Scleroderma is a condition that causes swelling of the hands and fingers, GERD and an excessive response to cold among other problems. Read and know all about the disorder, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options and more.
What is Scleroderma?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Scleroderma?
- 2 Scleroderma Types
- 3 Scleroderma Incidence
- 4 Scleroderma Causes
- 5 Scleroderma Symptoms
- 6 Scleroderma Diagnosis
- 7 Scleroderma Differential Diagnosis
- 8 Scleroderma Treatment
- 9 Scleroderma Risk Factors
- 10 Scleroderma Complications
- 11 Scleroderma Prognosis
- 12 Scleroderma Prevention
- 13 Scleroderma Foundation
- 14 Scleroderma Pictures
It refers to a chronic, progressive condition of the connective tissue. The name of this disease has been derived from two Greek terms – “skleros” meaning “hard” and “derma” standing for “skin.” Put simply, it is a disorder characterized by hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues of sufferers.
The condition is also known by the name Systemic sclerosis.
Scleroderma Types
There are two forms of this disorder:
Localized Scleroderma
It is classified mainly into two varieties:
Morphea Scleroderma
The condition is marked by thick, oval patches on the skin that have a purple border and a white middle. They arise only in a few regions on the body or may be more widespread.
Linear Scleroderma
It is more common in kids and is marked by the development of streaks or bands of hardened skin on the forehead or on one or both legs or arms.
Systemic Scleroderma
Also known as Systemic sclerosis, it not only affects the skin but also the internal organs and blood vessels. One of its variants are known as CREST syndrome or Limited Scleroderma.
Scleroderma Incidence
The condition has been estimated to have an incidence of 19 cases in every one million individuals. The prevalence has been estimated to be 240 cases per million. The prevalence has increased as a result of earlier diagnosis, improved diagnostic methods and longer rates of survival.
As misdiagnosis is common in this disorder, it is difficult to determine the exact rates of prevalence and incidence. Among US women in the 35-65 years age group, the prevalence of this disease has been determined to be as high as 400 cases in every one million.
Scleroderma Causes
The disorder occurs due to an accumulation or overproduction of collagen in the tissues of the body. Collagen is a form of fibrous protein that constitutes the connective tissues and even the skin of the body.
Doctors are not sure about the exact factors that are responsible for the abnormal production of collagen. However, they suspect the immune system of the body as a possible cause. Many of them have the opinion that the condition arises when the immune system of the body turns against the body due to unknown reasons, leading to overproduction of collagen and inflammation.
Scleroderma Symptoms
The symptoms of this disorder tend to vary in nature, depending on the organ systems that have been affected. Its detection can be difficult as some of its symptoms in the initial stages are common in the general population and are not always related to the disorder.
The most prevalent signs of this disease include:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Patients have suffer from acid reflux, which may damage the esophageal section close to the stomach. They may also have problems in absorbing nutrients if the intestinal muscles fail to properly move food particles through the intestines.
Raynaud’s phenomenon
It is characterized by an exaggerated response to emotional distress or cold temperatures, which squeezes the small blood vessels in the hands and feet – leading to pain, numbness or changes of color in the fingers or toes.
Changes in skin
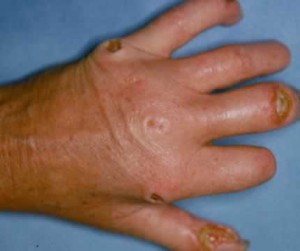
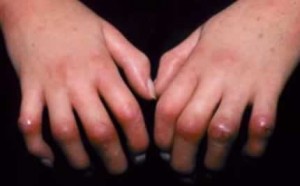
The changes may involve inflammation of the fingers and the hands. Other problems might include tightening of the skin around the face, mouth or hands. The skin, due to its tightness, may appear shiny. The motion of the affected region may be limited.
Scleroderma Diagnosis
The diagnosis of this disorder may involve the following tests:
Blood tests
Blood exams can reveal an increase in the amount of antibodies produced by the immune system in the bloodstream.
Skin analysis
Physicians generally evaluate the condition of the skin in as many as 17 particular regions to assess the level of skin involvement. This can indicate the possibility of life-threatening changes in the internal organs.
Biopsy of tissue
A small sample of tissue may be removed from the affected skin area and analyzed in the laboratory to determine the presence or absence of abnormalities.
On the basis of the results of the initial assessment, physicians may also recommend carrying out other diagnostic procedures to detect any gastrointestinal complications or complications in the heart, lung or kidney that may accompany Scleroderma.
Scleroderma Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of this disorder involves telling its symptoms apart from those of other conditions, that give rise to similar problems, such as:
- Eosinophilic fasciitis
- Graft versus host disease
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Scleromyxedema
- Mycosis fungoides
- Porphyria cutanea tarda
- Idiopathic Pulmonary fibrosis
- Amyloidosis
- Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus)
Physicians should ensure the absence of these abovementioned conditions before confirming the presence of Scleroderma.
Scleroderma Treatment
The condition does not have any specific cure as there is no medication that can stop the excessive production of collagen. However, the localized form of Scleroderma sometimes goes away on its own. Various medicines can help manage the symptoms of the disorder or help prevent the complications associated with it.
The treatment of this condition involves the use of:
Drugs
These involve medications for dilating the blood vessels of sufferers. Medicines used to control blood pressure and dilate the blood vessels may help prevent complications related to the kidney and lungs. Doctors also use immune-suppressant drugs in some cases. These drugs, such as those used after organ transplants, reduce the functionalities of the immune system and may decrease the symptoms of Scleroderma.
Therapy
Therapeutic procedures involve cosmetic procedures occupational or physical therapy. Therapists can help sufferers manage the painful sensations and improve their mobility and strength. They can also help patients perform important daily tasks and give sufferers a sense of independence in carrying out their functions. Therapy also includes cosmetic procedures. Exposure to ultraviolet light can help improve the appearance of skin lesions related with this condition. Laser surgery may also help remove these lesions or at least hide them.
Surgery
Surgical techniques for this disorder include:
Lung transplant
This method is carried out in people who suffer from Pulmonary hypertension or high blood pressure in the arteries to their lungs.
Amputation
It may be needed if gangrene occurs in finger ulcers caused due to acute cases of Raynaud’s disease.
Scleroderma Risk Factors
Various factors seem to elevate the risk of development of some types of this condition. These include:
Being female
Women are found to be more susceptible to this disorder than men. Females are four times likelier to get this disorder as compared to males.
Exposure to certain substances
The development of this disorder has also been associated to an exposure to various substances, which include:
- Some type of drugs used in chemotherapy
- Certain industrial solvents, like paint thinners
- Silica dust, that is common in rock quarries and coal mines
Belonging to certain races
People of certain racial origin are more prone to this disorder as compared to others. They include Native Americans and African Americans. Choctaw Native Americans residing in Oklahoma are at least 20 times or at greater risk of developing this disorder as compared to the general population. Odd though it may appear, the Choctaws residing in the Mississippi region are not at an elevated risk. African-Americans suffering from the disorder are more likely to have lung complications.
Scleroderma Complications
The disorder may give rise to a number of complications that can range from mild to severe in intensity. Some of these may even turn fatal for sufferers.
The problems include:
- Lung complications, such as Pulmonary fibrosis and Pulmonary hypertension
- Circulatory complications, marked by tissue damage, skin sores, gangrene and even amputation
- Kidney complications, such as renal crisis (characterized by sudden rise in blood pressure and rapid kidney failure)
- Digestive complications, like swallowing difficulties, constipation episodes alternating with diarrhea and acid reflux
- Dental complications, like changes in gum tissue, destruction of tooth enamel and loosening or even falling of teeth
- Sexual complications, like reduced sexual lubrication and constriction of vaginal aperture (for women) and erectile dysfunction (in men)
- Cardiac complications, such as scarring of heart tissues, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure and Pericarditis
Scleroderma Prognosis
In the majority of people suffering from localized Scleroderma, the condition is found to be self-limited. There are varying degrees of hand debilitation in sufferers.
The condition generally progresses over a span of several years. The 10 year survival-rates are around 60-70% in people with limited systemic involvement. The rates are around 20% in those with more diffused involvement.
There may be certain periods when the condition of sufferers is stable. In occasional circumstances, the signs may enter remission all through or in localized regions of the body. The disorder can become life-threatening in cases where they involve the kidneys or the lungs. In the absence of treatment, the condition may turn fatal within a span of a few years.
The factors that indicate a more acute outcome for the disease involves:
- Extensive involvement of skin with fast progression
- Being young when diagnosed with the disease
- Presence of anemia
- Higher Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
- Renal involvement
- Pulmonary involvement
- Being of African origin
Scleroderma Prevention
As its causes are unknown, it is not possible to avoid the development of this disorder. However, its complications can be avoided by seeking medical treatment on an early basis. The later complications can be avoided with the aid of:
- Rehabilitation exercises, to improve motion and strength
- Hydrotherapy and paraffin baths, to relieve symptoms and increase mobility
- Counseling, to manage depression arising due to restriction of activities
Scleroderma Foundation
The Scleroderma Foundation is a national organization for extending support and guidance to individuals affected by this disorder and their friends and family members. The organization also conducts researches associated with the disease.
You may contact the Foundation at:
Scleroderma Foundation – National Office
300 Rosewood Drive, Suite 105
Danvers, MA 01923
Ph: (978) 463-5843
Toll-free Information Line: (800) 722-HOPE (4673) – (8:30 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern, Monday through Friday)
Fax: (978) 463-5809
Scleroderma Pictures
The following images show how this disorder affects the appearance of the skin of people affected by Scleroderma.
Picture 1 – Scleroderma
Picture 2 – Scleroderma Image
If you are suspecting the symptoms of Scleroderma in yourself or any of your family members, get in touch with a professional medical care provider and get yourself tested as early as possible. This would help you get the condition diagnosed and treated on an early basis, and ensure a faster recovery.
References:
http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/scleroderma/DS00362
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/scleroderma.html
http://www.umm.edu/patiented/articles/what_symptoms_of_scleroderma_000088_2.htm
http://www.mdguidelines.com/scleroderma