What is Testicular Torsion?
Page Contents
- 1 What is Testicular Torsion?
- 2 Testicular Torsion Symptoms
- 3 Testicular Torsion Causes
- 4 Testicular Torsion Diagnosis
- 5 Testicular Torsion Treatment
- 6 Testicular Torsion Recovery
- 7 Testicular Torsion Complications
- 8 Intermittent Testicular Torsion
- 9 Torsion of a Testicular Appendage
- 10 Testicular Torsion Pictures
It is an emergency medical condition that leads to a twirled spermatic cord that consequently disrupts the supply of blood to the testicle and adjoining structures inside the scrotum.
Testicular Torsion Symptoms
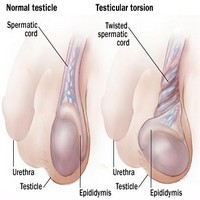
Picture 1 – Testicular Torsion
Source – nhatky
Some of the main symptoms of Testicular Torsion are :
Scrotal Inflammation
Swelling inside one side of the scrotum is one of the main signs of Testicular Torsion. Inflammation is localized and arises on one side of the scrotum while there is marked absence of symptoms in the other side.
Testicular Pain
The disorder also leads to acute pain that arises suddenly in one testicle, even in the absence of any predisposed condition.
Nausea
Patients of this condition also suffer from nausea and vomiting that can impair their daily activities and force them to take bed rest. There is also a light-headed sensation in many suffering individuals.
In some patients, there may be other discomforting symptoms like blood in the semen and the development of a lump in the testicle.
There can be severe inflammation and pain in an impacted testicle. This condition may arise in men belonging to any age group. The disorder is, however, most likely to be seen in adolescents and infants. This is because a high degree of developmental variation occurs inside the reproductive system at this age. An individual experiencing testicular torsion should be assessed and cured as an emergency measure.
Testicular Torsion Causes
Some of the main causes of Testicular Torsion are :
Trauma
Injury to the scrotum can lead to excessive inflammation and result in the development of this disorder.
Insufficient connective tissue
Testicular torsion may also occur due to inadequate scrotal connective tissues. Lack of enough connective tissue inside the scrotum can also increase the risk of having this condition.
Heavy exercise
Strenuous workouts can also increase this condition and lead to damages within the scrotum.
Genetic Defects
Doctors have also attributed this disorder to inheritable genes that impair testicular stability and make some people more susceptible to this condition than others.
Testicular Torsion Diagnosis
The aim of diagnosis is to detect enlargement and extreme tenderness in the testicular region, especially in the right area. Diagnosis also aims at detecting whether the testicle is located higher on the affected side.
An urologist can generally diagnose this condition by asking questions about the symptoms and by physical examination of the scrotum. Urine and blood samples may also be collected and diagnostic imaging tests may be conducted to eliminate other causes of pain in the testicles, such as a tumor or an infection.
Testicular Torsion Treatment
Treatment of Testicular Torsion usually involves a surgical operation. An urologist may arrange for surgery immediately after diagnosis of this condition. Following the appearance of symptoms, surgery should be carried out as early as possible. If done within six hours, surgery can help save most testicles.
During surgical correction, an experienced surgeon cuts into the scrotal area to detect the twisted region and manually disentangles the spermatic tube. The testicle is then anchored or stitched to the wall of the scrotum to lower the risk of recurrence of this syndrome.
While carrying out an operation, the surgeons generally anchor the unaffected testicle as a preventive step. In the absence of this measure, the unaffected testicle may develop Testicular Torsion sometime in future.
Testicular Torsion Recovery
If quickly diagnosed and treated, the testicular function may continue to be normal. Following a timely Testicular Torsion surgery recovery may be complete. If there is an obstruction in blood flow for over 6 hours, there is increased chance of surgically removing the affected testicle. In some cases, however, the loss of testicular functioning may be permanent even if blood supply has been cut of for less than 6 hours.
However, prognosis is generally good if surgical cure is administered within 6 hours after the onset of symptoms. Generally, patients are able to return to a normal life within three months of proper cure. They are able to perform physical activities and even have sex.
Testicular Torsion Complications
If the blood supply is obstructed to the testicle for an extended duration, there may be atrophy (shrinkage) of the testicle and there can be permanent damage to the tissues in the spermatic tube. This can result in infertility and necessitate surgical removal of the affected testicle. Testicular Atrophy may develop in a few days to a few months after the Testicular Torsion repair. If the flow of blood is restricted for a long time, there can be acute infection of the scrotum and the testicle. Unless cured in time, permanent loss of testicular activity may also occur.
Intermittent Testicular Torsion
It is an acute condition that leads to recurrent pain in the scrotum. The pain usually arises rapidly and goes away after some time. Other discomforting symptoms associated with this disease include nausea and vomiting. The scrotal pain is acute in this disorder and is usually treated by surgery. Surgical operation has been found to provide relief in majority of patients of this condition.
Torsion of a Testicular Appendage
This is a common cause of pain in the testicles of young boys, particularly those aged between 7 and 14. This condition can lead to acute scrotum. Appendix Testis and Appendix Epididymis are two such appendages. The former can be found in 92% of all testicles and the later, in 23% of testes. Acute inflammation and pain in the scrotum is frequently attributed to this condition. Torsion of a testicular appendage is a benign condition. However, it may present itself similar to Testicular Torsion, an emergency urologic condition.
Testicular Torsion Pictures
Check out these testicular torsion images to find out how a convoluted testicle looks like. You may find these Testicular Torsion photos useful for reference.
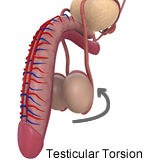
Picture 2 – Testicular Torsion Image
Source – michiganurology
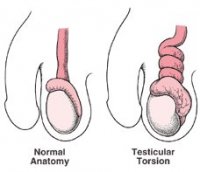
Picture 3 – Testicular Torsion Photo
Source – fbcdn
If you or anyone in your family is experiencing discomforting symptoms of this condition such as sudden testicular pain, one-sided scrotal inflammation and persistent vomiting, it is advisable that you seek immediate medical care. Testicular torsion is an acute condition and it is not sensible to ignore it. Early treatment and cure can help in making a complete recovery and maintain testicular function.
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/778170-overview
http://www.bettermedicine.com/article/testicular-torsion-1
http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/diseases/facts/testiculartorsion.htm
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16148646
