pressure of sufferers begins to drop (Hypotension), it may be stabilized with the aid of medications. Fluids may be administered to cure dehydration.
The toxins manufactured by the strep or staph bacteria and associated Hypotension may lead to kidney failure. If the kidneys fail, sufferers may need Dialysis.
Any foreign objects, like vaginal sponges, nasal packing or tampons, are removed. Sites of infection, like a surgical wound, are drained.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation therapy for TSS depends on any complications that occur due to the syndrome. The heart is the most susceptible organ to suffer from damage due to shock. As a result, physical therapists may develop a workout program to strengthen the heart and the lungs.
The condition also requires rehabilitation if the disorder leads to general fatigue and/or has an impact on the nervous system of patients. A gradual strengthening program may be started if a doctor determines the absence of any contraindications for physical activity.
Activities similar to aerobics aim at enhancing the ability of affected individuals to work and help build resistance to fatigue. A physical therapist is likely to address the issues of retraining and balance in case of damage to the nervous system.
When endurance is increased without symptoms like respiratory shortness, sufferers can start active light resistance training and progress to mild resistance workouts with the use of free weights and/or weight machines. Based on the general health status of sufferers, the frequency of the program tends to vary.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Prognosis
With the help of appropriate treatment, sufferers generally attain recovery within a span of two to three weeks. However, the disease can be life-threatening in a few hours. It can be fatal in up to half of all cases. Due to this reason, treatment is needed on an immediate basis in case of an occurrence of the condition.
There is risk of recurrence of this syndrome even in those patients who manage to survive.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Complications
The possible complications associated to TSS include the following problems:
- Shock
- Severe dysfunction of important organs, such as heart, liver or kidney
- Death
When bacterial toxins are released into the bloodstream, there may be abnormalities in the coagulation (clotting) of blood resulting in a loss of blood supply to various sections of the body (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation). The dysfunction of organs occurs as a result of deficiency of blood flow. Patients may also suffer from loss of a limb due to this reason. Lung problems may result in extreme difficulty in respiration, a condition known as Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). In acute cases, even death may occur.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Prevention
The occurrence of Menstrual TSS can be avoided by changing tampons on a frequent basis, at least after every 4 to 8 hours. Women should consider using the lowest absorbency tampon and try to change sanitary napkins and tampons whenever they can. They should practice complete avoidance of tampons when the flow is very light and use minipads as a substitute.
As aforesaid, there is a risk of recurrence associated with this syndrome. Those who get it can suffer from it again even after attaining recovery once. Due to this reason, those suffering from TSS or having a history of strep or staph infection should not use tampons at all.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Recovery Time
As already mentioned, patients usually take anywhere from two to three weeks for complete recovery. Heavy physical work may be prevented due to extended periods of weakness. Some amount of mental weakness may persist for a few weeks and may also reduce performance of sufferers in highly stressful situations.
Other accommodations for patients depend on how acute the damage of organ is, if any. Work restrictions tend to be minimal with complete recovery.
Toxic Shock Syndrome Pictures
The following images help you get an idea of the physical appearance of sufferers of this disorder.
Picture 1 – Toxic Shock Syndrome
Picture 2 – Toxic Shock Syndrome Image
In case you find the manifestation of symptoms of TSS such as rash and fever in yourself or anyone in your family, seek medical treatment as early as possible. As already said, the condition can be life-threatening without timely diagnosis and treatment. Due to this reason, it is important to undergo diagnosis and treatment as fast as possible.
References:
http://www.mdguidelines.com/toxic-shock-syndrome
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001676/
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/toxic-shock-syndrome/DS00221
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toxic_shock_syndrome