Serum sickness is a human immune response to proteins in the antiserum extracted from a non-human source, or from animals. Read and know all about this disorder, including its various causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options.
Serum sickness Definition
Page Contents
- 1 Serum sickness Definition
- 2 Serum sickness ICD9 Code
- 3 Serum sickness History
- 4 Serum sickness Causes
- 5 Serum sickness Risk Factors
- 6 Serum sickness Symptoms
- 7 Serum sickness Diagnosis
- 8 Serum sickness Differential Diagnosis
- 9 Serum sickness Treatment
- 10 Serum sickness Prognosis
- 11 Serum sickness Complications
- 12 Serum sickness Prevention
- 13 Serum sickness Pictures
It is an immune system response like an allergy. In this condition, the immune system shows a response to drugs containing injected proteins that are used to cure immune disorders. It may also arise as a result of antiserum, the liquid part of blood containing antibodies administered to protect patients from poisonous substances or germs.
Serum sickness is actually a form of hypersensitivity, particularly immune complex hypersensitivity (Type III).
Serum sickness ICD9 Code
The ICD9 Code for this disease is 999.5.
Serum sickness History
The characteristics of this condition were first reported in 1906 by Bela Schick and Clemens von Pirquet.
Serum sickness Causes
Sometimes, physicians use a blood product known as serum, extracted from animals or humans, to derive medicines that can help prevent infections of acute nature. Antiserums, such as tetanus vaccinations, are used for basic immunizations. Antiserum is manufactured from the plasma of an animal or a person having immunity against a toxic material or an infection. It may be used to protect an individual who has been exposed to a germ that the body of the person has not been vaccinated against.
Although rare, some individuals occasionally show an abnormal response (similar to allergenic response) to particular antiserum injected into them. This unusual response is Serum sickness.
The condition actually occurs as an inflammatory response to substances that it improperly perceives to be a harmful object. Sometimes, the ailment may also arise as a result of blood transfusions or due to the usage of techniques such as platelet transfusions.
The disorder is often considered to be very similar to allergic responses shown by people to antibiotics such as Penicillin. When exposure to the causative substance(s) occur again, the risk of health hazards are also similar in nature.
Serum sickness and Medications
Injected proteins like Rituximab (used to cure cancers and immune disorders) and Antithymocyte globulin (used to cure organ transplant rejection) can lead to Serum sickness responses.
Some of the medicines associated with the development of this disease include:
- Allopurinol
- Cephalosporin
- Captopril
- Barbiturate
- Penicillin
- Phenytoin
- Griseofulvin
- Streptokinase
- Sulfonamides
- Procainamide
- Quinidine
The condition may also arise as a response to certain hormones, vaccines or allergenic extracts.
Other causes
Some other causative agents for this disorder involve the following:
- Products that contain aspirin
- Many other medications
- Snake venom antiserum
- A type of diuretics known as Thiazides
- Barbiturates
- Bee or wasp sting (rare)
- Other antibiotics, including Cephalosporins
- Fluoxetine (Prozac) used for depression
However, Penicillin is regarded as the most common cause of the disorder.
Serum sickness Risk Factors
The risk factors associated with this disease include:
- Intake of a large quantity of snake venom antiserum
- Being injected with antitoxin or one of the medications that are known to result in Serum sickness
- Having a past history of exposure to antitoxin or one of the medications that are known to cause the disease
Serum sickness Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of this disorder include:
- Hives
- Fever
- Rash
- Joint pain
- Itching
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Malaise or general ill-feeling
Usually, the symptoms do not arise until 1-3 weeks after exposure to medications or the first dose of antiserum. Some individuals, however, may develop the signs in 1-3 days in case they have already been exposed to the substance responsible for the condition.
Serum sickness Diagnosis
In case patients have recently been exposed to any type of antiserum, doctors will look for symptoms typical of the condition. The diagnosis of this disorder usually begins with a physical examination. Doctors may look for enlargement of lymph nodes of sufferers and ask whether the affected regions are tender to touch. A urine analysis may show the presence of protein or blood in urine. Blood tests may reveal signs of swelling of blood vessels or immune complexes. In urine tests conducted in the lab, presence of high protein levels or blood may be detected in samples, which can confirm the presence of the ailment.
Serum sickness Differential Diagnosis
Physicians should consider the following problems during the differential diagnosis of Serum sickness:
- Still disease
- Shunt nephritis
- Microscopic polyangiitis
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Doctors should also ensure that the symptoms experienced by sufferers are those of Serum sickness and not of other disorders, such as:
- Viral Hepatitis
- Cryoglobulinemia
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Kawasaki Disease
- Infective Endocarditis
- Infectious Mononucleosis
- Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis
- Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serum sickness Treatment
The aim of therapy is to cure the condition arising from the effects of soluble circulating immune complexes forming under excess of antigen. The complexes can arise due to the administration of medicines that cause Serum sickness or Heterologous antisera.
The condition can be cured with the aid of various types of medications, such as:
Antihistamines
These drugs may reduce the duration of the ailment and provide relief from itchiness and rash.
Corticosteroid ointments or creams
These soothing medications for the skin may help alleviate the discomfort associated with rash and itchiness.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
These forms of drugs, such as Naproxen or Ibuprofen, may provide relief from pain in the joints. However, physicians should carefully use the NSAIDs as there is risk of kidney damage due to use of these medications. Administration of oral corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, may be prescribed for cases that are acute in nature.
In case the condition arises from the use of some type of medicines, the drug responsible for the disorder should be stopped. Patients should also avoid using that antiserum or medication in the future. In acute cases, physicians may prescribe corticosteroid drugs such as Prednisone. There is usually no need for hospitalization as medications are enough to address and resolve the problems arising due to the disease. Fever associated to the condition usually gets better within 2-3 days of medical treatment.
Serum sickness – Alternative Treatment
The alternative therapies for this disease include:
Acupuncture
The tendency of the body towards allergic hypersensitivity responses can be lowered with the use of acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine.
Herbs
Patients may notice an improvement in their health with the use of herbs like Cat’s claw, Reishi mushroom, turmeric, Bromelain, Rhodiola, Green tea and Gingko.
Homeopathy
The problems associated with this disorder such as hives and itchiness may be relieved by using homeopathic drugs like Urtica urens, Apis and Rhus toxicodendron.
Nutritional supplements
Certain nutrients may provide support to the immune system and decrease allergic reactions in general. These include eating iron and Vitamin B-rich foods, like dark leafy greens, sea vegetables and whole grains. However, there is no scientific evidence to support the view that nutritional supplements can prove to be effective in curing serum sickness.
Serum sickness – Home Remedy
The home remedial measures for this disorder, which can at least bring about a little improvement in the condition of sufferers, include:
- Drinking 6-8 glasses of filtered water on a daily basis.
- Avoiding refined foods, such as sugar, pasta and white breads.
- Using healthy oils, such as vegetable oil or olive oil, for cooking.
- Voiding beverages like coffee and other stimulants like tobacco and alcohol.
The nutritional deficiencies related with the disorder may be addressed with supplements like:
- Vitamin C
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Alpha-lipoic acid
- Multivitamins (to be taken daily)
- Resveratrol
Serum sickness Prognosis
The disorder is usually self-limited and resolves within a few days. In cases without involvement of internal organs, the outcome is good. Following proper diagnosis and treatment, the signs and symptoms of this disease generally resolve in a few days. Occasionally, however, death is reported to occur as a result of acute neurological complications or progressive Glomerulonephritis.
Serum sickness Complications
The risk of having a similar response is high in case patients use the antiserum or the drug that cause Serum sickness.
The primary complications associated with this disorder include:
- Swelling of the blood vessels
- An immediate infection of a fatal nature known as Anaphylactic shock
- Inflammation of the arms, face and legs (a condition referred to as Angioedema)
Some other complications arising due to this disorder involve:
- Acute renal failure
- Anaphylaxis
- Vasculitis
- Neuropathy
- Shock
- Glomerulonephritis (rare)
In case of a re-exposure to the material, Serum sickness tends to arise faster – within 1-4 days. Only a very small quantity of the material may produce a severe response.
Serum sickness Prevention
It is not known how a person can prevent the development of this disorder. Future use of causative drug or antiserum should be avoided by those who experience the following problems:
- Serum sickness
- Drug allergy
- Anaphylactic shock
If you have a history of sensitivity to a specific antiserum or drug, talk with your health care provider about it before getting any type of injection. In case of sensitivity to an antiserum, a doctor may use a technique that desensitizes patients to the antiserum, at least on a temporary basis. Before administering an antiserum, a doctor can carry out skin tests to check for serum sensitivity.
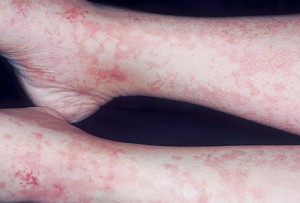
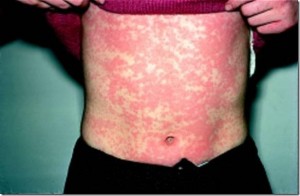
Serum sickness Pictures
The following images reveal the appearance of people affected by this disorder.
Picture 1 – Serum sickness
Picture 2 – Serum sickness Image
If you are experiencing the symptoms of Serum sickness and have received antiserum or medication in the past one month, get in touch with a physician and seek immediate diagnosis and treatment. When treated early, the condition shows a good prognosis and patients can attain a quick recovery.
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001823/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serum_sickness
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/332032-overview
http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/serum-sickness-000149.htm